Abstract
As the initial step in infection, group A streptococci (GAS) colonize either the nasopharyngeal mucosa or the skin of humans. A number of virulence factors have been implicated in the colonization phase of pathogenesis based upon their in vitro activities, but the in vivo data supporting their role in colonization of the host tissues is lacking. In this investigation, the potential requirement for M protein in pharyngeal colonization by GAS was explored by using near-isogenic strains in experimental animals studies. Fischer rats were infected by intranasal and oral inoculation with both M-positive and M-negative Streptococcus pyogenes strains. Colonization of the pharyngeal area by the streptococci was monitored at various time intervals. Both M-positive and M-negative strains colonized during the first week following infection, indicating that M protein was not necessary for this initial colonization. Two M-positive strains of S. pyogenes were recovered from the rats up to 23 weeks following inoculation, while the colonization levels for M-negative strains decreased rapidly in the second and third weeks, becoming negligible by the fourth week. This indicates a potential role for M protein in the persistence of colonization at this mucosal surface. Colonization of rats with either M-positive strain of S. pyogenes also resulted in the appearance of salivary and serum antibody responses. This in vivo model should allow further investigation into factors required for GAS disease, including the examination of the potential role of the host immune response both in modulation of the pharyngeal surface and in modulation of antigenic changes in M protein or other surface factors.
Full text
PDF


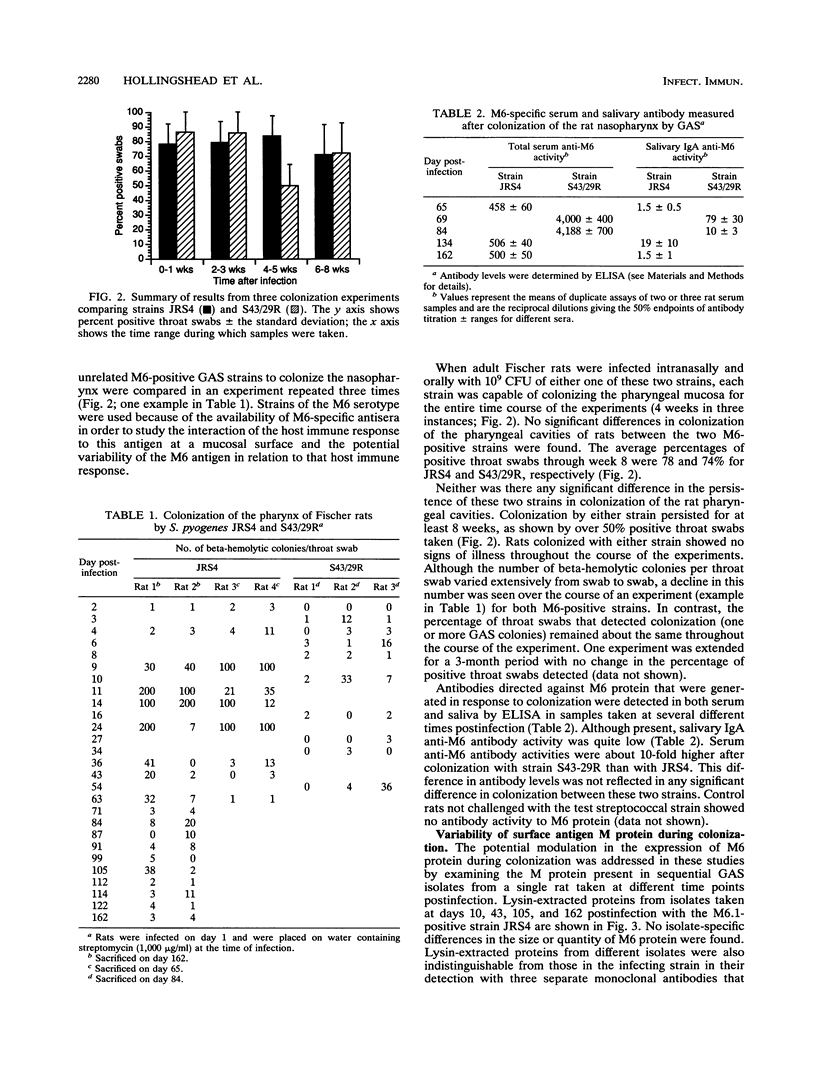



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H., Courtney H. S. Bacterial adherence: the attachment of group A streptococci to mucosal surfaces. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9 (Suppl 5):S475–S481. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_5.s475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessen D., Fischetti V. A. Influence of intranasal immunization with synthetic peptides corresponding to conserved epitopes of M protein on mucosal colonization by group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2666–2672. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2666-2672.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessen D., Fischetti V. A. Synthetic peptide vaccine against mucosal colonization by group A streptococci. I. Protection against a heterologous M serotype with shared C repeat region epitopes. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 15;145(4):1251–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D., Gibbons R. J. Antigenic variation of Streptococcus mutans colonizing gnotobiotic rats. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1231–1236. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1231-1236.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronze M. S., Courtney H. S., Dale J. B. Epitopes of group A streptococcal M protein that evoke cross-protective local immune responses. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):888–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronze M. S., McKinsey D. S., Beachey E. H., Dale J. B. Protective immunity evoked by locally administered group A streptococcal vaccines in mice. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2767–2770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Genetic manipulation of pathogenic streptococci. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:556–586. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04028-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Stephens D. S., Olsén A., Scott J. R. Role of M protein in adherence of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1811–1817. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1811-1817.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H. Derrick Edward Award Lecture. The pathogenic potential of mycoplasmas: Mycoplasma pulmonis as a model. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4 (Suppl):S18–S34. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_1.s18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Cleary P. P. Complete nucleotide sequence of the streptococcal C5a peptidase gene of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3161–3167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. M protein-associated adherence of Streptococcus pyogenes to epithelial surfaces: prerequisite for virulence. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):826–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.826-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Jones K. F., Manjula B. N., Scott J. R. Streptococcal M6 protein expressed in Escherichia coli. Localization, purification, and comparison with streptococcal-derived M protein. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1083–1095. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Jones K. F., Scott J. R. Size variation of the M protein in group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1384–1401. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A. Streptococcal M protein: molecular design and biological behavior. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jul;2(3):285–314. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J. Bacterial adhesion to oral tissues: a model for infectious diseases. J Dent Res. 1989 May;68(5):750–760. doi: 10.1177/00220345890680050101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski E., Caparon M. Protein F, a fibronectin-binding protein, is an adhesin of the group A streptococcus Streptococcus pyogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6172–6176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty D. L., Ofek I., Courtney H. S., Doyle R. J. Multiple adhesins of streptococci. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2147–2152. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2147-2152.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann S. The throat carrier rate of group A and other beta hemolytic streptococci among patients in general practice. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Oct;93(5):347–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of type 6 M protein of the group A Streptococcus. Repetitive structure and membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1677–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell T. H., Spinell D. M., Gibbons R. J. Antigenic variation in populations of Streptococcus salivarius isolated from the human mouth. Arch Oral Biol. 1979;24(5):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(79)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUSE R. M., RAMMELKAMP C. H., Jr, DENNY F. W., Jr, WANNAMAKER L. W. Studies of the carrier state following infection with group A streptococci. 1. Effect of climate. J Clin Invest. 1962 Mar;41:568–574. doi: 10.1172/JCI104510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUSE R. M., RAMMELKAMP C. H., Jr Studies of the carrier state following infection with group A streptococci. II. Infectivity of streptococci isolated during acute pharyngitis and during the carrier state. J Clin Invest. 1962 Mar;41:575–578. doi: 10.1172/JCI104511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan E. L. The group A streptococcal upper respiratory tract carrier state: an enigma. J Pediatr. 1980 Sep;97(3):337–345. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Hansen E. J. Antigenic and phenotypic variations of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipopolysaccharide and their relationship to virulence. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):69–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.69-79.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., Childers N. K. Development and outlook for a caries vaccine. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1990;1(1):37–54. doi: 10.1177/10454411900010010401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Smith A. L., Averill D. R., Smith D. H. Haemophilus influenzae meningitis in infant rats after intranasal inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):154–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgren M., Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. A method for allelic replacement that uses the conjugative transposon Tn916: deletion of the emm6.1 allele in Streptococcus pyogenes JRS4. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3846–3850. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3846-3850.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Casal J., Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Mry, a trans-acting positive regulator of the M protein gene of Streptococcus pyogenes with similarity to the receptor proteins of two-component regulatory systems. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2617–2624. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2617-2624.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. N., Jr, Flicker P. F., Cohen C., Manjula B. N., Fischetti V. A. Streptococcal M protein: alpha-helical coiled-coil structure and arrangement on the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4689–4693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier T. P., Kehoe M. A., Whitnack E., Dockter M. E., Beachey E. H. Fibrinogen binding and resistance to phagocytosis of Streptococcus sanguis expressing cloned M protein of Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):29–35. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.29-35.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn R. W., Lowry P. N. The anatomical area of involvement in streptococcal infections and the carrier state. Yale J Biol Med. 1970 Aug;43(1):1–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos J. I., Shigeoka A. O., Rote N. S., Hill H. R. Protective efficacy of a modified immune serum globulin in experimental group B streptococcal infection. J Pediatr. 1981 Dec;99(6):873–879. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. R., Guenthner P. C., Malone L. M., Fischetti V. A. Conversion of an M- group A streptococcus to M+ by transfer of a plasmid containing an M6 gene. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1641–1651. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigeoka A. O., Rote N. S., Santos J. I., Hill H. R. Assessment of the virulence factors of group B streptococci: correlation with sialic acid content. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):857–863. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Smith D. H., Averill D. R., Jr, Marino J., Moxon E. R. Production of Haemophilus influenzae b meningitis in infant rats by intraperitoneal inoculation. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):278–290. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.278-290.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Hunt D. A., Bansal G., McCartney-Francis N., Ellingsworth L., Allen J. B. Bacterial cell wall-induced immunosuppression. Role of transforming growth factor beta. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1403–1417. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnack E., Beachey E. H. Inhibition of complement-mediated opsonization and phagocytosis of Streptococcus pyogenes by D fragments of fibrinogen and fibrin bound to cell surface M protein. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1983–1997. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




