Abstract
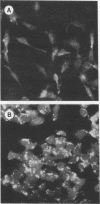
Salmonella abortusovis is a pathogenic bacterium highly specific to sheep, causing spontaneous abortion. In order to understand the role of genes involved in pathogenicity, we investigated S. abortusovis with the random mutagenic TnphoA transposon. A total of 95 S. abortusovis TnphoA mutants yielding alkaline phosphatase active fusion protein were obtained. In this way we created a bank of strains in order to identify any phenotypic modification which could affect the periplasmic and/or exported proteins involved in virulence. The TnphoA mutants were screened for the ability to adhere to epithelial cells: a total of 23 mutant strains lost this phenotypic feature. To detect the chromosomal TnphoA insertions, DNA was restricted by the enzyme EcoRV, which does not cleave the TnphoA sequence. Southern blotting analysis revealed the existence of four classes of integration. Colonies of adhesiveless mutants appear to be as smooth as the S. abortusovis wild type, and electrophoretic analysis indicates a normal lipopolysaccharide profile. To identify mutations affecting genes encoding for outer membrane proteins (OMPs), the alkaline phosphatase portion of the fusion proteins was revealed in TnphoA mutants by immunoblotting with specific antibodies. A mutation in OMPs was detected in seven mutants. Restriction analysis identified in four mutants a common region of 2 kb where alterations in genes coding for OMPs occur. We suggested that this region is involved in pathogenicity in mice, since a group of mutant strains has shown reduced virulence in mice and one mutant is completely avirulent. Furthermore, after mice were exposed orally to these mutants, significant protection against oral challenge with the parental virulent strain resulted.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chatfield S. N., Dorman C. J., Hayward C., Dougan G. Role of ompR-dependent genes in Salmonella typhimurium virulence: mutants deficient in both ompC and ompF are attenuated in vivo. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):449–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.449-452.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd, Kelly S. M., Gulig P. A., Nakayama K. Selective delivery of antigens by recombinant bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;146:35–49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74529-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Calderwood S. B., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Kaper J. B. Construction and analysis of TnphoA mutants of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli unable to invade HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1565–1571. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1565-1571.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Heffron F., Falkow S. Epithelial cell surfaces induce Salmonella proteins required for bacterial adherence and invasion. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):940–943. doi: 10.1126/science.2919285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Starnbach M. N., Francis C. L., Stocker B. A., Chatfield S., Dougan G., Falkow S. Identification and characterization of TnphoA mutants of Salmonella that are unable to pass through a polarized MDCK epithelial cell monolayer. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):757–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Distribution of the invA, -B, -C, and -D genes of Salmonella typhimurium among other Salmonella serovars: invA mutants of Salmonella typhi are deficient for entry into mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2901–2908. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2901-2908.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. B., DiRita V. J., Calderwood S. B. Identification of an iron-regulated virulence determinant in Vibrio cholerae, using TnphoA mutagenesis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):55–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.55-60.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A. Virulence plasmids of Salmonella typhimurium and other salmonellae. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jan;8(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantke K. Regulation of ferric iron transport in Escherichia coli K12: isolation of a constitutive mutant. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):288–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00269672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kido N., Ohta M., Kato N. Detection of lipopolysaccharides by ethidium bromide staining after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1145–1147. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1145-1147.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantier F., Pardon P., Marly J. Immunogenicity of a low-virulence vaccinal strain against Salmonella abortus-ovis infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):601–607. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.601-607.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantier F., Pardon P., Marly J. Vaccinal properties of Salmonella abortus ovis mutants for streptomycin: screening with a murine model. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):492–497. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.492-497.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Mekalanos J. J., Beckwith J. Alkaline phosphatase fusions: sensors of subcellular location. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):515–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.515-518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller I., Maskell D., Hormaeche C., Johnson K., Pickard D., Dougan G. Isolation of orally attenuated Salmonella typhimurium following TnphoA mutagenesis. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2758–2763. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2758-2763.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara O., Dorit R. L., Gilbert W. Direct genomic sequencing of bacterial DNA: the pyruvate kinase I gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6883–6887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardon P., Sanchis R., Marly J., Lantier F., Guilloteau L., Buzoni-Gatel D., Oswald I. P., Pépin M., Kaeffer B., Berthon P. Experimental ovine salmonellosis (Salmonella abortusovis): pathogenesis and vaccination. Res Microbiol. 1990 Sep-Oct;141(7-8):945–953. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90134-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardon P., Sanchis R., Marly J., Lantier F., Pépin M., Popoff M. Salmonellose ovine due à Salmonella abortusovis. Ann Rech Vet. 1988;19(4):221–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M. Y., Miras I., Coynault C., Lasselin C., Pardon P. Molecular relationships between virulence plasmids of Salmonella serotypes typhimurium and dublin and large plasmids of other Salmonella serotypes. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1984 May-Jun;135A(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(84)80080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J. Salmonella O antigens and virulence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:443–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta D., Datta-Roy K., Banerjee K., Ghose A. C. Identification of some antigenically related outer-membrane proteins of strains of Vibrio cholerae O1 and non-O1 serovars involved in intestinal adhesion and the protective role of antibodies to them. J Med Microbiol. 1989 May;29(1):33–39. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P., Cockerill F., 3rd, Soni R., Brunton J. Outer membranes are competitive inhibitors of Escherichia coli O157:H7 adherence to epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):890–899. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.890-899.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Manoil C., Mekalanos J. J. Broad-host-range vectors for delivery of TnphoA: use in genetic analysis of secreted virulence determinants of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1870–1878. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1870-1878.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udhayakumar V., Muthukkaruppan V. R. Protective immunity induced by outer membrane proteins of Salmonella typhimurium in mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):816–821. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.816-821.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson C. M., Baird G. D., Manning E. J. A common virulence region on plasmids from eleven serotypes of Salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):975–982. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafriri D., Oron Y., Eisenstein B. I., Ofek I. Growth advantage and enhanced toxicity of Escherichia coli adherent to tissue culture cells due to restricted diffusion of products secreted by the cells. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1210–1216. doi: 10.1172/JCI112939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Melo M. A., Pechère J. C. Identification of Campylobacter jejuni surface proteins that bind to Eucaryotic cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1749–1756. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1749-1756.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]