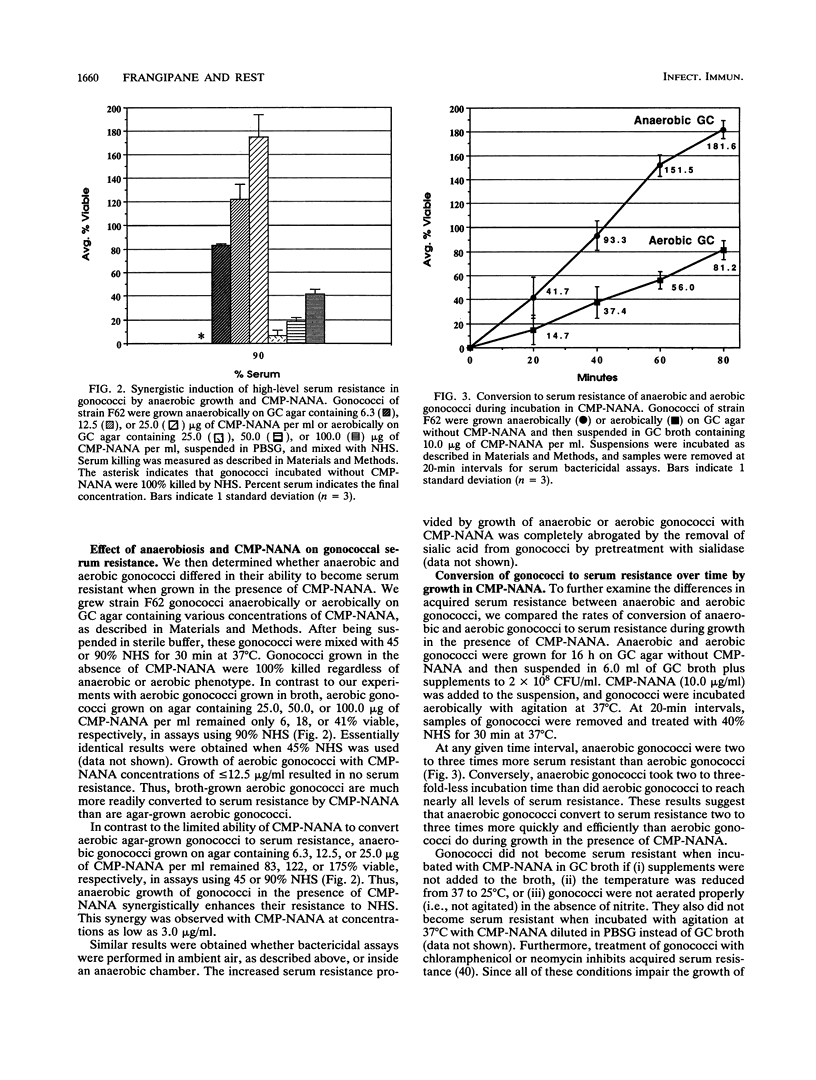
Abstract
In vivo, gonococci encounter a myriad of conditions not present in vitro. At some stages of infection and disease, gonococci may grow anaerobically, probably by using sodium nitrite as a terminal electron acceptor. Also, gonococci sialylate their lipooligosaccharide (LOS) in vivo, by using low concentrations of cytidine 5'-monophospho-N-acetylneuraminic acid (CMP-NANA) present in host tissue. This sialylation is responsible for the acquired resistance of gonococci to both normal and immune human serum. Given that gonococci grown in the absence of oxygen or in the presence of CMP-NANA probably more closely resemble gonococci grown inside a human host, we studied the serum resistance of gonococci cultivated under these conditions. In the absence of CMP-NANA, anaerobically grown (anaerobic) gonococci were somewhat less sensitive to serum killing than were aerobically grown (aerobic) gonococci. However, anaerobic gonococci grown with 6 micrograms of CMP-NANA per ml exhibited almost complete serum resistance, while aerobic gonococci required 16-fold-higher CMP-NANA concentrations to achieve significant serum resistance. Anaerobic gonococci incubated in CMP-NANA converted to serum resistance two to three times faster than did similarly treated aerobic gonococci and incorporated up to six times as much sialic acid into their LOS. Gonococci can express several different LOS molecules. Anaerobic gonococci expressed the LOS molecule that acts as an acceptor for sialic acid from CMP-NANA in greater quantity than aerobic gonococci did. Finally, Triton X-100 extracts of anaerobic gonococci contained about four times more sialyltransferase activity than did extracts of aerobic gonococci. Sialyltransferase activity in these extracts was not inhibited by oxygen or enhanced by anaerobiosis. These data indicate that anaerobic conditions lead to altered LOS biosynthesis and to induction of sialyltransferase activity in gonococci. In vivo, where decreased oxygen levels and relevant concentrations of CMP-NANA are found, gonococci could readily become resistant to killing by normal and immune human serum.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A., Mandrell R. E., Shero M., Wilson M. E., Griffiss J. M., Brooks G. F., Lammel C., Breen J. F., Rice P. A. Modification by sialic acid of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharide epitope expression in human urethral exudates: an immunoelectron microscopic analysis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):506–512. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apicella M. A., Westerink M. A., Morse S. A., Schneider H., Rice P. A., Griffiss J. M. Bactericidal antibody response of normal human serum to the lipooligosaccharide of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):520–526. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackmann T., Geldmeyer S., Jahn R., Söling H. D. Radioenzymatic determination of CMP-N-acetylsialic acid and free N-acetylsialic acid in biological material. Anal Biochem. 1983 Apr 15;130(2):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90601-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnakis T. G., Hildebrandt N. B. Pelvic inflammatory disease: a review with emphasis on antimicrobial therapy. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;8(1):86–116. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow A. W., Malkasian K. L., Marshall J. R., Guze L. B. The bacteriology of acute pelvic inflammatory disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Aug 1;122(7):876–879. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(75)90731-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark V. L., Campbell L. A., Palermo D. A., Evans T. M., Klimpel K. W. Induction and repression of outer membrane proteins by anaerobic growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1359–1364. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1359-1364.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark V. L., Knapp J. S., Thompson S., Klimpel K. W. Presence of antibodies to the major anaerobically induced gonococcal outer membrane protein in sera from patients with gonococcal infections. Microb Pathog. 1988 Nov;5(5):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinidou C., Beadle D., Zhou X. H., Parsons N. J., Sammons C. C., Cole J. A., Smith H. A high Mr factor in human blood which confers serum resistance on gonococci: some properties and synergism with CMP-NANA. Microb Pathog. 1992 Jun;12(6):421–432. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demarco de Hormaeche R., van Crevel R., Hormaeche C. E. Neisseria gonorrhoeae LPS variation, serum resistance and its induction by cytidine 5'-monophospho-N-acetylneuraminic acid. Microb Pathog. 1991 Apr;10(4):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkins C., Carbonetti N. H., Varela V. A., Stirewalt D., Klapper D. G., Sparling P. F. Antibodies to N-terminal peptides of gonococcal porin are bactericidal when gonococcal lipopolysaccharide is not sialylated. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2617–2628. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01439.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Regulation by membrane sialic acid of beta1H-dependent decay-dissociation of amplification C3 convertase of the alternative complement pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1971–1975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangipane J. V., Rest R. F. Anaerobic growth of gonococci does not alter their Opa-mediated interactions with human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1793–1799. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1793-1799.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Ward M. E. Nature and Heterogeneity of the Antigens of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Involved in the Serum Bactericidal Reaction. Infect Immun. 1970 Aug;2(2):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.2.162-168.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldner M., Penn C. W., Sanyal S. C., Veale D. R., Smith H. Phenotypically determined resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to normal human serum: environmental factors in subcutaneous chambers in guinea pigs. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):169–177. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., Jarvis G. A., O'Brien J. P., Eads M. M., Schneider H. Lysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae initiated by binding of normal human IgM to a hexosamine-containing lipooligosaccharide epitope(s) is augmented by strain-specific, properdin-binding-dependent alternative complement pathway activation. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):298–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., O'Brien J. P., Yamasaki R., Williams G. D., Rice P. A., Schneider H. Physical heterogeneity of neisserial lipooligosaccharides reflects oligosaccharides that differ in apparent molecular weight, chemical composition, and antigenic expression. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1792–1800. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1792-1800.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J. Analyses of gonococcal lipopolysaccharide in whole-cell lysates by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: stable association of lipopolysaccharide with the major outer membrane protein (protein I) of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):202–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.202-212.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis G. A., Vedros N. A. Sialic acid of group B Neisseria meningitidis regulates alternative complement pathway activation. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):174–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.174-180.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Crawford J. A., Callaway C. S. Cultivation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae under low-oxygen conditions. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):178–184. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.178-184.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp J. S., Clark V. L. Anaerobic growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae coupled to nitrite reduction. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):176–181. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.176-181.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesse A. J., Campagnari A. A., Bittner W. E., Apicella M. A. Increased resolution of lipopolysaccharides and lipooligosaccharides utilizing tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Jan 24;126(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90018-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Lesse A. J., Sugai J. V., Shero M., Griffiss J. M., Cole J. A., Parsons N. J., Smith H., Morse S. A., Apicella M. A. In vitro and in vivo modification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharide epitope structure by sialylation. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1649–1664. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. M., Patel P. V., Parsons N. J., Smith H. Induction in gonococci of phenotypic resistance to killing by human serum by human genital secretions. Br J Vener Dis. 1982 Dec;58(6):363–365. doi: 10.1136/sti.58.6.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. M., Patel P. V., Parsons N. J., Smith H. Induction of phenotypically determined resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human serum by factors in human serum. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Nov;127(1):213–217. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-1-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. M., Patel P. V., Parsons N. J., Smith H. Induction of phenotypically determined resistance of neisseria gonorrhoeae to human serum by sera from patients with gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1982 Oct;58(5):302–304. doi: 10.1136/sti.58.5.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Mintz C. S., Sarafian S. K., Bartenstein L., Bertram M., Apicella M. A. Effect of dilution rate on lipopolysaccharide and serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae grown in continuous culture. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):74–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.74-82.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn C. A., Cole J. A., Patel P. V., Parsons N. J., Fox J. E., Smith H. Cytidine 5'-monophospho-N-acetylneuraminic acid or a related compound is the low Mr factor from human red blood cells which induces gonococcal resistance to killing by human serum. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Dec;134(12):3295–3306. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-12-3295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Yasuda T., Okada H. Restriction of alternative complement pathway activation by sialosylglycolipids. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):261–263. doi: 10.1038/299261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons N. J., Andrade J. R., Patel P. V., Cole J. A., Smith H. Sialylation of lipopolysaccharide and loss of absorption of bactericidal antibody during conversion of gonococci to serum resistance by cytidine 5'-monophospho-N-acetyl neuraminic acid. Microb Pathog. 1989 Jul;7(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons N. J., Cole J. A., Smith H. Resistance to human serum of gonococci in urethral exudates is reduced by neuraminidase. Proc Biol Sci. 1990 Jul 23;241(1300):3–5. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons N. J., Patel P. V., Tan E. L., Andrade J. R., Nairn C. A., Goldner M., Cole J. A., Smith H. Cytidine 5'-monophospho-N-acetyl neuraminic acid and a low molecular weight factor from human blood cells induce lipopolysaccharide alteration in gonococci when conferring resistance to killing by human serum. Microb Pathog. 1988 Oct;5(4):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. V., Martin P. M., Goldner M., Parsons N. J., Smith H. Red blood cells, a source of factors which induce Neisseria gonorrhoeae to resistance to complement-mediated killing by human serum. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):2767–2770. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-2767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. V., Martin P. M., Tan E. L., Nairn C. A., Parsons N. J., Goldner M., Smith H. Protein changes associated with induced resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to killing by human serum are relatively minor. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Feb;134(2):499–507. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-2-499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. V., Veale D. R., Fox J. E., Martin P. M., Parsons N. J., Smith H. Fractionation of guinea pig serum for an inducer of gonococcal resistance to killing by human serum: active fractions containing glucopeptides similar to those from human red blood cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):2757–2766. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-2757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Frangipane J. V. Growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid inhibits nonopsonic (opacity-associated outer membrane protein-mediated) interactions with human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):989–997. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.989-997.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. A. Molecular basis for serum resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2 (Suppl):S112–S117. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.suppl.s112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock J. P., Rest R. F. Rapid damage to membranes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae caused by human neutrophil granule extracts. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Feb;134(2):509–519. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-2-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Griffiss J. M., Boslego J. W., Hitchcock P. J., Zahos K. M., Apicella M. A. Expression of paragloboside-like lipooligosaccharides may be a necessary component of gonococcal pathogenesis in men. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1601–1605. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Griffiss J. M., Williams G. D., Pier G. B. Immunological basis of serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Jan;128(1):13–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Hammack C. A., Shuman B. A., Griffiss J. M. Stability of expression of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharides. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):924–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.924-927.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Ochs H. D., Buchanan T. M. Immunoglobulin class responsible for gonococcal bactericidal activity of normal human sera. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1771–1779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scudder P. R., Chantler E. N. Glycosyltransferases of the human cervical epithelium. II. Characterization of a CMP-N-acetylneuraminate: galactosyl-glycoprotein sialyltransferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 24;660(1):136–141. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90118-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short H. B., Clark V. L., Kellogg D. S., Jr, Young F. E. Anaerobic survival of clinical isolates and laboratory strains of Neisseria gonorrhoea: use in transfer and storage. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):915–919. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.915-919.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Pathogenicity and the microbe in vivo. The 1989 Fred Griffith Review Lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Mar;136(3):377–393. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-3-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Colony opacity and protein II compositions of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):359–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.359-368.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XII. Colony color and opacity varienats of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):320–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.320-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. L., Patel P. V., Parsons N. J., Martin P. M., Smith H. Lipopolysaccharide alteration is associated with induced resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to killing by human serum. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 May;132(5):1407–1413. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-5-1407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veale D. R., Penn C. W., Smith H. Factors affecting the induction of phenotypically determined serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae grown in media containing serum or its diffusible components. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Feb;122(2):235–245. doi: 10.1099/00221287-122-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Watt P. J., Glynn A. A. Gonococci in urethral exudates possess a virulence factor lost on subculture. Nature. 1970 Jul 25;227(5256):382–384. doi: 10.1038/227382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzler L. M., Barry K., Blake M. S., Gotschlich E. C. Gonococcal lipooligosaccharide sialylation prevents complement-dependent killing by immune sera. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):39–43. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.39-43.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki R., Bacon B. E., Nasholds W., Schneider H., Griffiss J. M. Structural determination of oligosaccharides derived from lipooligosaccharide of Neisseria gonorrhoeae F62 by chemical, enzymatic, and two-dimensional NMR methods. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10566–10575. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki R., Nasholds W., Schneider H., Apicella M. A. Epitope expression and partial structural characterization of F62 lipooligosaccharide (LOS) of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: IgM monoclonal antibodies (3F11 and 1-1-M) recognize non-reducing termini of the LOS components. Mol Immunol. 1991 Nov;28(11):1233–1242. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90010-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





