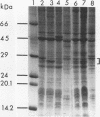
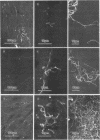
Abstract
Haemophilus ducreyi is the etiologic agent of the localized genital ulcer disease known as chancroid. The pathogenesis of this organism is poorly understood. The role of attachment in the disease process has not been evaluated. In this study, 125I-H. ducreyi was used to quantitatively evaluate the interaction of virulent and avirulent H. ducreyi strains with human foreskin cells. Using this in vitro model system, we demonstrated that, at 22 and 35 degrees C, the attachment of virulent H. ducreyi 35000 to human foreskin cells was significantly more marked than that of avirulent H. ducreyi A77. Although H. ducreyi penetrated between human foreskin cells, internalization was not a major component. Our competition assay data suggest that the attachment mechanism of H. ducreyi may be similar to that of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. We speculate that the attachment and microcolony formation of virulent H. ducreyi may provide a mechanism for bacterial localization and evasion of host defenses.
Full text
PDF
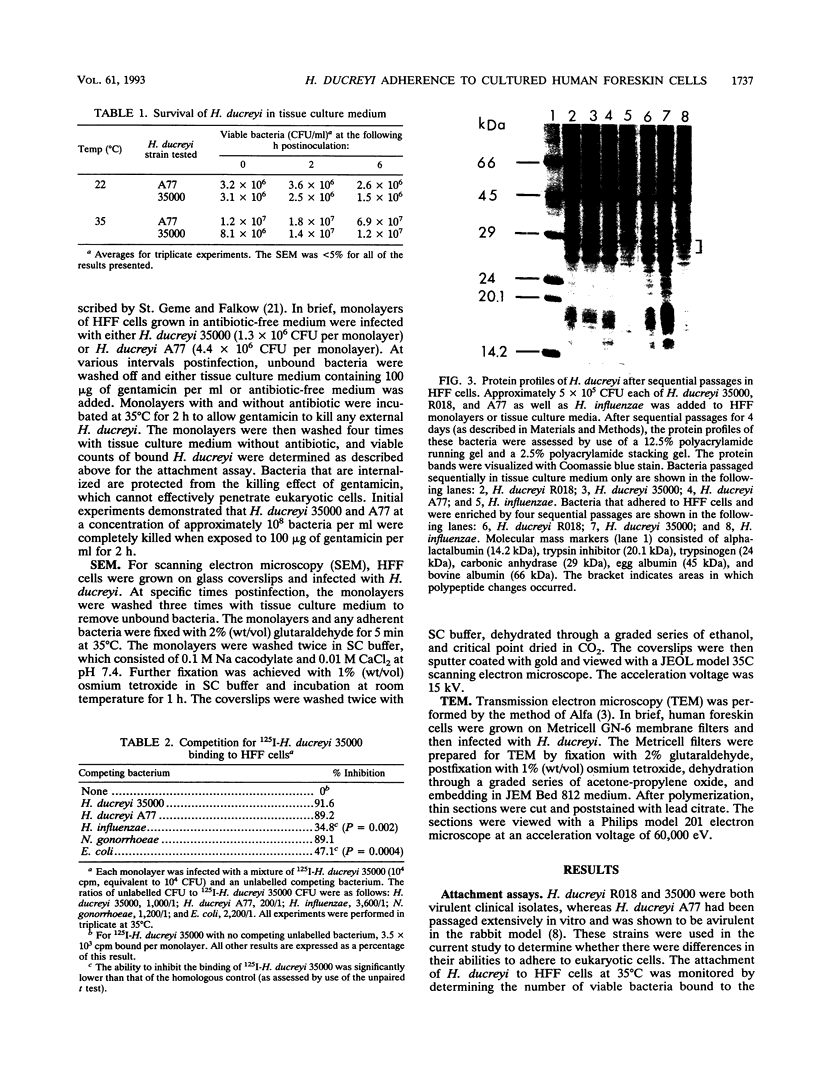




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton W. L. Biology of Haemophilus ducreyi. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):377–389. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.377-389.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfa M. J. Cytopathic effect of Haemophilus ducreyi for human foreskin cell culture. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Jul;37(1):43–50. doi: 10.1099/00222615-37-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campagnari A. A., Wild L. M., Griffiths G. E., Karalus R. J., Wirth M. A., Spinola S. M. Role of lipooligosaccharides in experimental dermal lesions caused by Haemophilus ducreyi. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2601–2608. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2601-2608.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel A. L. Histological aspects of sexually transmitted genital lesions. Histopathology. 1987 Aug;11(8):819–831. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1987.tb01885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Lian C. J., Wilt J. C., Ronald A. R. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Haemophilus ducreyi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):608–612. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Slutchuk M., Scatliff J., Sherman E., Wilt J. C., Ronald A. R. Epidemiologic, clinical, laboratory, and therapeutic features of an urban outbreak of chancroid in North America. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Nov-Dec;2(6):867–879. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.6.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsch W. C., Haas N., Stüttgen G. Ultrastructural detection of Haemophilus ducreyi in biopsies of chancroid. Arch Dermatol Res. 1978 Nov 10;263(2):153–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00446436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A. Chancroid and Haemophilus ducreyi. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2(2):137–157. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Museyi K., Van Dyck E., Vervoort T., Taylor D., Hoge C., Piot P. Use of an enzyme immunoassay to detect serum IgG antibodies to Haemophilus ducreyi. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):1039–1043. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odumeru J. A., Ronald A. R., Albritton W. L. Characterization of cell proteins of Haemophilus ducreyi by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):710–714. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purvén M., Lagergård T. Haemophilus ducreyi, a cytotoxin-producing bacterium. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1156–1162. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1156-1162.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinola S. M., Castellazzo A., Shero M., Apicella M. A. Characterization of pili expressed by Haemophilus ducreyi. Microb Pathog. 1990 Dec;9(6):417–426. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Geme J. W., 3rd, Falkow S. Haemophilus influenzae adheres to and enters cultured human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4036–4044. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4036-4044.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Geme J. W., 3rd, Falkow S. Loss of capsule expression by Haemophilus influenzae type b results in enhanced adherence to and invasion of human cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1325–1333. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1325-1333.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuffrey M., Alexander F., Ballard R. C., Taylor-Robinson D. Characterization of skin lesions in mice following intradermal inoculation of Haemophilus ducreyi. J Exp Pathol (Oxford) 1990 Apr;71(2):233–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]