Abstract
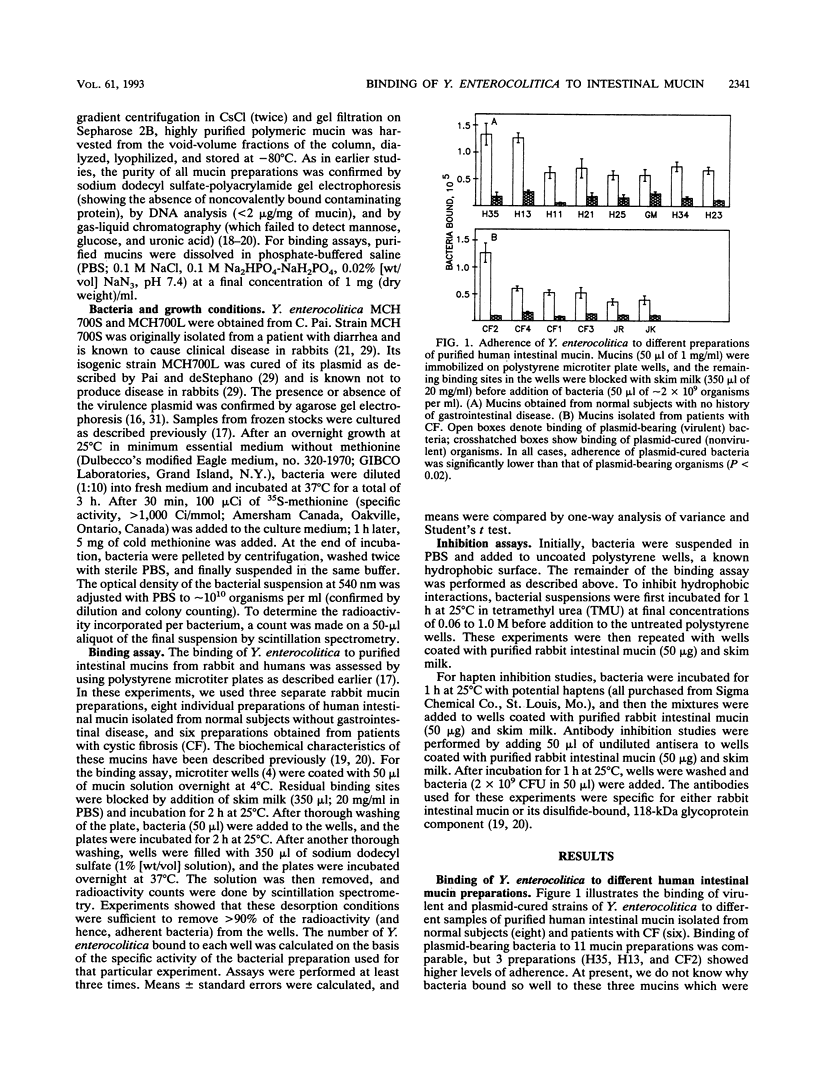
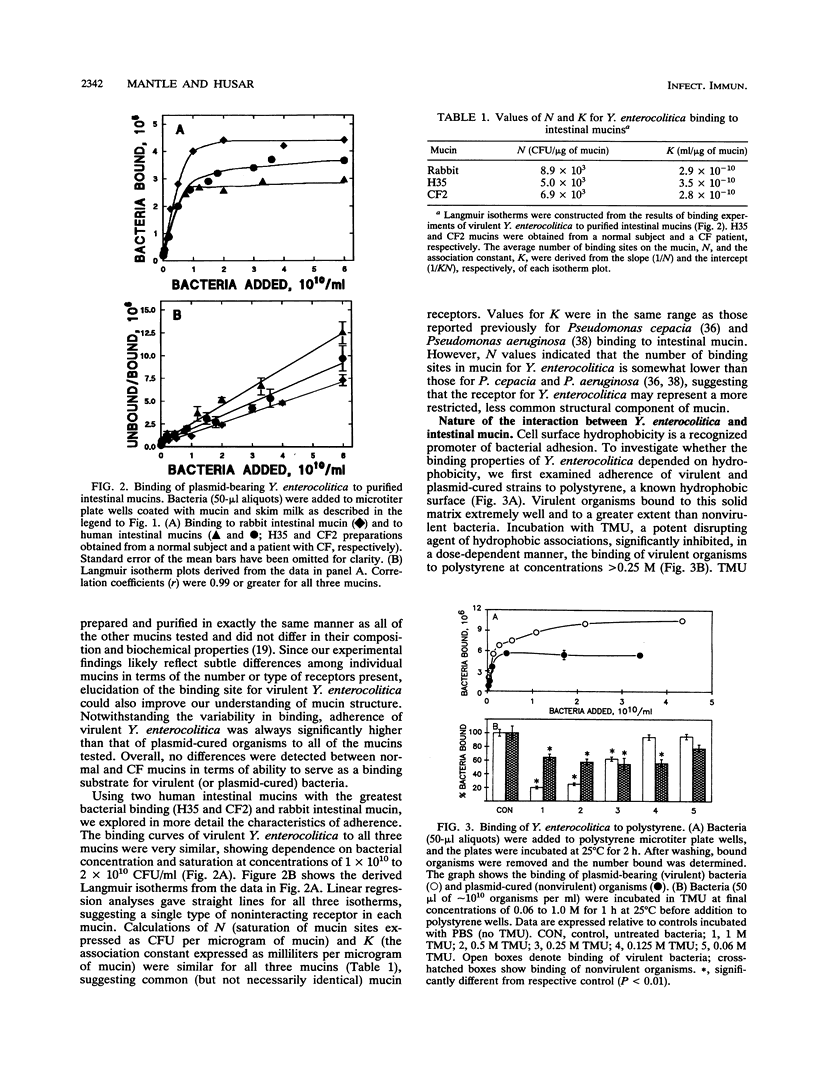
Interactions between Yersinia enterocolitica and purified intestinal mucins from rabbit and humans were investigated. Plasmid-bearing virulent organisms (but not plasmid-free nonvirulent bacteria) bound well to both mucins, suggesting that adherence was controlled by the virulence plasmid. Examination of binding to 14 different preparations of purified human intestinal mucin (8 preparations obtained from normal subjects and 6 samples from patients with cystic fibrosis) revealed no differences between normal and cystic fibrotic mucins in ability to serve as a binding substrate for virulent Y. enterocolitica. Analyses of binding curves suggested the presence of a single type of noninteracting receptor for Y. enterocolitica in both rabbit and human mucins with similar (but not necessarily identical) structures. Virulent bacteria bound to polystyrene through hydrophobic interactions that could be disrupted by treating the organisms with tetramethyl urea. In contrast, binding of plasmid-bearing Y. enterocolitica to intestinal mucin was not susceptible to tetramethyl urea and therefore does not appear to involve hydrophobic interactions. Prior incubation of organisms with mucin significantly inhibited binding to polystyrene, suggesting that mucin can mask hydrophobic adhesins on the bacterial surface. Hapten inhibition studies revealed that the monosaccharides galactose and N-acetylgalactosamine and the disaccharide lactose could markedly reduce (but not abolish) bacterial adherence to mucin but other monosaccharides and the RGD peptide had no effect on mucin binding. We conclude that virulent Y. enterocolitica is capable of interacting with the carbohydrate moiety of intestinal mucin. These interactions appear to be plasmid mediated and not hydrophobic.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balligand G., Laroche Y., Cornelis G. Genetic analysis of virulence plasmid from a serogroup 9 Yersinia enterocolitica strain: role of outer membrane protein P1 in resistance to human serum and autoagglutination. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):782–786. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.782-786.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergey E. J., Levine M. J., Reddy M. S., Bradway S. D., Al-Hashimi I. Use of the photoaffinity cross-linking agent N-hydroxysuccinimidyl-4-azidosalicylic acid to characterize salivary-glycoprotein-bacterial interactions. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):43–48. doi: 10.1042/bj2340043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. S., Arruda J. C., Williams T. J., Laux D. C. Adhesion of a human fecal Escherichia coli strain to mouse colonic mucus. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):139–145. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.139-145.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Aber R. C. Yersinia enterocolitica. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 6;321(1):16–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907063210104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drumm B., Neumann A. W., Policova Z., Sherman P. M. Bacterial cell surface hydrophobicity properties in the mediation of in vitro adhesion by the rabbit enteric pathogen Escherichia coli strain RDEC-1. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1588–1594. doi: 10.1172/JCI114336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Qureshi J. V. Selective binding of blood group-reactive salivary mucins by Streptococcus mutans and other oral organisms. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):665–671. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.665-671.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwozdzinski K., Slomiany A., Nishikawa H., Okazaki K., Slomiany B. L. Gastric mucin hydrophobicity: effects of associated and covalently bound lipids, proteolysis, and reduction. Biochem Int. 1988 Nov;17(5):907–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Swain A., Falkow S. Analysis of expression and thermoregulation of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis inv gene with hybrid proteins. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2133–2138. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2133-2138.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Namork E., Skurnik M., Nesbakken T. Plasmid-mediated surface fibrillae of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica: relationship to the outer membrane protein YOP1 and possible importance for pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2247–2254. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2247-2254.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Zink D. L. Plasmid-associated cell surface charge and hydrophobicity of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):540–543. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.540-543.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W. J., Cavanaugh D. C. Correlation of autoagglutination and virulence of yersiniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):430–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.430-432.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian C. J., Hwang W. S., Pai C. H. Plasmid-mediated resistance to phagocytosis in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1176–1183. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1176-1183.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian C. J., Pai C. H. Inhibition of human neutrophil chemiluminescence by plasmid-mediated outer membrane proteins of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):145–151. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.145-151.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle M., Basaraba L., Peacock S. C., Gall D. G. Binding of Yersinia enterocolitica to rabbit intestinal brush border membranes, mucus, and mucin. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3292–3299. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3292-3299.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle M., Forstner G. G., Forstner J. F. Biochemical characterization of the component parts of intestinal mucin from patients with cystic fibrosis. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):345–354. doi: 10.1042/bj2240345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle M., Stewart G. Intestinal mucins from normal subjects and patients with cystic fibrosis. Variable contents of the disulphide-bound 118 kDa glycoprotein and different reactivities with an anti-(118 kDa glycoprotein) antibody. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):243–253. doi: 10.1042/bj2590243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle M., Thakore E., Hardin J., Gall D. G. Effect of Yersinia enterocolitica on intestinal mucin secretion. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):G319–G327. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.2.G319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle M., Thakore E. Rabbit intestinal and colonic mucins: isolation, partial characterization, and measurement of secretion using an enzyme-linked immunoassay. Biochem Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;66(10):1045–1054. doi: 10.1139/o88-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J. Plasmid-mediated and temperature-regulated surface properties of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):921–930. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.921-930.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J. Thermoregulation-dependent expression of Yersinia enterocolitica protein 1 imparts serum resistance to Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3732–3739. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3732-3739.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels T., Cornelis G. R. Secretion of hybrid proteins by the Yersinia Yop export system. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1677–1685. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1677-1685.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels T., Wattiau P., Brasseur R., Ruysschaert J. M., Cornelis G. Secretion of Yop proteins by Yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2840–2849. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2840-2849.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hill W. E., Falkow S. The ail locus is found uniquely in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes commonly associated with disease. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):121–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.121-131.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paerregaard A., Espersen F., Baker N. The influence of properties encoded by the Yersinia virulence plasmid on adhesion of Yersinia enterocolitica to ileal brush border membrane vesicles. APMIS. 1990 Oct;98(10):927–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paerregaard A., Espersen F., Jensen O. M., Skurnik M. Interactions between Yersinia enterocolitica and rabbit ileal mucus: growth, adhesion, penetration, and subsequent changes in surface hydrophobicity and ability to adhere to ileal brush border membrane vesicles. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):253–260. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.253-260.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., DeStephano L. Serum resistance associated with virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):605–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.605-611.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierson D. E., Falkow S. Nonpathogenic isolates of Yersinia enterocolitica do not contain functional inv-homologous sequences. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1059–1064. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1059-1064.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H., Bolin I., Beeder A. B., Falkow S. Characterization of common virulence plasmids in Yersinia species and their role in the expression of outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.108-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Carnoy C., Fievre S., Michalski J. C., Houdret N., Lamblin G., Strecker G., Roussel P. Pseudomonas aeruginosa recognizes carbohydrate chains containing type 1 (Gal beta 1-3GlcNAc) or type 2 (Gal beta 1-4GlcNAc) disaccharide units. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):700–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.700-704.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Houdret N., Koo L., Lamblin G., Roussel P. Differences in adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mucin glycopeptides from sputa of patients with cystic fibrosis and chronic bronchitis. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3066–3071. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3066-3071.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Pyle M. Evidence for mucins and sialic acid as receptors for Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the lower respiratory tract. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):339–344. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.339-344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajjan S. U., Forstner J. F. Characteristics of binding of Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7 strain CL-49 to purified intestinal mucin. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):860–867. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.860-867.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajjan U. S., Corey M., Karmali M. A., Forstner J. F. Binding of Pseudomonas cepacia to normal human intestinal mucin and respiratory mucin from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):648–656. doi: 10.1172/JCI115631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajjan U., Reisman J., Doig P., Irvin R. T., Forstner G., Forstner J. Binding of nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa to normal human intestinal mucin and respiratory mucin from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):657–665. doi: 10.1172/JCI115632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford B. A., Thomas V. L., Ramsay M. A. Binding of staphylococci to mucus in vivo and in vitro. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3735–3742. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3735-3742.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Koops H., Burkhardt H., Heesemann J., von der Mark K., Emmrich F. Plasmid-encoded outer membrane protein YadA mediates specific binding of enteropathogenic yersiniae to various types of collagen. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2153–2159. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2153-2159.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankar V., Naziruddin B., Reyes de la Rocha S., Sachdev G. P. Evidence of hydrophobic domains in human respiratory mucins. Effect of sodium chloride on hydrophobic binding properties. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5856–5864. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M. Expression of antigens encoded by the virulence plasmid of Yersinia enterocolitica under different growth conditions. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):183–190. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.183-190.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slomiany B. L., Murty V. L., Sarosiek J., Piotrowski J., Slomiany A. Role of associated and covalently bound lipids in salivary mucin hydrophobicity: effect of proteolysis and disulfide bridge reduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 30;151(3):1046–1053. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80471-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. F., LaMont J. T. Hydrophobic binding properties of bovine gallbladder mucin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12170–12177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tertti R., Skurnik M., Vartio T., Kuusela P. Adhesion protein YadA of Yersinia species mediates binding of bacteria to fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):3021–3024. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.3021-3024.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzouvelekis L. S., Mentis A. F., Makris A. M., Spiliadis C., Blackwell C., Weir D. M. In vitro binding of Helicobacter pylori to human gastric mucin. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4252–4254. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4252-4254.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanke C. A., Cronan S., Goss C., Chadee K., Guerrant R. L. Characterization of binding of Escherichia coli strains which are enteropathogens to small-bowel mucin. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):794–800. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.794-800.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesley A., Forstner J., Qureshi R., Mantle M., Forstner G. Human intestinal mucin in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Res. 1983 Jan;17(1):65–69. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198301000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


