Abstract
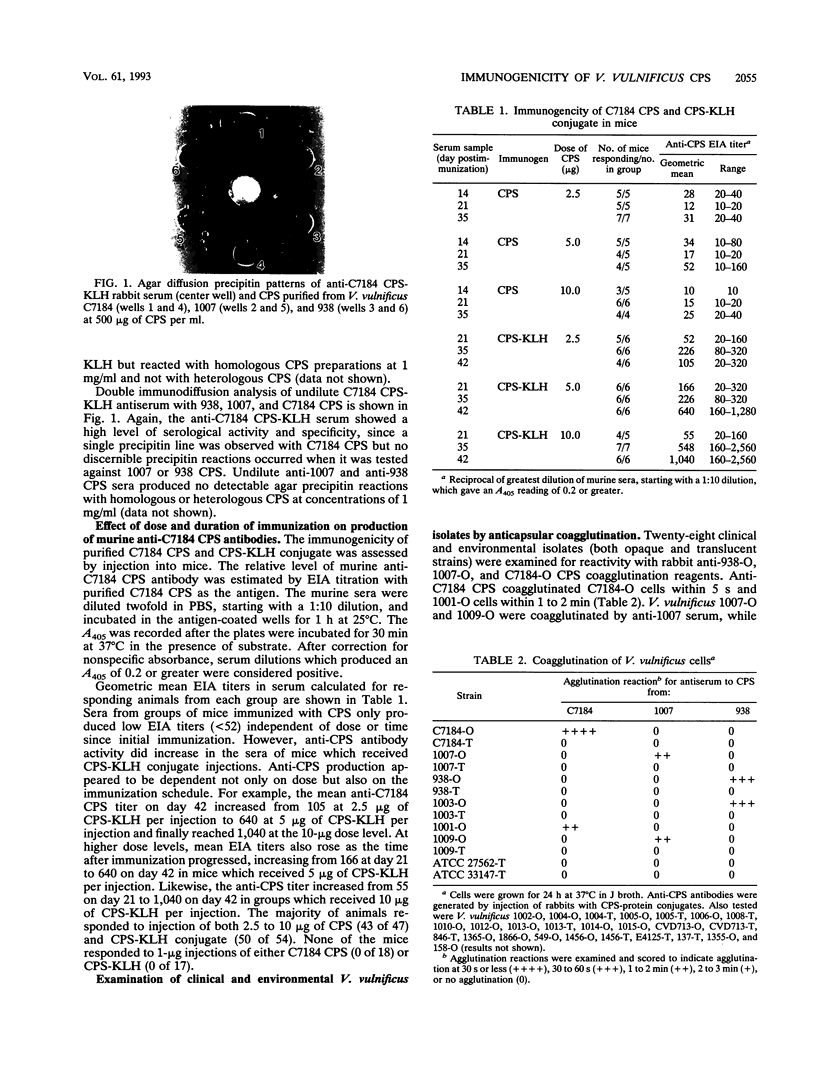
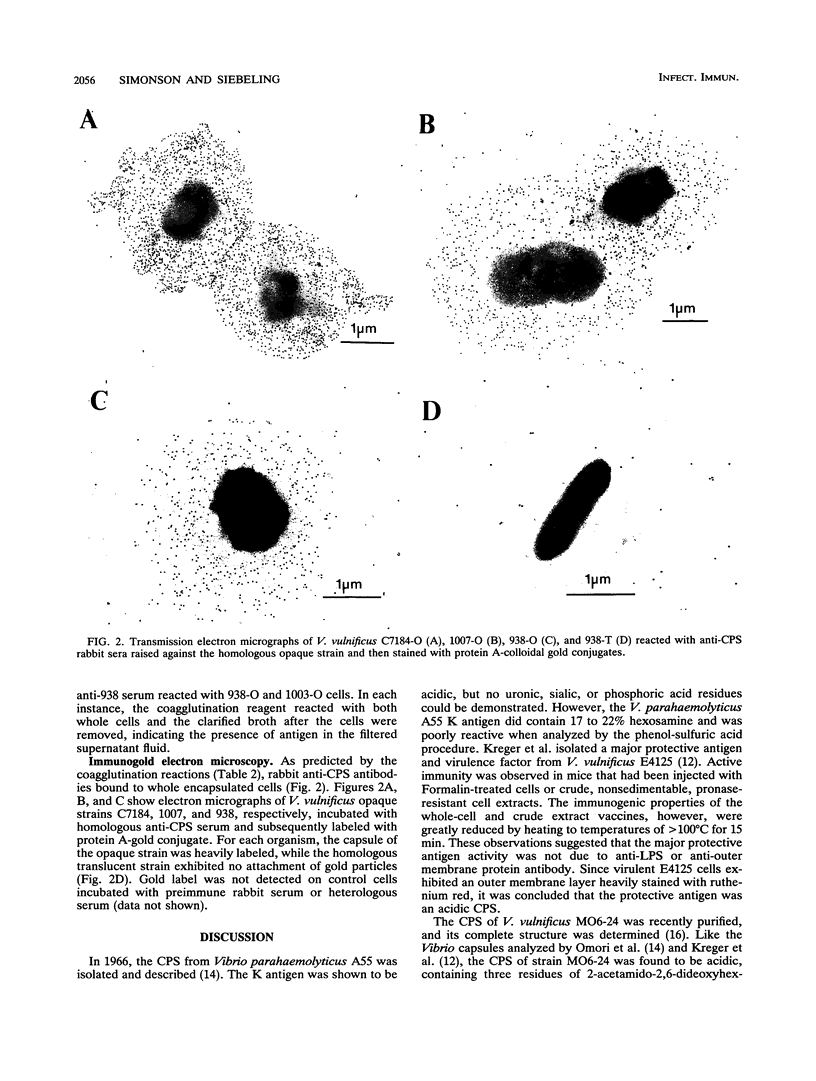
Opaque colony morphology has been correlated to Vibrio vulnificus virulence. However, the number of capsular serotypes expressed by virulent isolates is unknown. In an effort to produce anticapsule sera, capsular polysaccharide (CPS) from three opaque V. vulnificus strains was purified and characterized. Purified CPSs were acidic and contained considerable amounts of hexosamine and trace quantities of protein and nucleic acid. CPS purified from strain C7184 was poorly immunogenic for rabbits and mice, since repeated injection produced little detectable anticapsular antibody. To improve immunogenicity, CPS-protein conjugates were prepared from adipic acid hydrazide derivatives of CPS purified from each strain and carbodiimide as a coupling reagent. The immunogenicity of C7184 CPS was enhanced by conjugation to keyhole limpet hemocyanin, since injection into mice elicited production of anticapsular antibodies, the level of which was dependent on the dose and time since initial immunization. Injection of rabbits with CPS-protein conjugates also produced anticapsular antibodies. Staphylococcus aureus cells armed with each of the three anticapsular antibodies coagglutinated only the homologous opaque strain, indicating the existence of at least three capsular types. Further screening of 32 opaque and translucent V. vulnificus isolates revealed only three cross-reacting strains. These results suggest the presence of numerous V. vulnificus capsular types.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Merson M. H., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G., Heublein P. C. Disease caused by a marine Vibrio. Clinical characteristics and epidemiology. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 4;300(1):1–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901043000101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G. Diseases of humans (other than cholera) caused by vibrios. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:341–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C., Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., Rastogi S. C. Further studies on the immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type b and pneumococcal type 6A polysaccharide-protein conjugates. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):245–256. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.245-256.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S. The biologic significance of bacterial encapsulation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:87–95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Fürer E. Synthesis and characterization of Escherichia coli O18 O-polysaccharide conjugate vaccines. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):373–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.373-377.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Germanier R. Purification and vaccine potential of Klebsiella capsular polysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):225–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.225-230.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb A. F. Determination of free amino groups in proteins by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1966 Mar;14(3):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90275-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J. Capsular polysaccharides as vaccine candidates. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:97–127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Gray L. D., Testa J. Protection of mice against Vibrio vulnificus disease by vaccination with surface antigen preparations and anti-surface antigen antisera. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):537–543. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.537-543.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagergard T., Shiloach J., Robbins J. B., Schneerson R. Synthesis and immunological properties of conjugates composed of group B streptococcus type III capsular polysaccharide covalently bound to tetanus toxoid. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):687–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.687-694.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I. The serology of capsular antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:43–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy G. P., Hayat U., Abeygunawardana C., Fox C., Wright A. C., Maneval D. R., Jr, Bush C. A., Morris J. G., Jr Purification and determination of the structure of capsular polysaccharide of Vibrio vulnificus M06-24. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2620–2630. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2620-2630.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Barrera O., Sutton A., Robbins J. B. Preparation, characterization, and immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-protein conjugates. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):361–376. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., Chu C., Sutton A., Vann W., Vickers J. C., London W. T., Curfman B., Hardegree M. C., Shiloach J. Serum antibody responses of juvenile and infant rhesus monkeys injected with Haemophilus influenzae type b and pneumococcus type 6A capsular polysaccharide-protein conjugates. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):582–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.582-591.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda S., Kobayashi M., Yamada H., Yoshida S., Ogawa M., Mizuguchi Y. Inhibitory effect of capsular antigen of Vibrio vulnificus on bactericidal activity of human serum. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(5):393–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb03102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson J. G., Siebeling R. J. Coagglutination of Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio mimicus, and Vibrio vulnificus with anti-flagellar monoclonal antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):1962–1966. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.1962-1966.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson J., Siebeling R. J. Rapid serological identification of Vibrio vulnificus by anti-H coagglutination. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Dec;52(6):1299–1304. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.6.1299-1304.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. M., White V. K., Zane S. F., Oliver J. D. Correlation between virulence and colony morphology in Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):269–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.269-272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Gilkerson E. Quantitation of glycosaminoglycan hexosamine using 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolone hydrazone hydrochloride. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):478–480. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A., Vann W. F., Karpas A. B., Stein K. E., Schneerson R. An avidin-biotin based ELISA for quantitation of antibody to bacterial polysaccharides. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Oct 10;82(2):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Brenner F., Blake P. A. Clinical features and an epidemiological study of Vibrio vulnificus infections. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):558–561. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamplin M. L., Specter S., Rodrick G. E., Friedman H. Vibrio vulnificus resists phagocytosis in the absence of serum opsonins. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):715–718. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.715-718.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. E., Bright R. T-cell modulation of the antibody response to bacterial polysaccharide antigens. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):180–185. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.180-185.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann W. F., Sutton A., Schneerson R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Methods Enzymol. 1990;184:537–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. C., Simpson L. M., Oliver J. D., Morris J. G., Jr Phenotypic evaluation of acapsular transposon mutants of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1769–1773. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1769-1773.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyle F. A., Artenstein M. S., Brandt B. L., Tramont E. C., Kasper D. L., Altieri P. L., Berman S. L., Lowenthal J. P. Immunologic response of man to group B meningococcal polysaccharide vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):514–521. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Ogawa M., Mizuguchi Y. Relation of capsular materials and colony opacity to virulence of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):446–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.446-451.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





