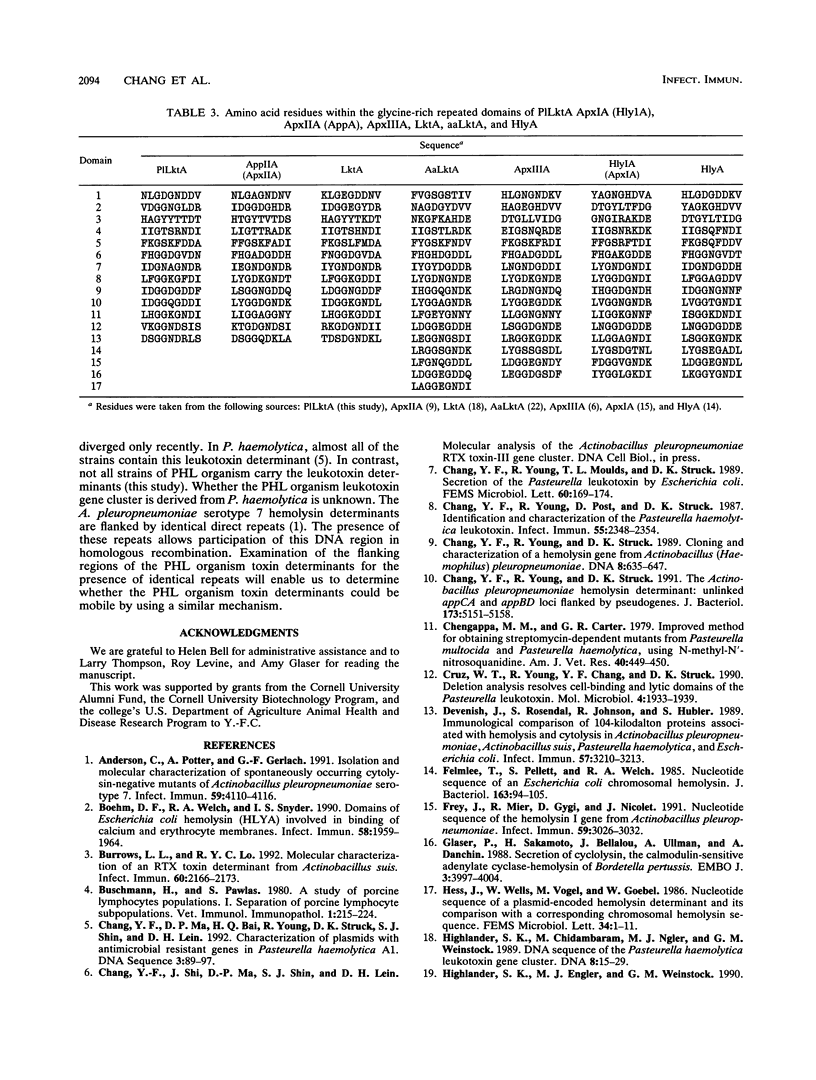
Abstract
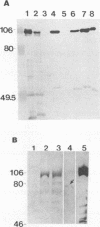
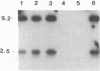
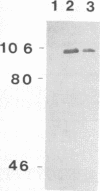
A Pasteurella haemolytica-like organism, a new species of bacterium isolated from piglets with diarrhea, secretes a leukotoxin into the culture media. Western blot (immunoblot) analysis indicated that this leukotoxin cross-reacted with antileukotoxin antibody derived from cattle immunized with P. haemolytica. Five overlapping recombinant bacteriophages carrying the gene for this 105-kDa polypeptide were identified with a DNA probe containing sequences from the P. haemolytica lktCA genes from a P. haemolytica-like organism strain 5943 genomic library. Sequence analysis of a region of the cloned DNA revealed two open reading frames encoding proteins with predicted masses of 19.4 and 101.6 kDa. These genes, which we designate pllktC (P. haemolytica-like organism leukotoxin C gene) and pllktA (A gene), respectively, are similar in sequence to the RTX (repeat of toxin) toxin family. The structure of the 101.6-kDa protein derived from the DNA sequence shows three transmembrane domains in the N-terminal part of the protein, 13 glycine-rich repeat domains in the second half of the protein, and a hydrophobic C-terminal part. pllktC and pllktA are strongly homologous to P. haemolytica lktC and lktA genes. However, this leukotoxin kills both BL-3 and pig leukocytes and is not hemolytic.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C., Potter A. A., Gerlach G. F. Isolation and molecular characterization of spontaneously occurring cytolysin-negative mutants of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 7. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4110–4116. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4110-4116.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm D. F., Welch R. A., Snyder I. S. Domains of Escherichia coli hemolysin (HlyA) involved in binding of calcium and erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1959–1964. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1959-1964.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows L. L., Lo R. Y. Molecular characterization of an RTX toxin determinant from Actinobacillus suis. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2166–2173. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2166-2173.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschmann H., Pawlas S. A study of porcine lymphocyte populations. I. Separation of porcine lymphocyte subpopulations. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Aug;1(3):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(80)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Ma D. P., Bai H. Q., Young R., Struck D. K., Shin S. J., Lein D. H. Characterization of plasmids with antimicrobial resistant genes in Pasteurella haemolytica A1. DNA Seq. 1992;3(2):89–97. doi: 10.3109/10425179209034001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Young R., Moulds T. L., Struck D. K. Secretion of the Pasteurella leukotoxin by Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 15;51(1):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90502-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Young R., Post D., Struck D. K. Identification and characterization of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2348–2354. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2348-2354.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Young R., Struck D. K. Cloning and characterization of a hemolysin gene from Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) pleuropneumoniae. DNA. 1989 Nov;8(9):635–647. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Young R., Struck D. K. The Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae hemolysin determinant: unlinked appCA and appBD loci flanked by pseudogenes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5151–5158. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5151-5158.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chengappa M. M., Carter G. R. Improved method for obtaining streptomycin-dependent mutants from Pasteurella multocida and Pasteurella haemolytica, using N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Mar;40(3):449–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz W. T., Young R., Chang Y. F., Struck D. K. Deletion analysis resolves cell-binding and lytic domains of the Pasteurella leukotoxin. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1933–1939. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenish J., Rosendal S., Johnson R., Hubler S. Immunoserological comparison of 104-kilodalton proteins associated with hemolysis and cytolysis in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Actinobacillus suis, Pasteurella haemolytica, and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3210–3213. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3210-3213.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Welch R. A. Nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli chromosomal hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):94–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.94-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Meier R., Gygi D., Nicolet J. Nucleotide sequence of the hemolysin I gene from Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3026–3032. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3026-3032.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser P., Sakamoto H., Bellalou J., Ullmann A., Danchin A. Secretion of cyclolysin, the calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase-haemolysin bifunctional protein of Bordetella pertussis. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3997–4004. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highlander S. K., Chidambaram M., Engler M. J., Weinstock G. M. DNA sequence of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin gene cluster. DNA. 1989 Jan-Feb;8(1):15–28. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):468–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Cross M., Senior B., Koronakis E., Hughes C. The secreted hemolysins of Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Morganella morganii are genetically related to each other and to the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1509–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1509-1515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraig E., Dailey T., Kolodrubetz D. Nucleotide sequence of the leukotoxin gene from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: homology to the alpha-hemolysin/leukotoxin gene family. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):920–929. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.920-929.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lally E. T., Golub E. E., Kieba I. R., Taichman N. S., Rosenbloom J., Rosenbloom J. C., Gibson C. W., Demuth D. R. Analysis of the Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin gene. Delineation of unique features and comparison to homologous toxins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15451–15456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo R. Y., Strathdee C. A., Shewen P. E. Nucleotide sequence of the leukotoxin genes of Pasteurella haemolytica A1. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1987–1996. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1987-1996.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig A., Jarchau T., Benz R., Goebel W. The repeat domain of Escherichia coli haemolysin (HlyA) is responsible for its Ca2+-dependent binding to erythrocytes. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):553–561. doi: 10.1007/BF00330494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Gray L., Holland I. B. Genetical and functional organisation of the Escherichia coli haemolysin determinant 2001. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(2):282–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00425672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin B. G., Greer S. C., Chengappa M. M., Singh S., Maddux R. L., Kadel W. L., McLaughlin P. S. Association of a Pasteurella haemolytica-like organism with enteritis in swine. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1991 Oct;3(4):324–327. doi: 10.1177/104063879100300409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWhinney D. R., Chang Y. F., Young R., Struck D. K. Separable domains define target cell specificities of an RTX hemolysin from Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):291–297. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.291-297.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Hawley D. K., Entriken R., McClure W. R. Escherichia coli promoter sequences predict in vitro RNA polymerase selectivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):789–800. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smits M. A., Briaire J., Jansen R., Smith H. E., Kamp E. M., Gielkens A. L. Cytolysins of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 9. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4497–4504. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4497-4504.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. S., Lubinsky-Mink S., Jackson C. G., Cassel A., Kuhn J. pHG165: a pBR322 copy number derivative of pUC8 for cloning and expression. Plasmid. 1986 May;15(3):172–181. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and characterization of genes encoding the secretion function of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin determinant. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):916–928. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.916-928.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Pellett S. Transcriptional organization of the Escherichia coli hemolysin genes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1622–1630. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1622-1630.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]