Abstract
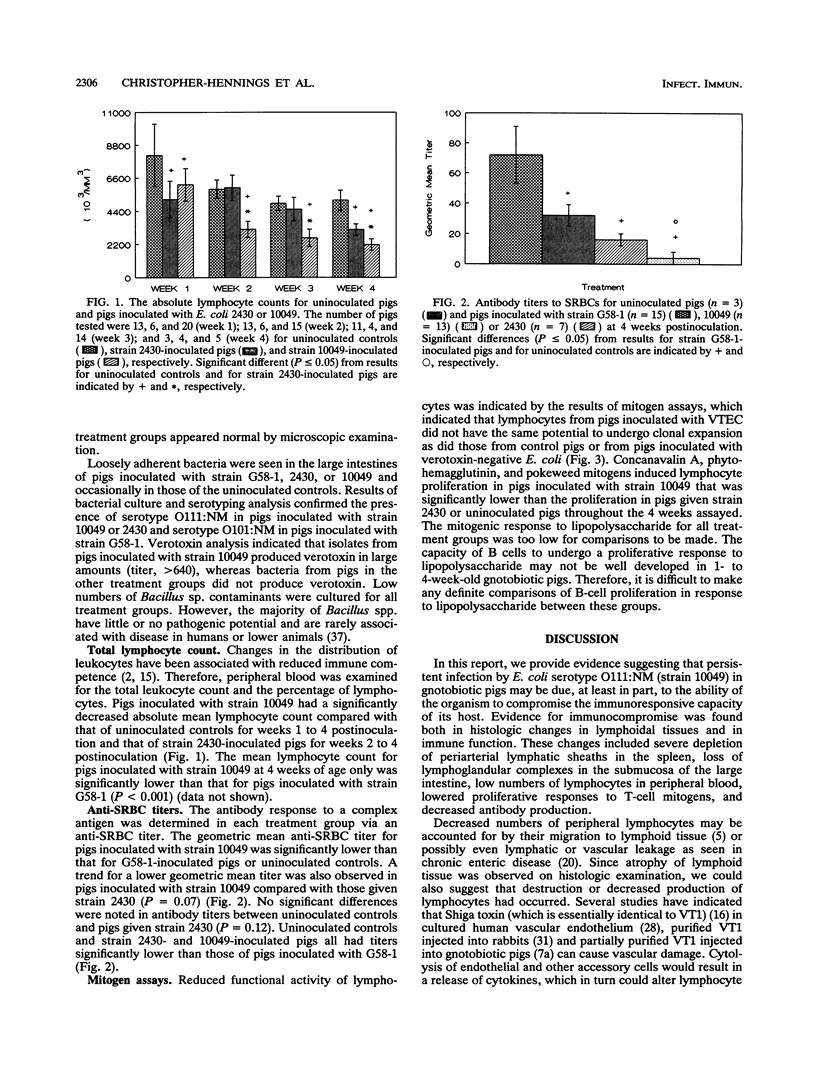
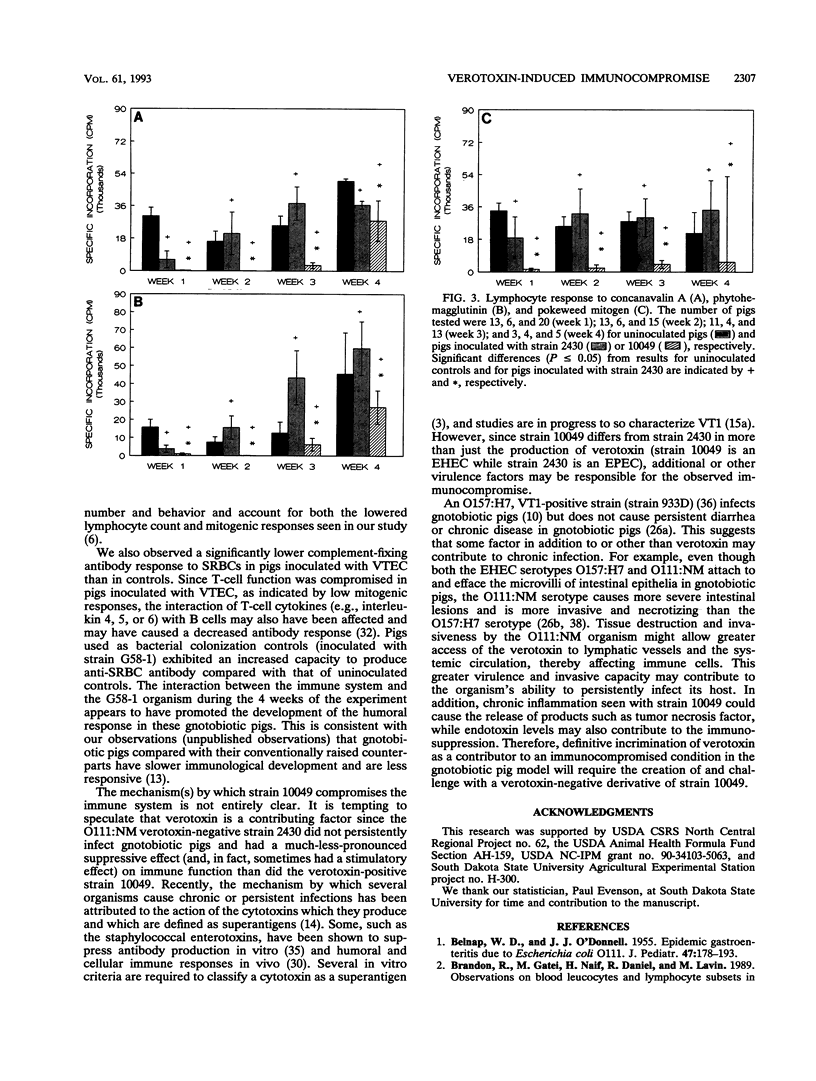
A verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli serotype O111:NM strain (strain 10049; verotoxin 1 positive) persistently infected experimentally inoculated gnotobiotic pigs, causing attaching-effecting intestinal lesions and chronic diarrhea. Experiments were performed to determine whether persistent infection might be associated with immunocompromise of the host of this organism. Pigs inoculated with this strain had a significant reduction in peripheral blood lymphocytes and lower antibody titers to sheep erythrocytes compared with control pigs. Compared with pigs given a verotoxin-negative pathogenic strain of the same serotype (O111:NM, strain 2430), pigs inoculated with the verotoxin-positive strain had lower peripheral lymphocyte counts and proliferative responses to concanavalin A, phytohemagglutinin, and pokeweed mitogens. The results of this study suggest that strain 10049 has an immunocompromising effect on gnotobiotic pigs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELNAP W. D., O'DONNELL J. J. Epidemic gastroenteritis due to Escherichia coli 0-111; a review of the literature, with the epidemiology, bacteriology, and clinical findings of a large outbreak. J Pediatr. 1955 Aug;47(2):178–193. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(55)80029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan J. E., Herman A., Kappler J. W., Marrack P. Stimulation of B10.BR T cells with superantigenic staphylococcal toxins. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2473–2479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen C. R., Christie D. L. Chronic diarrhea in infants caused by adherent enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Pediatr. 1982 Mar;100(3):358–361. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80429-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and its biologically related cytokines. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:153–205. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60642-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker M. M., Polliack A., Yeivin R., Sacks T. G. Immunofluorescent demonstration of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in tissues of infants dying with enteritis. Pediatrics. 1970 Dec;46(6):855–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong J. S., de Chadarevian J. P., Kaplan B. S. Hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Current concepts and management. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1982 Aug;29(4):835–856. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)34216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. H., Collins J. E., Duimstra J. R. Infection of gnotobiotic pigs with an Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain associated with an outbreak of hemorrhagic colitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):953–956. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.953-956.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. H., Moxley R. A., Andraos C. Y. Edema disease-like brain lesions in gnotobiotic piglets infected with Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1339–1342. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1339-1342.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. K., Dalrymple J. M. Quantitative microtiter cytotoxicity assay for Shigella toxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):361–366. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.361-366.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall G. A., Chanter N., Bland A. P. Comparison in gnotobiotic pigs of lesions caused by verotoxigenic and non-verotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Vet Pathol. 1988 May;25(3):205–210. doi: 10.1177/030098588802500304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerberg C., Schurig G. G., Ochs D. L. Immunodeficiency in young pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Jun;50(6):868–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman M. "Superantigens" may shed light on immune puzzle. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):685–686. doi: 10.1126/science.2333520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A., Rackowski J. L., Haggarty B. S., Gaulton G. N. T4 endocytosis and phosphorylation induced by phorbol esters but not by mitogen or HIV infection. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):786–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. P., Newland J. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the structural genes for Shiga-like toxin I encoded by bacteriophage 933J from Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1987 Feb;2(2):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janke B. H., Francis D. H., Collins J. E., Libal M. C., Zeman D. H., Johnson D. D., Neiger R. D. Attaching and effacing Escherichia coli infection as a cause of diarrhea in young calves. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1990 Mar 15;196(6):897–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. K., Pai C. H., Jadusingh I. H., Macinnis M. L., Shaffer E. A., Hershfield N. B. The histopathology of rectosigmoid biopsies from adults with bloody diarrhea due to verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jul;88(1):78–82. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/88.1.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Edelman R. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of classic serotypes associated with infant diarrhea: epidemiology and pathogenesis. Epidemiol Rev. 1984;6:31–51. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Xu J. G., Kaper J. B., Lior H., Prado V., Tall B., Nataro J., Karch H., Wachsmuth K. A DNA probe to identify enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli of O157:H7 and other serotypes that cause hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):175–182. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miniats O. P., Jol D. Gnotobiotic pigs-derivation and rearing. Can J Comp Med. 1978 Oct;42(4):428–437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. M., Tyrrell D. L., Jewell L. D. Colonic biopsy in verotoxin-induced hemorrhagic colitis and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jul;86(1):108–112. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D., Thompson M. R., Formal S. B. Production of Shigella dysenteriae type 1-like cytotoxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):763–769. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T. G., Del Vecchio P. J., Brown J. E., Moran T. P., Rowland B. M., Judge T. K., Rothman S. W. Direct cytotoxic action of Shiga toxin on human vascular endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2373–2378. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2373-2378.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto M., Torten M., Birnbaum S. C. Suppression of the in vivo humoral and cellular immune response by staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB). Transplantation. 1978 Jun;25(6):320–323. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197806000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson S. E., Rotman T. A., Jay V., Smith C. R., Becker L. E., Petric M., Olivieri N. F., Karmali M. A. Experimental verocytotoxemia in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4154–4167. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4154-4167.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. G., Johnson H. M. The effect of staphylococcal enterotoxins on the primary in vitro immune response. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):575–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Newland J. W., Smith H. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Two toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 933 encode antigenically distinct toxins with similar biologic activities. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.135-140.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Gibson R., Montanaro J. Nature and distribution of mucosal lesions associated with enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli in piglets and the role of plasmid-mediated factors. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1142–1150. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1142-1150.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Karch H., Wachsmuth K. I., Robins-Browne R. M., O'Brien A. D., Lior H., Cohen M. L., Smithers J., Levine M. M. Role of a 60-megadalton plasmid and Shiga-like toxins in the pathogenesis of infection caused by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 in gnotobiotic piglets. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3117–3125. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3117-3125.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Wachsmuth I. K., Chapman C., Birden R., Brittingham J., Jackson C., Hogg J. The pathogenesis of hemorrhagic colitis caused by Escherichia coli O157:H7 in gnotobiotic piglets. J Infect Dis. 1986 Oct;154(4):712–716. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.4.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Wachsmuth K. I., Smithers J., Jackson C. Studies in gnotobiotic piglets on non-O157:H7 Escherichia coli serotypes isolated from patients with hemorrhagic colitis. Gastroenterology. 1988 Mar;94(3):590–597. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



