Abstract
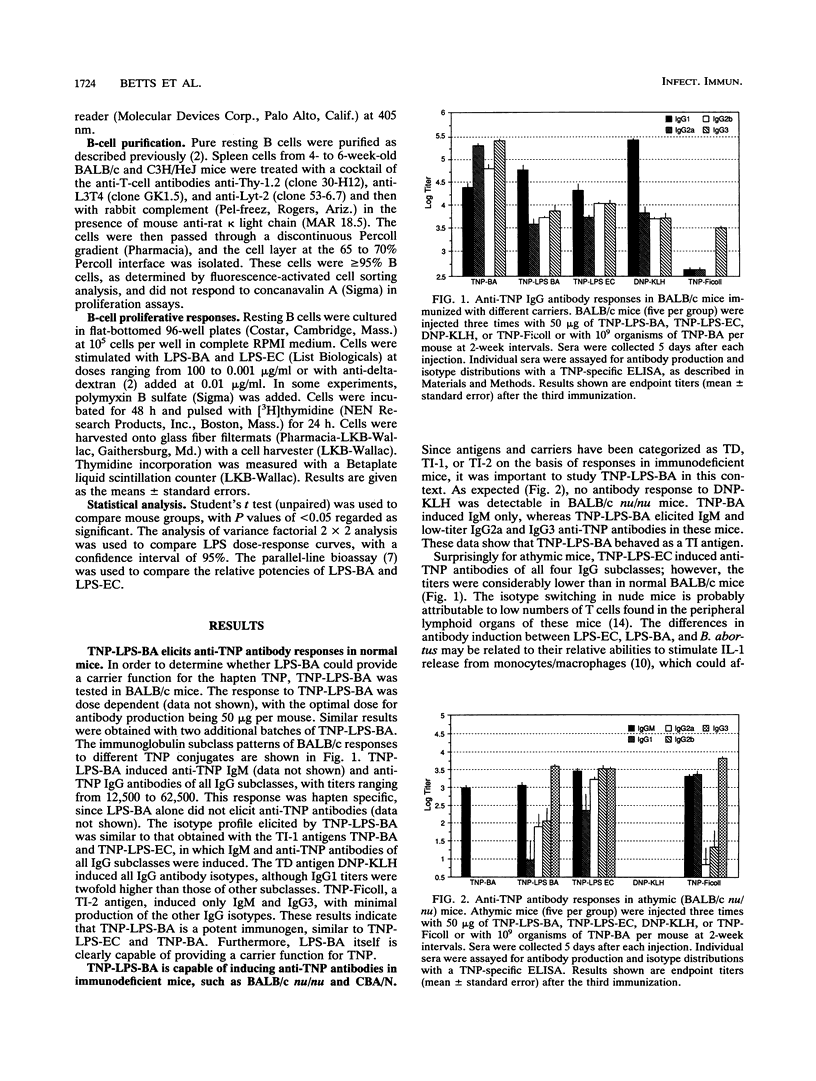
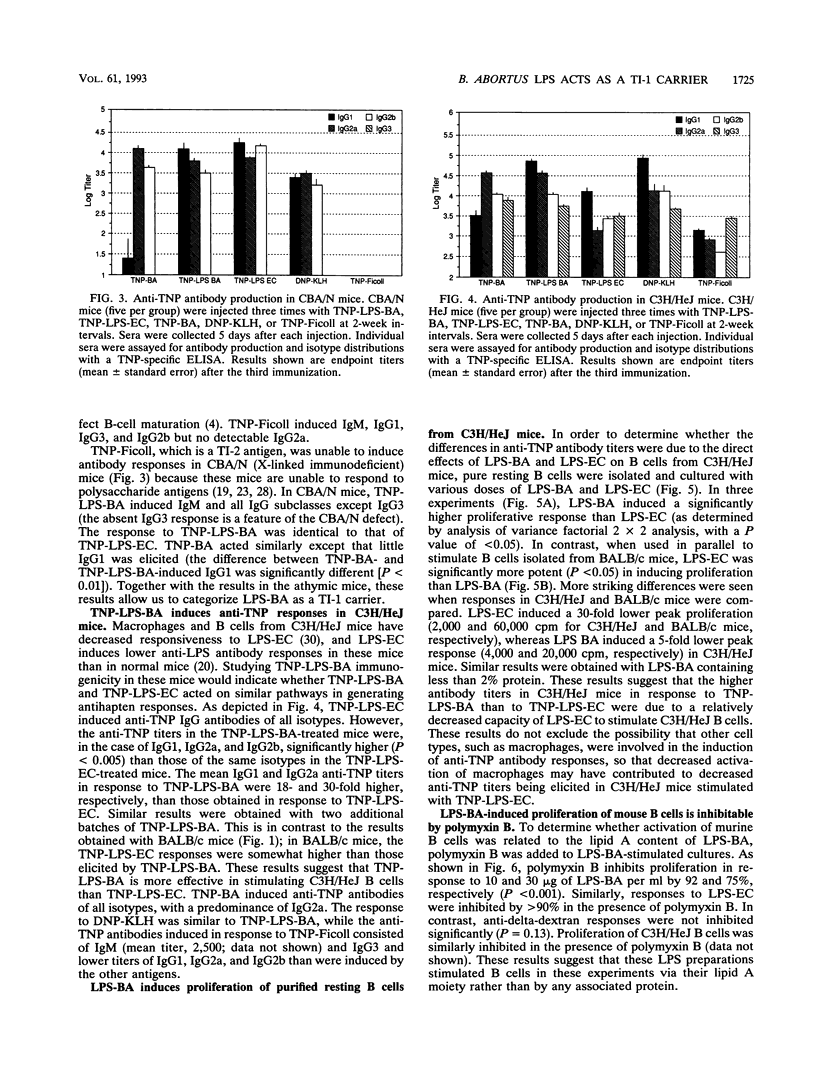
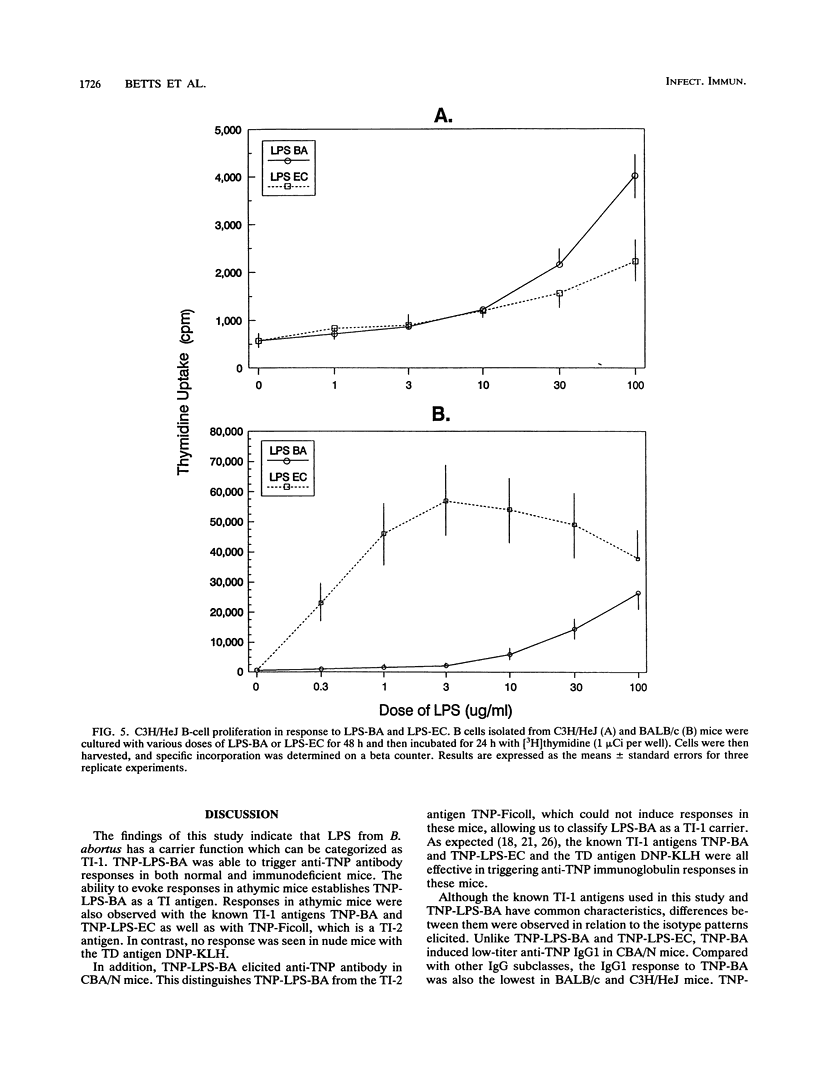
In order to determine the carrier nature of lipopolysaccharide from Brucella abortus (LPS-BA) in evoking humoral responses, normal and immunodeficient mice were immunized with trinitrophenyl (TNP)-conjugated LPS-BA (TNP-LPS-BA) and the responses were compared with those to known T-dependent and T-independent antigens. TNP-LPS-BA, like T-independent type 1 (TI-1) antigens such as TNP-BA and TNP-LPS from Escherichia coli (TNP-LPS-EC), generated anti-TNP responses in BALB/c, athymic BALB/c nu/nu, and CBA/N mice. In contrast, N-2,4-dinitrophenyl-beta-alanylglycylglycyl-substituted keyhole limpet hemocyanin, a typical T-dependent antigen, was not immunogenic in athymic mice, and TNP-Ficoll (T-independent type 2) was ineffective in eliciting humoral responses in CBA/N mice. These results indicate that LPS from B. abortus acts as a TI-1 carrier in generating antibody responses. In C3H/HeJ mice, TNP-LPS-BA generated higher-titer immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1), IgG2a, and IgG2b anti-TNP antibodies than TNP-LPS-EC. Compared with those from BALB/c mice, pure resting B cells isolated from C3H/HeJ mice exhibited a 30-fold lower proliferative response to LPS-EC, whereas the LPS-BA response was reduced to a lesser extent (5-fold). This suggests that the disparity observed in antibody titers was due to different abilities of LPS from B. abortus and E. coli to stimulate C3H/HeJ B cells. The ability of LPS from B. abortus to act as a carrier in generating humoral immune responses indicates that LPS-BA can be substituted for whole B. abortus organisms in vaccine development.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blay R., Hernandez D., Betts M., Clerici M., Lucey D. R., Hendrix C., Hoffman T., Golding B. Brucella abortus stimulates human T cells from uninfected and HIV-infected individuals to secrete IFN gamma: implications for use of Brucella abortus as a carrier in development of human vaccines. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Apr;8(4):479–486. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunswick M., Finkelman F. D., Highet P. F., Inman J. K., Dintzis H. M., Mond J. J. Picogram quantities of anti-Ig antibodies coupled to dextran induce B cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3364–3372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman F. D., Katona I. M., Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. IFN-gamma regulates the isotypes of Ig secreted during in vivo humoral immune responses. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1022–1027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri J. G., Kincade P. W., Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1-mediated induction of kappa-light chain synthesis and surface immunoglobulin expression on pre-B cells. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):223–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding B., Chang S. P., Golding H., Jones R. E., Pratt K. L., Burger D. R., Rittenberg M. B. Human lymphocytes can generate thymus-independent as well as thymus-dependent anti-hapten plaque-forming cell responses in vitro. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):220–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding B., Muchmore A. V., Blaese R. M. Newborn and Wiskott-Aldrich patient B cells can be activated by TNP-Brucella abortus: evidence that TNP-Brucella abortus behaves as a T-independent type 1 antigen in humans. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2966–2971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding B., Tsokos G. C., Fleisher T., Muchmore A. V., Blaese R. M. The role of nonactivated and interferon-gamma activated monocytes in regulating normal and SLE patient B cell responses to TNP-Brucella abortus. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):103–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J., Hoffman T., Frasch C., Lizzio E. F., Beining P. R., Hochstein D., Lee Y. L., Angus R. D., Golding B. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from Brucella abortus is less toxic than that from Escherichia coli, suggesting the possible use of B. abortus or LPS from B. abortus as a carrier in vaccines. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1385–1389. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1385-1389.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman J. K., Merchant B., Claflin L., Tacey S. E. Coupling of large haptens to proteins and cell surfaces: preparation of stable, optimally sensitized erythrocytes for hapten-specific, hemolytic plaque assays. Immunochemistry. 1973 Mar;10(3):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman J. K., Merchant B., Tacey S. E. Synthesis of large haptenic compounds having a common functional group that permits covalent linkage to proteins, cell surfaces, and adsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1973 Mar;10(3):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman J. K. Thymus-independent antigens: the preparation of covalent, hapten-ficoll conjugates. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):704–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. P., Pierce C. W., Kennedy J. D. T cell receptor expression by T cells that mature extrathymically in nude mice. Cell Immunol. 1991 Jun;135(1):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90270-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Immunologic abnormalities in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:477–500. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Specific endotoxic lipopolysaccharide-binding proteins on murine splenocytes. I. Detection of lipopolysaccharide-binding sites on splenocytes and splenocyte subpopulations. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):996–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner K. C., Finkelstein R. A. Bioassay of endotoxin: correlation between pyrogenicity for rabbits and lethality for chick embryos. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):529–536. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Farrar J., Paul W. E., Fuller-Farrar J., Schaefer M., Howard M. T cell dependence and factor reconstitution of in vitro antibody responses to TNP-B. Abortus and TNP-Ficoll: restoration of depleted responses with chromatographed fractions of a T cell-derived factor. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):633–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Scher I., Mosier D. E., Baese M., Paul W. E. T-independent responses in B cell-defective CBA/N mice to Brucella abortus and to trinitrophenyl (TNP) conjugates of Brucella abortus. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Jul;8(7):459–463. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Berman D. T., Boettcher L. A. Biological activities of Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):362–370. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.362-370.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Kurtz R. S., Berman D. T. Induction of immune and adjuvant immunoglobulin G responses in mice by Brucella lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):74–80. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.74-80.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Betz S. J., Jacobs D. M. Isolation of a lipid A bound polypeptide responsible for "LPS-initiated" mitogenesis of C3H/HeJ spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):840–846. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Mond J. J., Goldings E. A. The ontogeny of thymic independent antibody responses in vitro in normal mice and mice with an X-linked B cell defect. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):1874–1878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Site of synthesis of lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3973–3986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M., Pugh G. W., Jr, Deyoe B. L. Chemical and protective properties of Brucella lipopolysaccharide obtained by butanol extraction. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Mar;50(3):311–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Marshall J. D., Shultz L. D., Gray P. W., Johnson H. M. Gamma-interferon is one of several direct B cell-maturing lymphokines. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):801–804. doi: 10.1038/309801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J., Der-Balian G. P., Nahm M., Davie J. M. Subclass restriction of murine antibodies. II. The IgG plaque-forming cell response to thymus-independent type 1 and type 2 antigens in normal mice and mice expressing an X-linked immunodeficiency. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):853–862. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M., Goodman G. W. Endotoxin protein: a B-cell mitogen and polyclonal activator of C3H/HeJ lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):821–827. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetvicka V., Lee G., Kincade P. W. Intrinsic B lymphocyte and macrophage defects in C3H/HeJ mice. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2370–2374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Fellous M., Revel M. Preferential effect of gamma interferon on the synthesis of HLA antigens and their mRNAs in human cells. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):833–836. doi: 10.1038/299833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein S. L., Gold M. R., DeFranco A. L. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide stimulates protein tyrosine phosphorylation in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4148–4152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



