Abstract
Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) is one of the leading causative agents of bacterial otitis media, and no vaccine has been shown to be effective against it. Three outer membrane lipoproteins of NTHi have been investigated extensively and are leading candidates for inclusion in a vaccine against this organism. Hi-PAL (P6), recombinant PCP (rPCP), and e (P4) proteins are antigenically conserved among NTHi strains and elicit bactericidal and protective antibodies. A genetic fusion of the rPCP and Hi-PAL proteins has also been reported. Mixtures of these proteins were used for active immunization experiments in the chinchilla model of otitis media. Chinchillas were immunized either with a mixture of all three lipoproteins or with the mixture of rPCP-PAL hybrid plus e protein. When these animals were challenged with a NTHi strain injected directly into the middle ears, no protection from infection or disease, as measured by otoscopy, was observed in either group. However, effusion and inflammation measured by tympanometry were significantly reduced in animals immunized with the three lipoproteins. Animals that had been immunized with either whole NTHi cells or total outer membranes and then challenged with the homologous strain were significantly protected from both infection and disease, as determined by tympanometry and otoscopy. Unlike other animals antisera, chinchilla antisera against the purified proteins had no bactericidal activity against NTHi but did fix complement on the cell surface. Thus, the chinchilla immune responses to mixtures of these lipoproteins differ from the immune responses observed in other animal species. Further evaluation of these proteins for their vaccine potential remains to be done.
Full text
PDF



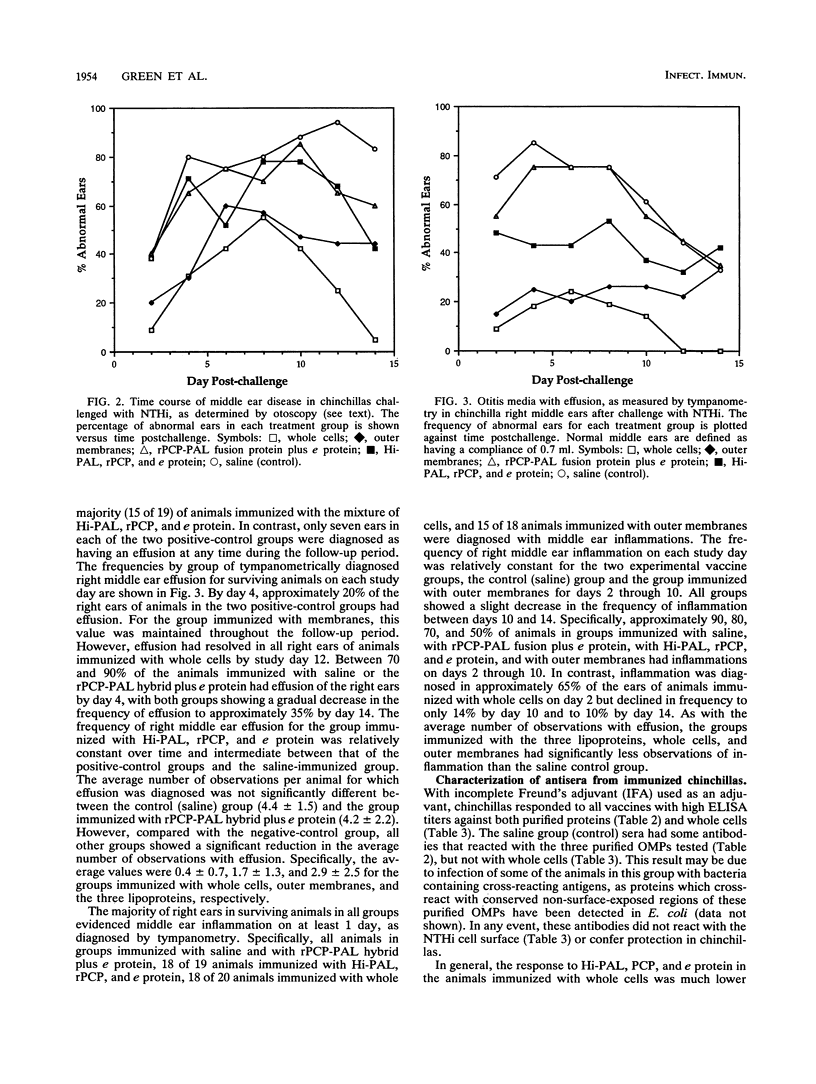
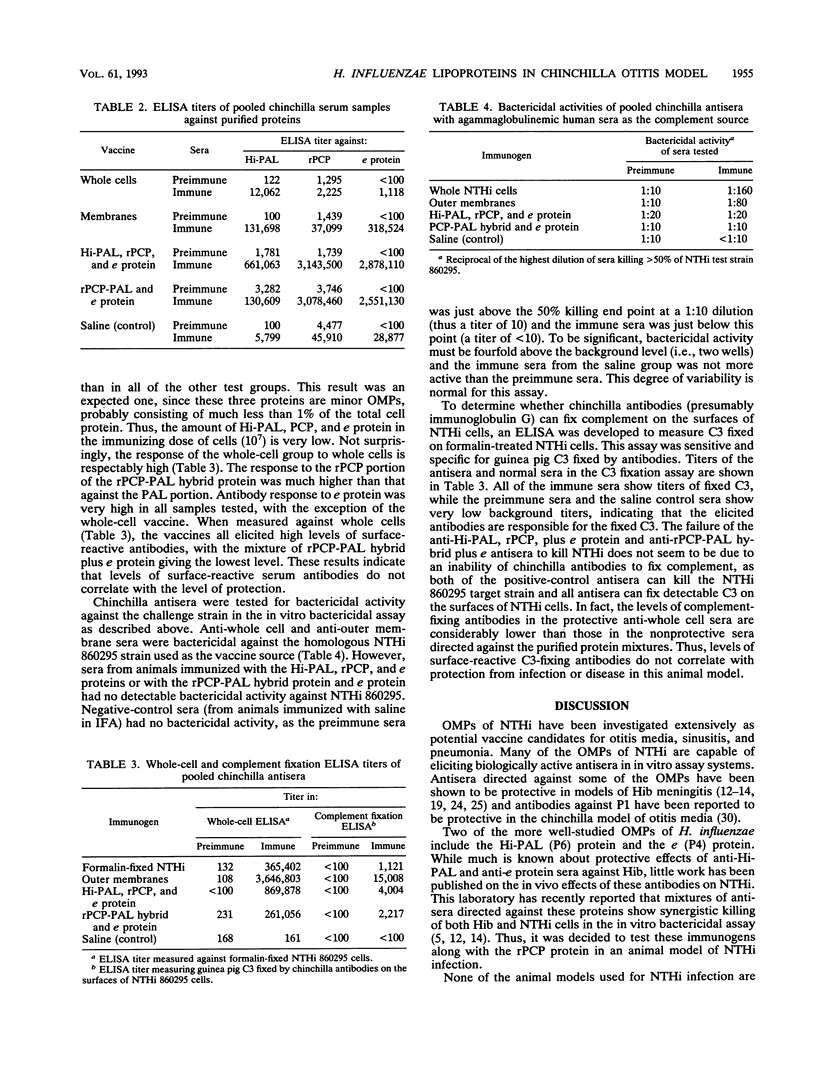


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barenkamp S. J. Protection by serum antibodies in experimental nontypable Haemophilus influenzae otitis media. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):572–578. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.572-578.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein J. M., Faden H. S., Ogra P. L. Nasopharyngeal colonization by nontypeable Hemophilus influenzae in children: the effect of serum bactericidal antibody. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1991 Sep;105(3):406–410. doi: 10.1177/019459989110500309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMaria T. F., Briggs B. R., Lim D. J., Okazaki N. Experimental otitis media with effusion following middle ear inoculation of nonviable H influenzae. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1984 Jan-Feb;93(1 Pt 1):52–56. doi: 10.1177/000348948409300113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deich R. A., Anilionis A., Fulginiti J., Metcalf B. J., Quataert S., Quinn-Dey T., Zlotnick G. W., Green B. A. Antigenic conservation of the 15,000-dalton outer membrane lipoprotein PCP of Haemophilus influenzae and biologic activity of anti-PCP antisera. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3388–3393. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3388-3393.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle W. J., Supance J. S., Marshak G., Cantekin E. I., Bluestone C. D., Rohn D. D. An animal model of acute otitis media consequent to beta-lactamase-producing nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1982 Nov-Dec;90(6):831–836. doi: 10.1177/019459988209000627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H., Bernstein J., Brodsky L., Stanievich J., Krystofik D., Shuff C., Hong J. J., Ogra P. L. Otitis media in children. I. The systemic immune response to nontypable Hemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):999–1004. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebink G. S., Payne E. E., Mills E. L., Juhn S. K., Quie P. G. Experimental otitis media due to Streptococcus pneumoniae: immunopathogenic response in the chinchilla. J Infect Dis. 1976 Dec;134(6):595–604. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.6.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebink G. S., Ripley-Petzoldt M. L., Juhn S. K., Aeppli D., Tomasz A., Tuomanen E. Contribution of pneumococcal cell wall to experimental otitis media pathogenesis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1988 May-Jun;132:28–30. doi: 10.1177/00034894880970s308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. A., Farley J. E., Quinn-Dey T., Deich R. A., Zlotnick G. W. The e (P4) outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae: biologic activity of anti-e serum and cloning and sequencing of the structural gene. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3191–3198. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3191-3198.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. A., Metcalf B. J., Quinn-Dey T., Kirkley D. H., Quataert S. A., Deich R. A. A recombinant non-fatty acylated form of the Hi-PAL (P6) protein of Haemophilus influenzae elicits biologically active antibody against both nontypeable and type b H. influenzae. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3272–3278. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3272-3278.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. A., Quinn-Dey T., Zlotnick G. W. Biologic activities of antibody to a peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein of Haemophilus influenzae against multiple clinical isolates of H. influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2878–2883. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2878-2883.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase E. M., Campagnari A. A., Sarwar J., Shero M., Wirth M., Cumming C. U., Murphy T. F. Strain-specific and immunodominant surface epitopes of the P2 porin protein of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1278–1284. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1278-1284.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Hart D. A., McGehee J. L., Toews G. B. Immune enhancement of pulmonary clearance of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):182–190. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.182-190.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermansson A., Emgård P., Prellner K., Hellström S. A rat model for pneumococcal otitis media. Am J Otolaryngol. 1988 May-Jun;9(3):97–101. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0709(88)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasic R. B., Beste D. J., To S. C., Doyle W. J., Wood S. W., Carter M. J., To A. C., Tanpowpong K., Bluestone C. D., Brinton C. C., Jr Evaluation of pilus vaccines for prevention of experimental otitis media caused by nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Jan;8(1 Suppl):S62–S65. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198901001-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Loftus T. A., Hansen E. J. A minor high-molecular-weight outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b is a protective antigen. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):253–259. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.253-259.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills R., Gilsdorf J. Middle-ear effusions following acute otitis media in the chinchilla animal model. J Laryngol Otol. 1986 Mar;100(3):255–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Purification and partial characterization of outer membrane proteins P5 and P6 from Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.544-549.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Shenep J. L., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M. Purification and comparison of outer membrane protein P2 from Haemophilus influenzae type b isolates. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):677–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI111017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Campagnari A. A., Nelson M. B., Apicella M. A. Antigenic characterization of the P6 protein of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):774–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.774-779.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Rice P. A., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Apicella M. A. Identification of a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein on nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae as a target for human serum bactericidal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):1020–1027. doi: 10.1172/JCI112656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. Identification of a specific epitope of Haemophilus influenzae on a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1300–1307. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly J. S., Doyle W. J., Cantekin E. I., Supance J. S., Kim H. K., Rohn D. D., Bluestone C. D. Treatment of ampicillin-resistant acute otitis media in the chinchilla. Arch Otolaryngol. 1983 Aug;109(8):533–535. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1983.00800220039010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurin P. A., Giebink G. S., Wegman D. L., Ambrosino D., Rholl J., Overman M., Bauer T., Siber G. R. Prevention of pneumococcal otitis media in chinchillas with human bacterial polysaccharide immune globulin. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):755–759. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.755-759.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater L. N. A rat model of prolonged pulmonary infection due to nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Dec;142(6 Pt 1):1429–1435. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.6_Pt_1.1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnick G. W., Sanfilippo V. T., Mattler J. A., Kirkley D. H., Boykins R. A., Seid R. C., Jr Purification and characterization of a peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein from Haemophilus influenzae. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9790–9794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]