Abstract
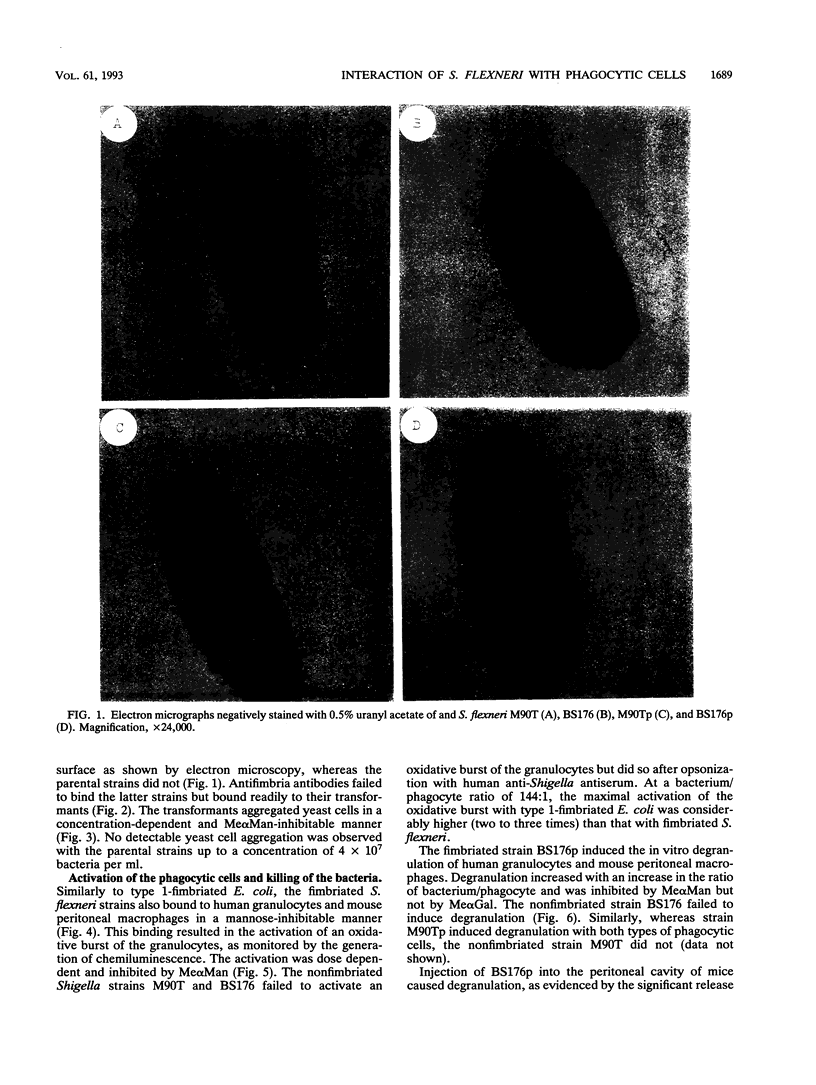
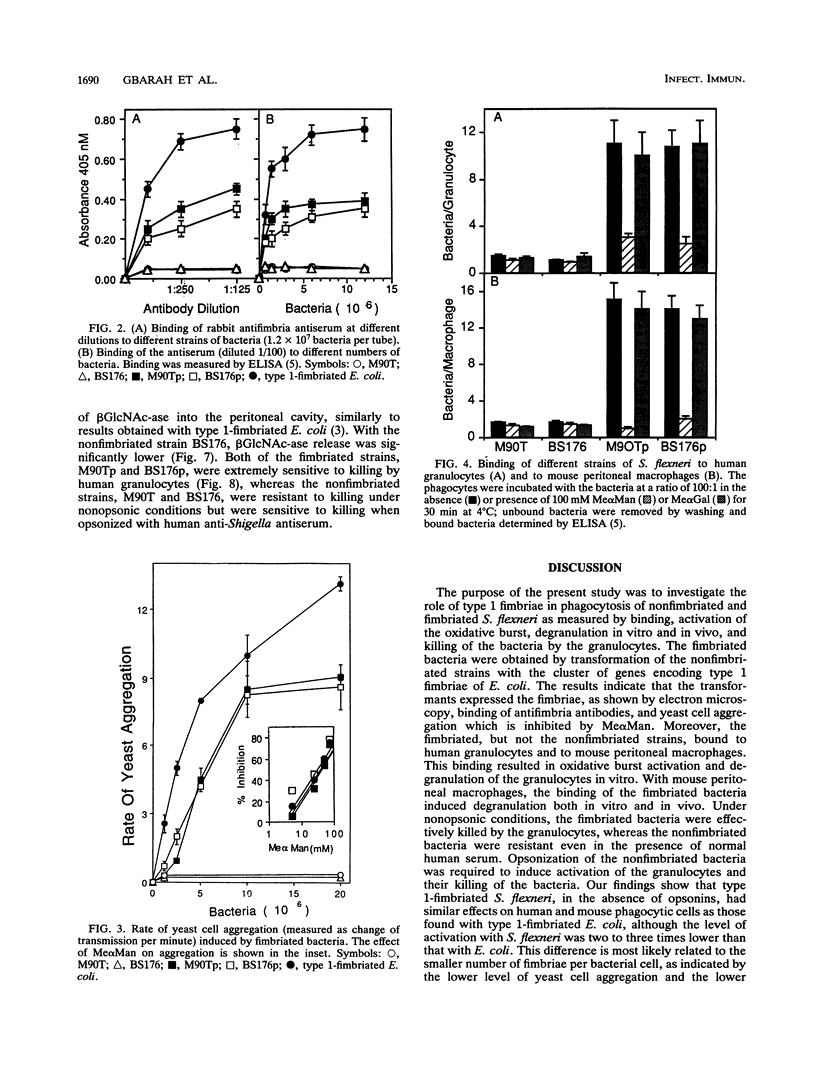
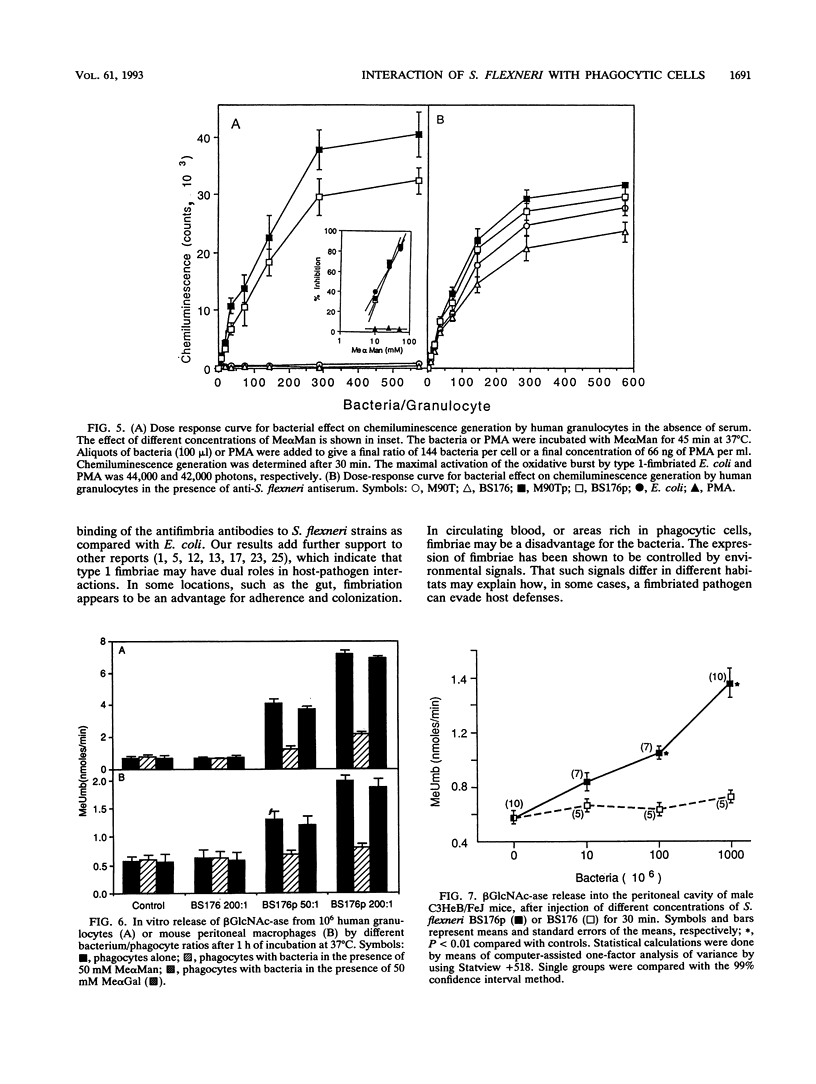
Shigella flexneri M90T (invasive) and BS176 (noninvasive) are typical nonfimbriated organisms that do not bind to or activate phagocytic cells. We demonstrate that S. flexneri M90Tp and BS176p, obtained by transformation of the strains named above with the cluster of genes encoding type 1 (mannose-specific) fimbriae of Escherichia coli, express the functional fimbriae, as shown by electron microscopy, by binding of antifimbria antibodies and by yeast cell aggregation. The transformants, but not the parental strains, bound to human granulocytes and mouse peritoneal macrophages. This binding was inhibited by methyl alpha-D-mannoside but not by methyl alpha-D-galactoside. The bound bacteria induced oxidative burst activation and degranulation of the granulocytes in vitro. With mouse peritoneal macrophages, the binding of the fimbriated bacteria induced degranulation in vitro. Injection of the bacteria into mouse peritoneum also induced degranulation of the macrophages in vivo; no such effect was observed with the nonfimbriated strains. The bound fimbriated transformants were effectively killed by the human granulocytes in vitro in the absence of opsonins or after opsonization with human anti-S. flexneri antiserum. The nonfimbriated strains were killed only after opsonization. These results provide further evidence for the role of type 1 fimbriae in lectin-mediated nonopsonic phagocytosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkan M. L., Wong L., Silverblatt F. J. Change in degree of type 1 piliation of Escherichia coli during experimental peritonitis in the mouse. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):549–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.549-554.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit Z., Goldman R., Ofek I., Sharon N., Mirelman D. Mannose-binding activity of Escherichia coli: a determinant of attachment and ingestion of the bacteria by macrophages. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):417–424. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.417-424.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard W., Gbarah A., Sharon N. Lectinophagocytosis of type 1 fimbriated (mannose-specific) Escherichia coli in the mouse peritoneum. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Sep;52(3):343–348. doi: 10.1002/jlb.52.3.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boner G., Mhashilkar A. M., Rodriguez-Ortega M., Sharon N. Lectin-mediated, nonopsonic phagocytosis of type 1 Escherichia coli by human peritoneal macrophages of uremic patients treated by peritoneal dialysis. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Sep;46(3):239–245. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Green M. S., Block C., Rouach T., Ofek I. Serum antibodies to lipopolysaccharide and natural immunity to shigellosis in an Israeli military population. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):1068–1071. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English D., Andersen B. R. Single-step separation of red blood cells. Granulocytes and mononuclear leukocytes on discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Hypaque. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshdat Y., Silverblatt F. J., Sharon N. Dissociation and reassembly of Escherichia coli type 1 pili. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):308–314. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.308-314.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzon V. L., Arondel J., Sansonetti P. J. Contribution of superoxide dismutase and catalase activities to Shigella flexneri pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):529–535. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.529-535.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gbarah A., Gahmberg C. G., Ofek I., Jacobi U., Sharon N. Identification of the leukocyte adhesion molecules CD11 and CD18 as receptors for type 1-fimbriated (mannose-specific) Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4524–4530. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4524-4530.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gbarah A., Mhashilkar A. M., Boner G., Sharon N. Involvement of protein kinase C in activation of human granulocytes and peritoneal macrophages by type 1 fimbriated (mannose specific) Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1243–1249. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92735-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerina N. G., Kessler T. W., Guerina V. J., Neutra M. R., Clegg H. W., Langermann S., Scannapieco F. A., Goldmann D. A. The role of pili and capsule in the pathogenesis of neonatal infection with Escherichia coli K1. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):395–405. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Hull R., Hull S., Falkow S., Freter R., Svanborg Edén C. Contribution of adhesion to bacterial persistence in the mouse urinary tract. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):265–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.265-272.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogfelt K. A., Bergmans H., Klemm P. Direct evidence that the FimH protein is the mannose-specific adhesin of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1995–1998. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1995-1998.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg E. M., Cohen S. N. Transformation of Salmonella typhimurium by plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):1072–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.1072-1074.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock R., Dahlgren C., Lindén M., Stendahl O., Svensbergh A., Ohman L. Neutrophil killing of two type 1 fimbria-bearing Escherichia coli strains: dependence on respiratory burst activation. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):37–42. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.37-42.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Altmann G., Eshdat Y. Screening of bacterial isolates for mannose-specific lectin activity by agglutination of yeasts. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):328–331. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.328-331.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Mannose binding and epithelial cell adherence of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):247–254. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.247-254.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Sharon N. Lectinophagocytosis: a molecular mechanism of recognition between cell surface sugars and lectins in the phagocytosis of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):539–547. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.539-547.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman L., Hed J., Stendahl O. Interaction between human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and two different strains of type 1 fimbriae-bearing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):751–757. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer A. J., Schwan W. R., Hultgren S. J., Duncan J. L. Relationship of type 1 pilus expression in Escherichia coli to ascending urinary tract infections in mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):373–380. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.373-380.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdon R., Mirelman D., Sansonetti P. J. A model of interaction between Entamoeba histolytica and Shigella flexneri. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jan;143(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90035-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]