Abstract
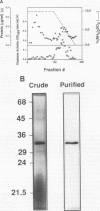
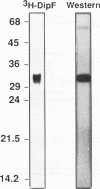
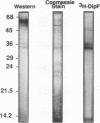
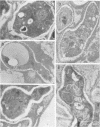
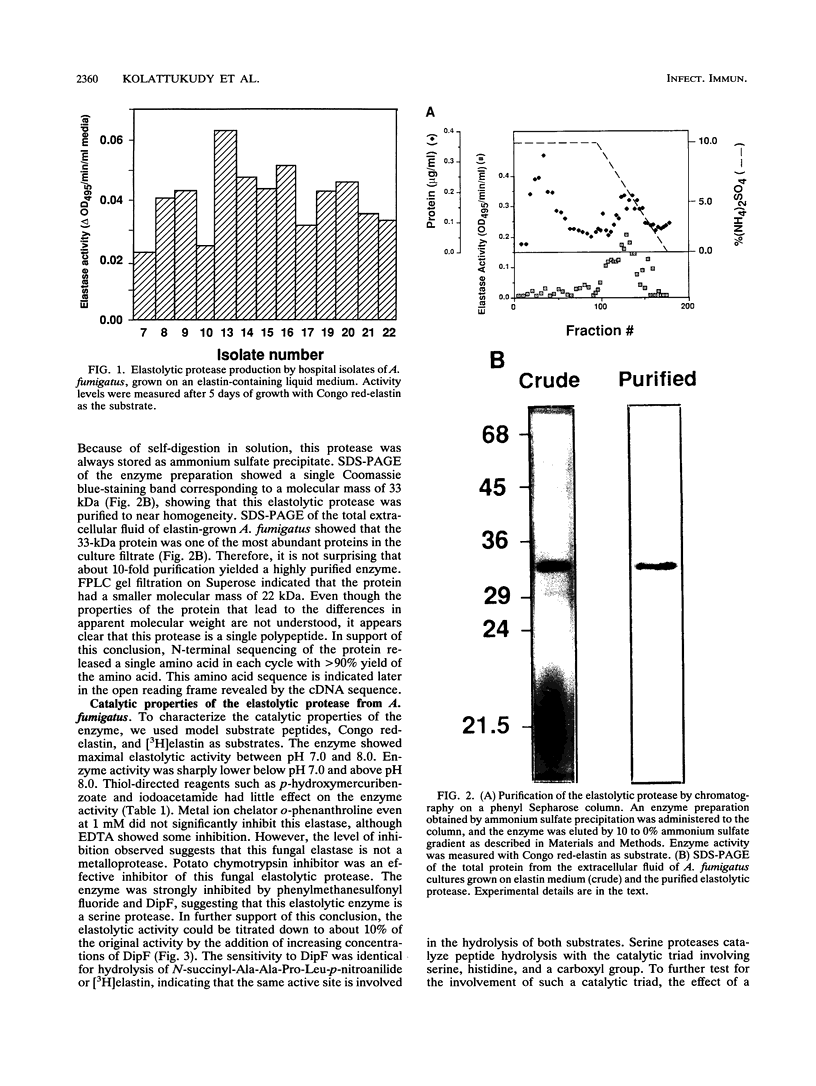
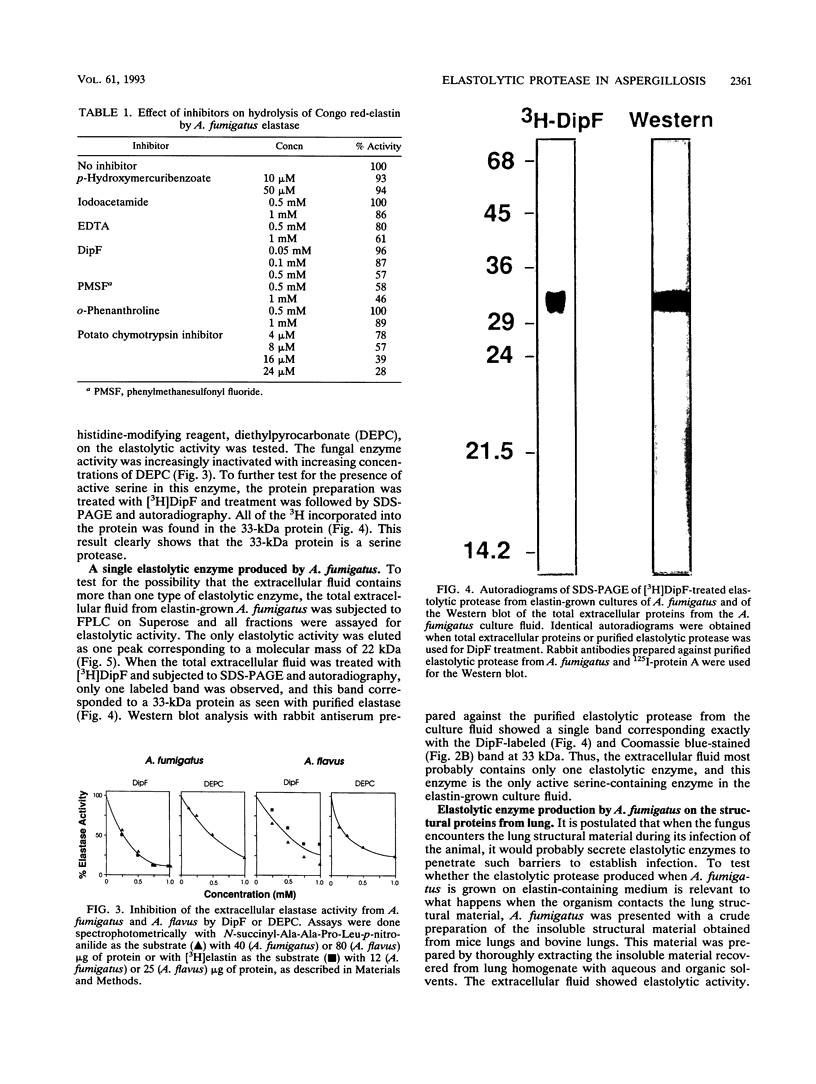
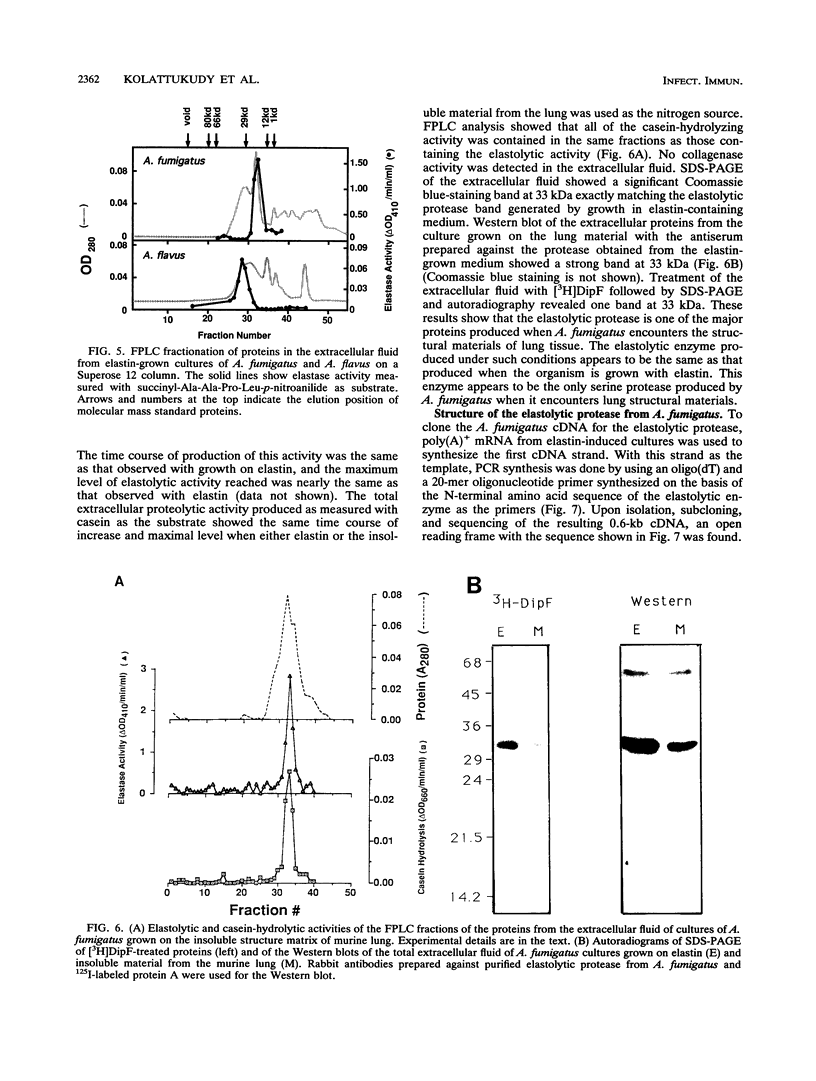
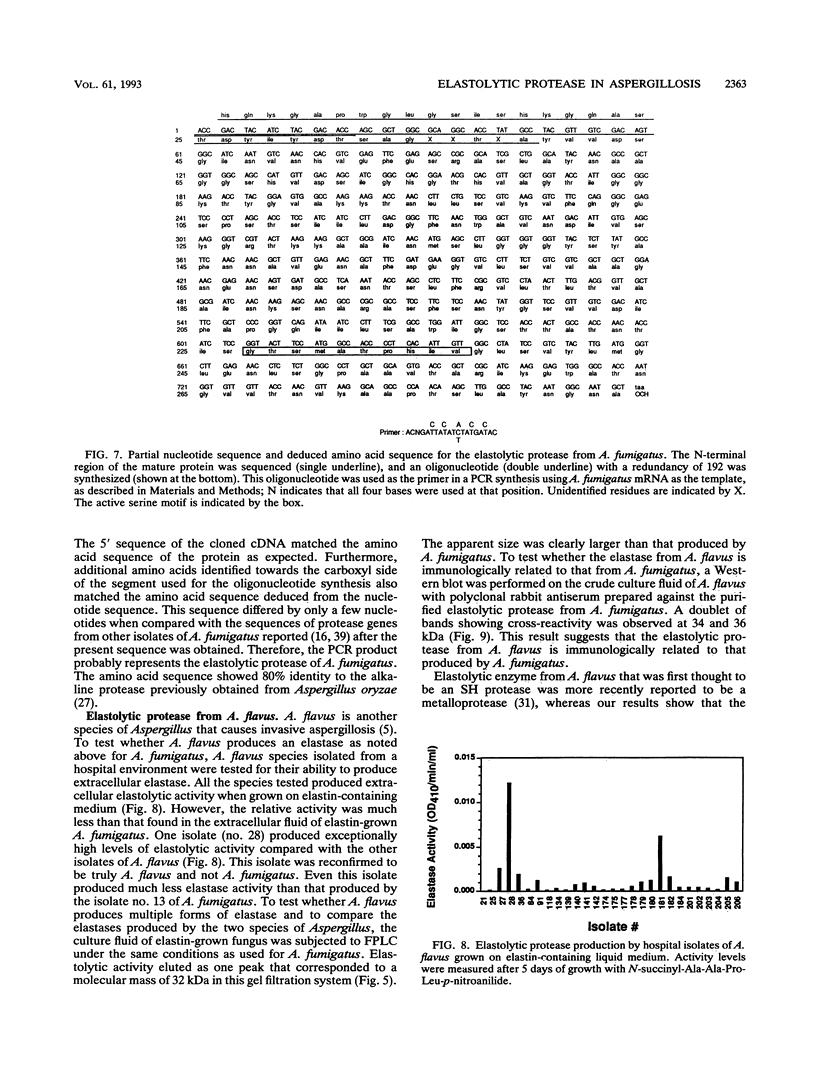
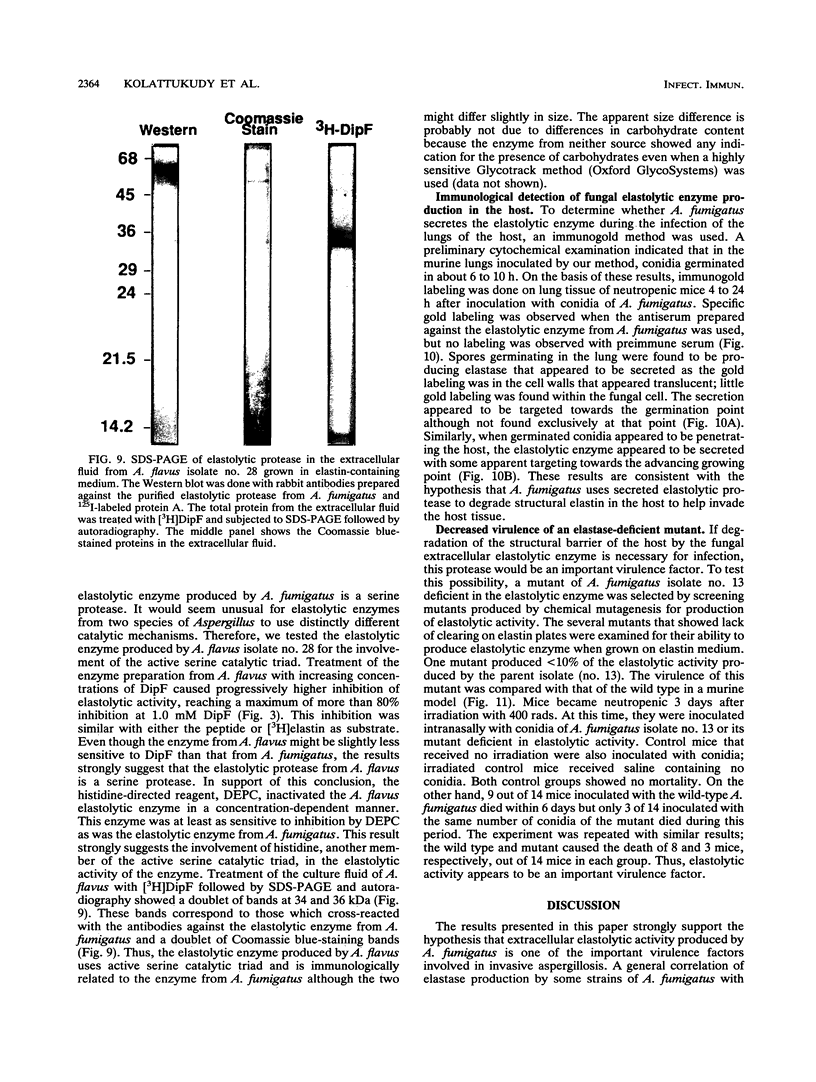
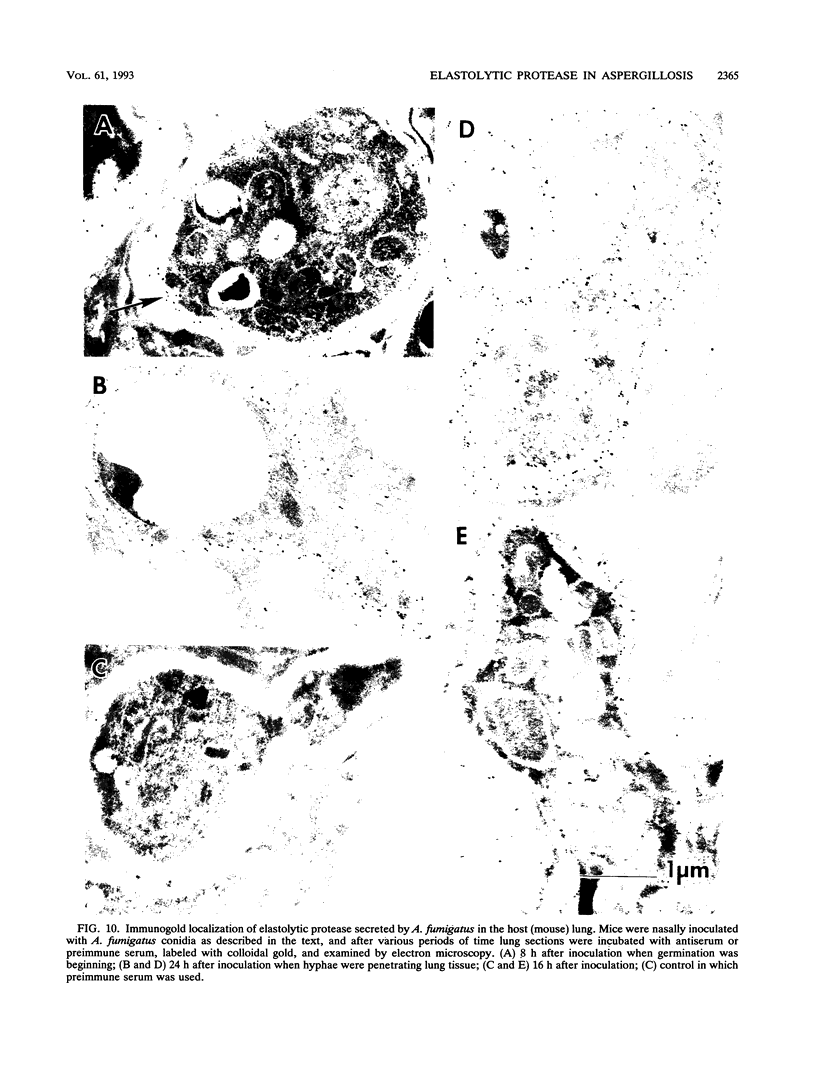
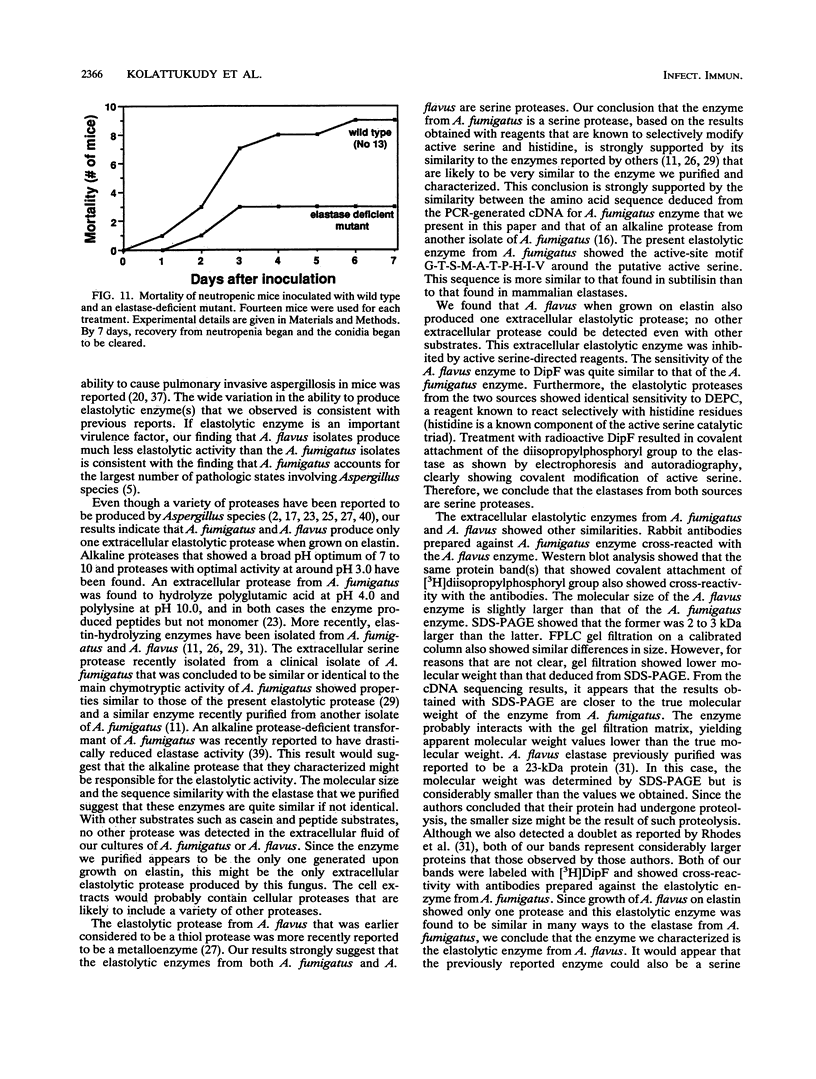
A number of isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus obtained from the hospital environment produced extracellular elastolytic activity. This activity was found to be catalyzed by a single 33-kDa protein which was purified and characterized to be a serine protease. A. fumigatus, when grown on the insoluble structural material obtained from murine and bovine lung, produced the same extracellular 33-kDa elastolytic protease, indicating that this enzyme is likely to be produced when the organism infects the lung. Polymerase chain reaction with an oligonucleotide primer based on the N-terminal amino acid sequence of the elastolytic enzyme yielded a cDNA which was cloned and sequenced. The active serine motif showed more similarity to subtilisin than to mammalian elastase. The amino acid sequence showed 80% identity to the alkaline protease from Aspergillus oryzae. Screening of hospital isolates of Aspergillus flavus showed great variation in the production of elastolytic activity and a much lower level of activity than that produced by A. fumigatus. The elastolytic protease from A. flavus was shown to be a serine protease susceptible to modification and inactivation by active serine and histidine-directed reagents. This protease cross-reacted with the antibodies prepared against the elastolytic protease from A. fumigatus. Immunogold localization of the elastolytic enzyme showed that A. fumigatus germinating and penetrating into the lungs of neutropenic mice secreted the elastolytic protease. An elastase-deficient mutant generated from a highly virulent isolate of A. fumigatus caused drastically reduced mortality when nasally introduced into the lung of neutropenic mice. All of the evidence suggests that extracellular elastolytic protease is a significant virulence factor in invasive aspergillosis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banda M. J., Werb Z. Mouse macrophage elastase. Purification and characterization as a metalloproteinase. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 1;193(2):589–605. doi: 10.1042/bj1930589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieth J., Spiess B., Wermuth C. G. The synthesis and analytical use of a highly sensitive and convenient substrate of elastase. Biochem Med. 1974 Dec;11(4):350–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(74)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Vartivarian S. Aspergillosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 May;8(5):413–437. doi: 10.1007/BF01964057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford M. S., Kolattukudy P. E. Pectate lyase from Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi: purification, characterization, in vitro translation of the mRNA, and involvement in pathogenicity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Oct;258(1):196–205. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90336-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning D. W., Stevens D. A. Antifungal and surgical treatment of invasive aspergillosis: review of 2,121 published cases. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Nov-Dec;12(6):1147–1201. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.6.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosco M., Chase T., Jr, Macmillan J. D. Purification and properties of the elastase from Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):728–734. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.728-734.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Candelas L., Kolattukudy P. E. Isolation and analysis of a novel inducible pectate lyase gene from the phytopathogenic fungus Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi (Nectria haematococca, mating population VI). J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6343–6349. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6343-6349.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton-Ogay K., Suter M., Crameri R., Falchetto R., Fatih A., Monod M. Nucleotide sequence of a genomic and a cDNA clone encoding an extracellular alkaline protease of Aspergillus fumigatus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Apr 15;71(2):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90506-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolattukudy P. E. Biopolyester membranes of plants: cutin and suberin. Science. 1980 May 30;208(4447):990–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.208.4447.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latgé J. P., Moutaouakil M., Debeaupuis J. P., Bouchara J. P., Haynes K., Prévost M. C. The 18-kilodalton antigen secreted by Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2586–2594. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2586-2594.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Swift G. H., Przybyla A. E., Chirgwin J. M. Isolation of RNA using guanidinium salts. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:219–227. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. M., Jönsson A. G. An extracellular protease from Aspergillus fumigatus. Can J Biochem. 1965 Oct;43(10):1745–1753. doi: 10.1139/o65-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikes O., Turková J., Toan N. B., Sorm F. Serine-containing active center of alkaline proteinase of Aspergillus flavus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 18;178(1):112–117. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monod M., Togni G., Rahalison L., Frenk E. Isolation and characterisation of an extracellular alkaline protease of Aspergillus fumigatus. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Jul;35(1):23–28. doi: 10.1099/00222615-35-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panneerselvam M., Dhar S. C. Chromatographic purification and homogeneity of extracellular acid proteinase of Aspergillus Fumigatus. Ital J Biochem. 1980 Mar-Apr;29(2):102–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichard U., Büttner S., Eiffert H., Staib F., Rüchel R. Purification and characterisation of an extracellular serine proteinase from Aspergillus fumigatus and its detection in tissue. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Dec;33(4):243–251. doi: 10.1099/00222615-33-4-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. C., Amlung T. W., Miller M. S. Isolation and characterization of an elastinolytic proteinase from Aspergillus flavus. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2529–2534. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2529-2534.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. C., Bode R. B., McCuan-Kirsch C. M. Elastase production in clinical isolates of Aspergillus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;10(3):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(88)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi M. G. Invasive aspergillosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5(6):1061–1077. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.6.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler-Ludwig R., Braunsteiner H. Cationic proteins from human neutrophil granulocytes. Evidence for their chymotrypsin-like properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 27;379(2):606–617. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starcher B. C. Elastin and the lung. Thorax. 1986 Aug;41(8):577–585. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.8.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Cohen J., Holden D. W. An Aspergillus fumigatus alkaline protease mutant constructed by gene disruption is deficient in extracellular elastase activity. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(12):1663–1671. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00891.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkovã J., Mikes O., Hayashi K., Danno G., Polgãr L. Alkaline proteinases of the genus Aspergillus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WUENSCH E., HEIDRICH H. G. ZUR QUANTITATIVEN BESTIMMUNG DER KOLLAGENASE. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1963;333:149–151. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1963.333.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewers M. D., Herzyk D. J., Gadek J. E. Alveolar fluid neutrophil elastase activity in the adult respiratory distress syndrome is complexed to alpha-2-macroglobulin. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1260–1267. doi: 10.1172/JCI113724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]