Abstract
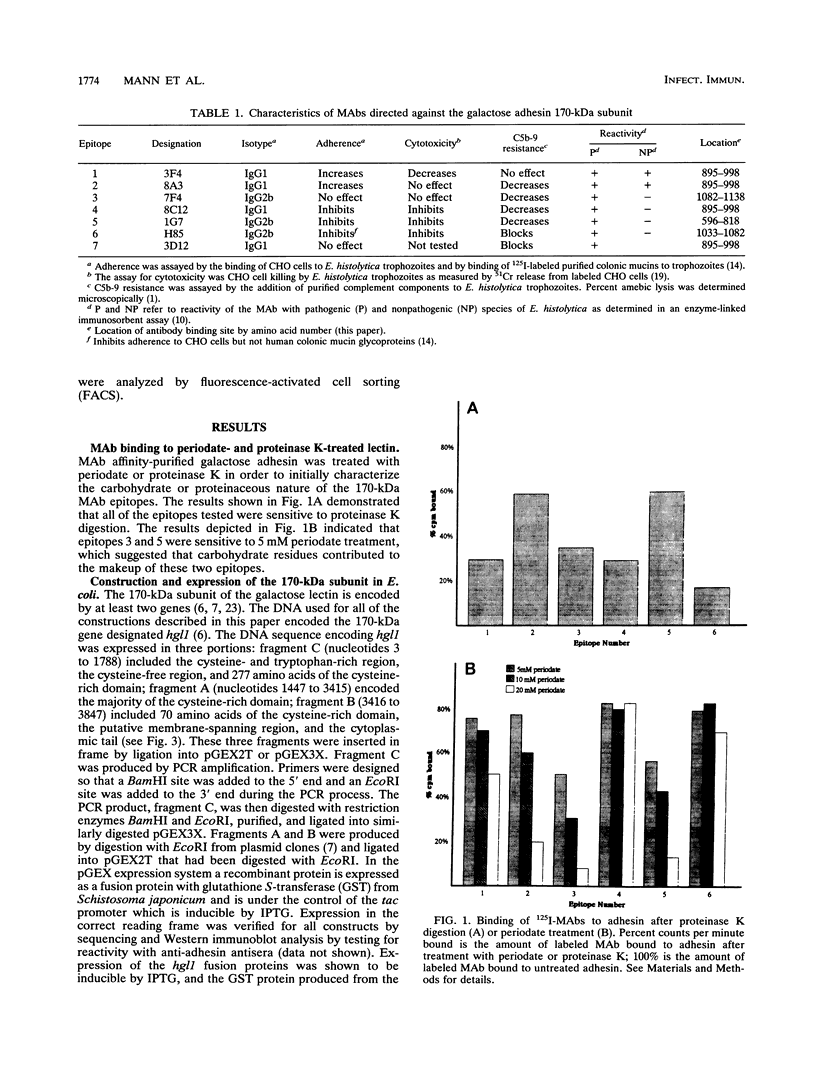
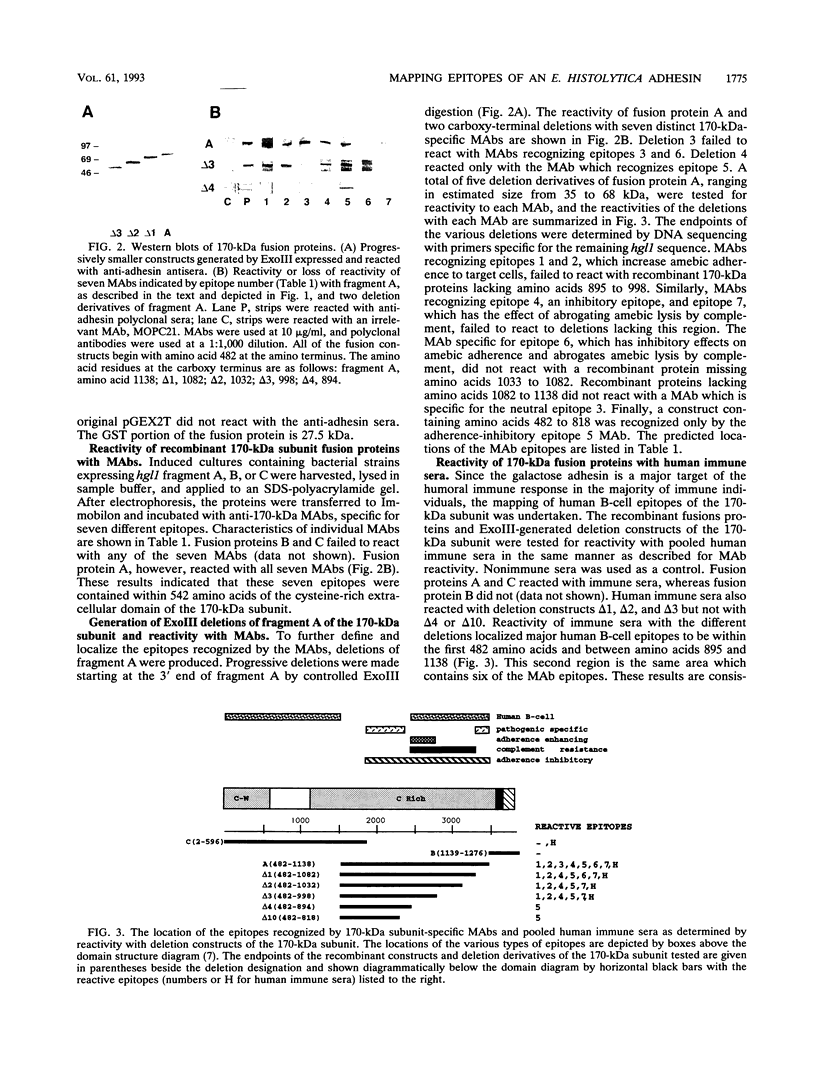
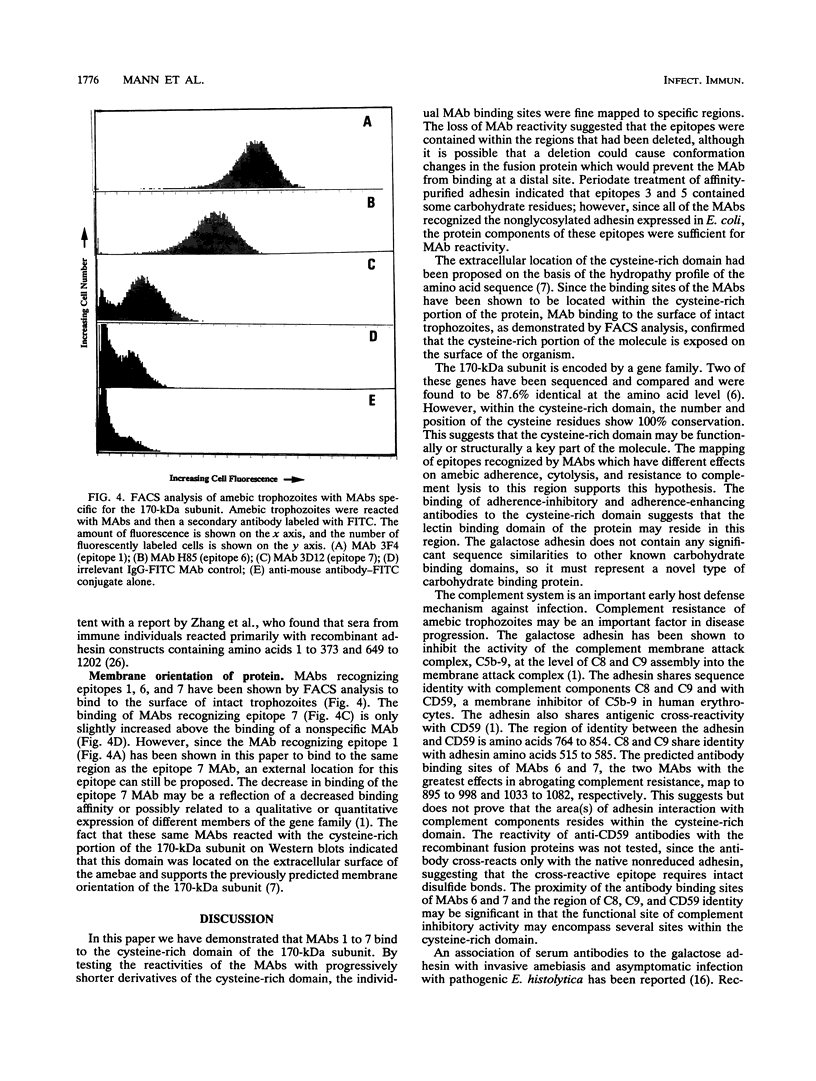
Entamoeba histolytica adheres to human colonic mucins and colonic epithelial cells via a galactose-binding adhesin. The adhesin is a heterodimeric glycoprotein composed of 170- and 35-kDa subunits. Fragments of the hgl1 gene encoding the 170-kDa subunit were expressed as recombinant fusion proteins in Escherichia coli and reacted with anti-adhesin monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) or pooled human immune sera. The MAbs tested recognize seven distinct epitopes on the 170-kDa subunit and have distinct effects on the adherence and complement-inhibitory activities of the adhesin. All seven MAbs reacted with a fusion protein containing the cysteine-rich domain of the protein. Pooled human immune sera reacted with the same cysteine-rich domain as the MAbs and also with a construct containing the first 596 amino acids. Reactivity of three MAbs with the surface of intact trophozoites confirmed that the cysteine-rich domain was located extracellularly. The location of individual epitopes was fine mapped by constructing carboxy-terminal deletions in the cysteine-rich region of the fusion protein. The locations of adherence-enhancing and -inhibiting epitopes were partially distinguished, and the epitopes where complement-inhibitory MAbs bound were demonstrated to be near the adhesin's area of sequence identity with the human complement inhibitor CD59.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braga L. L., Ninomiya H., McCoy J. J., Eacker S., Wiedmer T., Pham C., Wood S., Sims P. J., Petri W. A., Jr Inhibition of the complement membrane attack complex by the galactose-specific adhesion of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1131–1137. doi: 10.1172/JCI115931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard G. D., Bilke R. Adherence of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica strains to neutrophils. Parasitol Res. 1992;78(2):146–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00931657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadee K., Petri W. A., Jr, Innes D. J., Ravdin J. I. Rat and human colonic mucins bind to and inhibit adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1245–1254. doi: 10.1172/JCI113199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieslak P. R., Virgin H. W., 4th, Stanley S. L., Jr A severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mouse model for infection with Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1605–1609. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irusen E. M., Jackson T. F., Simjee A. E. Asymptomatic intestinal colonization by pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica in amebic liver abscess: prevalence, response to therapy, and pathogenic potential. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Apr;14(4):889–893. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.4.889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann B. J., Petri W. A., Jr Cell surface proteins of Entamoeba histolytica. Parasitol Today. 1991 Jul;7(7):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(91)90125-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann B. J., Torian B. E., Vedvick T. S., Petri W. A., Jr Sequence of a cysteine-rich galactose-specific lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3248–3252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Broman J., Healy G., Quinn T., Ravdin J. I. Antigenic stability and immunodominance of the Gal/GalNAc adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. Am J Med Sci. 1989 Mar;297(3):163–165. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198903000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Chapman M. D., Snodgrass T., Mann B. J., Broman J., Ravdin J. I. Subunit structure of the galactose and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine-inhibitable adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):3007–3012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Jackson T. F., Gathiram V., Kress K., Saffer L. D., Snodgrass T. L., Chapman M. D., Keren Z., Mirelman D. Pathogenic and nonpathogenic strains of Entamoeba histolytica can be differentiated by monoclonal antibodies to the galactose-specific adherence lectin. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1802–1806. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1802-1806.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Joyce M. P., Broman J., Smith R. D., Murphy C. F., Ravdin J. I. Recognition of the galactose- or N-acetylgalactosamine-binding lectin of Entamoeba histolytica by human immune sera. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2327–2331. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2327-2331.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Ravdin J. I. Protection of gerbils from amebic liver abscess by immunization with the galactose-specific adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.97-101.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Smith R. D., Schlesinger P. H., Murphy C. F., Ravdin J. I. Isolation of the galactose-binding lectin that mediates the in vitro adherence of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1238–1244. doi: 10.1172/JCI113198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Guerrant R. L. Role of adherence in cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. Study with mammalian tissue culture cells and human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Jackson T. F., Petri W. A., Jr, Murphy C. F., Ungar B. L., Gathiram V., Skilogiannis J., Simjee A. E. Association of serum antibodies to adherence lectin with invasive amebiasis and asymptomatic infection with pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):768–772. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., John J. E., Johnston L. I., Innes D. J., Guerrant R. L. Adherence of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites to rat and human colonic mucosa. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):292–297. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.292-297.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer L. D., Petri W. A., Jr Role of the galactose lectin of Entamoeba histolytica in adherence-dependent killing of mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4681–4683. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4681-4683.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Martinez-Palomo A., Murray H. W., Conales L., Trevino N., Segovia E., Murphy C. F., Ravdin J. I. Patients treated for amebic liver abscess develop cell-mediated immune responses effective in vitro against Entamoeba histolytica. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2633–2639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schain D. C., Salata R. A., Ravdin J. I. Human T-lymphocyte proliferation, lymphokine production, and amebicidal activity elicited by the galactose-inhibitable adherence protein of Entamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):2143–2146. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.2143-2146.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannich E., Ebert F., Horstmann R. D. Primary structure of the 170-kDa surface lectin of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):228–238. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. P., Young W. W., Jr, Bloodgood R. A. Detection of monoclonal antibodies specific for carbohydrate epitopes using periodate oxidation. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Apr 8;78(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Li E., Jackson T. F., Zhang T., Gathiram V., Stanley S. L., Jr Use of a recombinant 170-kilodalton surface antigen of Entamoeba histolytica for serodiagnosis of amebiasis and identification of immunodominant domains of the native molecule. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2788–2792. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2788-2792.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




