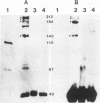
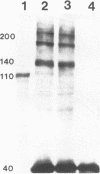
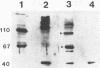
Abstract
In order to characterize the interaction of human complement with Chlamydia trachomatis, flow cytometry was used to quantitate binding of complement component C3 to elementary bodies of C. trachomatis serovar L2 preincubated in fresh serum in the presence or absence of human polyclonal chlamydial antibody. Isolation of each of the complement activation pathways revealed that C3 was activated most effectively by the alternative pathway. The degree of binding by the classical pathway was proportional to the concentration of antibody, but dual-pathway-mediated binding was not greater than antibody-independent alternative pathway binding. Electrophoresis and immunoblotting of detergent-extracted outer membrane protein-C3b complexes indicated that the chlamydial major outer membrane protein was the primary cell surface moiety binding C3b in both the presence and absence of specific antibody. Hydroxylamine cleavage of outer membrane protein-C3b complexes provided evidence that the majority of C3b is bound to the major outer membrane protein by hydroxyl ester bonds. This result was also unchanged by the presence of specific antibody. An unexpected finding was the apparent binding of anti-C3 antibody to a 40-kDa protein of the chlamydial outer membrane complex, perhaps indicating C3 mimicry on the part of the chlamydial major outer membrane protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehr W., Zhang Y. X., Joseph T., Su H., Nano F. E., Everett K. D., Caldwell H. D. Mapping antigenic domains expressed by Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4000–4004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Hitchcock P. J. Monoclonal antibody against a genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia species: location of the epitope on chlamydial lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):306–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.306-314.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kromhout J., Schachter J. Purification and partial characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1161–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1161-1176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Perry L. J. Neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis infectivity with antibodies to the major outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):745–754. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.745-754.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett B. A., Newhall W. J., Jersild R. A., Jr, Jones R. B. Detection of surface-exposed epitopes on Chlamydia trachomatis by immune electron microscopy. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jan;135(1):85–94. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. P., Marney S. R., Jr, Colley D. G., Sergent J. S., Des Prez R. M. C3 shunt activation in human serum chelated with EGTA. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):807–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. P., Osborn M. F., Rowntree S., Thomas B. J., Taylor-Robinson D. A study of inactivation of Chlamydia trachomatis by normal human serum. Br J Vener Dis. 1983 Dec;59(6):369–372. doi: 10.1136/sti.59.6.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochi S. K., Johnson R. C., Dalmasso A. P. Complement-mediated killing of the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. Role of antibody in formation of an effective membrane attack complex. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3964–3970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Lichtenberg N. A., Levine R. P. Evidence for an ester linkage between the labile binding site of C3b and receptive surfaces. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1388–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. S., Yan L. L., Ho Y., Rice P. A. Early complement components enhance neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis infectivity by human sera. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2547–2550. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2547-2550.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclean I. W., Peeling R. W., Brunham R. C. Characterization of Chlamydia trachomatis antigens with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Feb;34(2):141–147. doi: 10.1139/m88-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megran D. W., Stiver H. G., Bowie W. R. Complement activation and stimulation of chemotaxis by Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):670–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.670-673.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megran D. W., Stiver H. G., Peeling R., Maclean I. W., Brunham R. C. Complement enhancement of neutralizing antibody to the structural proteins of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Sep;158(3):661–663. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.3.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Interaction of chlamydiae and host cells in vitro. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):143–190. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.143-190.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Batteiger B., Jones R. B. Analysis of the human serological response to proteins of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1181–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1181-1189.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeling R., Maclean I. W., Brunham R. C. In vitro neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis with monoclonal antibody to an epitope on the major outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):484–488. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.484-488.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E. M., Hoshiko M., Markoff B. A., Lauermann M. W., de la Maza L. M. Differences in susceptibilities of the lymphogranuloma venereum and trachoma biovars of Chlamydia trachomatis to neutralization by immune sera. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):938–943. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.938-943.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. G., Wright S. D. Complement receptor type 3 (CR3) binds to an Arg-Gly-Asp-containing region of the major surface glycoprotein, gp63, of Leishmania promastigotes. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):279–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su H., Caldwell H. D. In vitro neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis by monovalent Fab antibody specific to the major outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2843–2845. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2843-2845.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su H., Watkins N. G., Zhang Y. X., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydia trachomatis-host cell interactions: role of the chlamydial major outer membrane protein as an adhesin. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1017-1025.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Reddy P. A., Jong M. T., Erickson B. W. C3bi receptor (complement receptor type 3) recognizes a region of complement protein C3 containing the sequence Arg-Gly-Asp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1965–1968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Y., Zhang Y. X., Watkins N. G., Caldwell H. D. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences for the four variable domains of the major outer membrane proteins of the 15 Chlamydia trachomatis serovars. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1040-1049.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn M. H., Fey G. H. Human complement component C3: cDNA coding sequence and derived primary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):708–712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]