Abstract
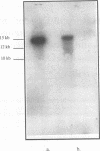
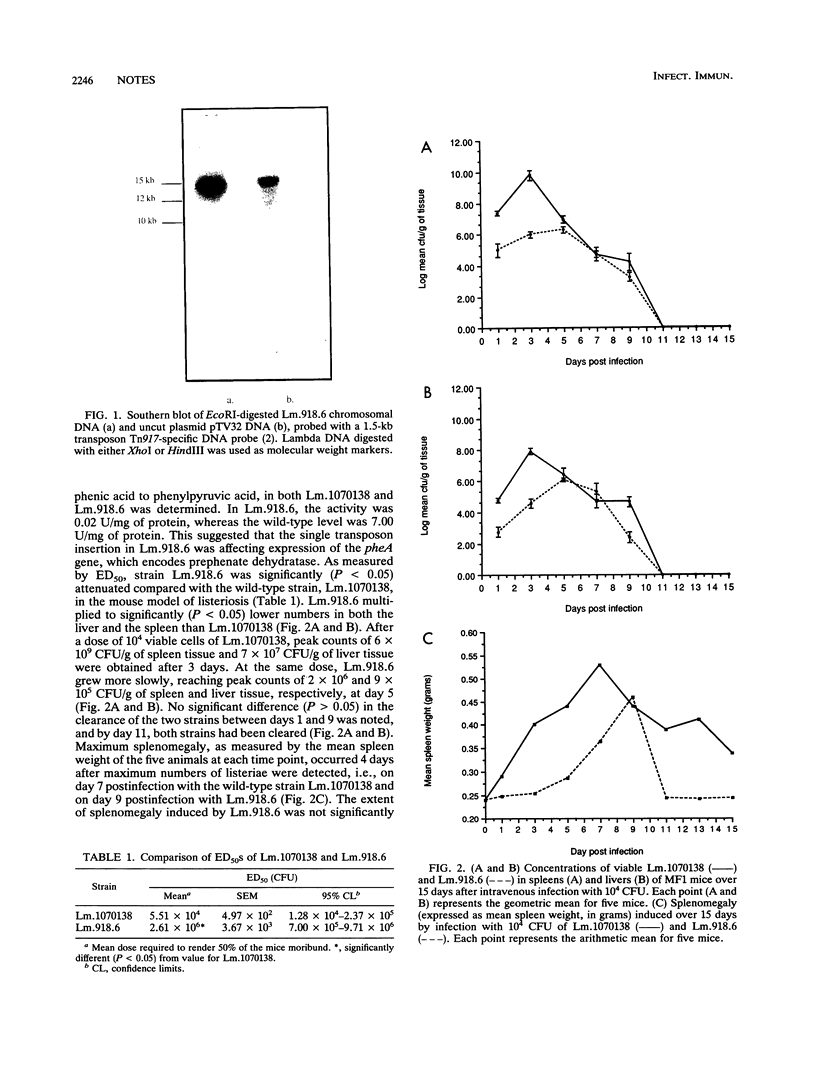
A transposon insertion mutant of Listeria monocytogenes was shown to be deficient in prephenate dehydratase, an enzyme acting late in the pathway for biosynthesis of phenylalanine. This mutant had reduced virulence in mice. The mutant and parent strains persisted to the same extent in the tissues of infected mice and elicited similar degrees of splenomegaly. Mice vaccinated with the mutant were protected significantly from subsequent challenge with virulent L. monocytogenes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG A. S., SWORD C. P. CELLULAR RESISTANCE IN LISTERIOSIS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Jun;114:258–264. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilli A., Portnoy A., Youngman P. Insertional mutagenesis of Listeria monocytogenes with a novel Tn917 derivative that allows direct cloning of DNA flanking transposon insertions. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3738–3744. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3738-3744.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel S., Youmans G. P. Specificity of Acquired Resistance Produced by Immunization with Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria Fractions. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):121–126. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.121-126.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G., Chatfield S., Pickard D., Bester J., O'Callaghan D., Maskell D. Construction and characterization of vaccine strains of Salmonella harboring mutations in two different aro genes. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1329–1335. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M. E., ROESSLER W. G. Growth of Listeria monocytogenes in defined media. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:528–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.528-533.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENSEN R. A., NESTER E. W. THE REGULATORY SIGNIFICANCE OF INTERMEDIARY METABOLITES: CONTROL OF AROMATIC ACID BIOSYNTHESIS BY FEEDBACK INHIBITION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:468–481. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80270-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. W., Dougan G., Hayward C., Mackensie N., Collins P., Chatfield S. N. Oral vaccination of calves against experimental salmonellosis using a double aro mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Vaccine. 1991 Jan;9(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90313-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Herrington D., Murphy J. R., Morris J. G., Losonsky G., Tall B., Lindberg A. A., Svenson S., Baqar S., Edwards M. F. Safety, infectivity, immunogenicity, and in vivo stability of two attenuated auxotrophic mutant strains of Salmonella typhi, 541Ty and 543Ty, as live oral vaccines in humans. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):888–902. doi: 10.1172/JCI112899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde K., Abraham A. A., Beer J. Stable Listeria monocytogenes live vaccine candidate strains with graded attenuation on the mouse model. Vaccine. 1991 Feb;9(2):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90264-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel E., Reich K. A., Favier R., Berche P., Cossart P. Attenuated mutants of the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes obtained by single amino acid substitutions in listeriolysin O. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2167–2178. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nester E. W., Jensen R. A. Control of aromatic acid biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis: sequenial feedback inhibition. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1594–1598. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1594-1598.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan D., Maskell D., Liew F. Y., Easmon C. S., Dougan G. Characterization of aromatic- and purine-dependent Salmonella typhimurium: attention, persistence, and ability to induce protective immunity in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):419–423. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.419-423.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. P., Reina-Guerra M., Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A., Habasha F., Johnson E., Merritt F. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium as modified live vaccines for calves. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Jan;45(1):59–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. C., Roberts I. S., Jones D., Andrew P. W. Effect of growth temperature on virulence of strains of Listeria monocytogenes in the mouse: evidence for a dose dependence. J Appl Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;70(3):239–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1991.tb02931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilesmith J. W., Gitter M. Epidemiology of ovine listeriosis in Great Britain. Vet Rec. 1986 Nov 8;119(19):467–470. doi: 10.1136/vr.119.19.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]