Abstract
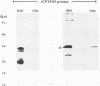
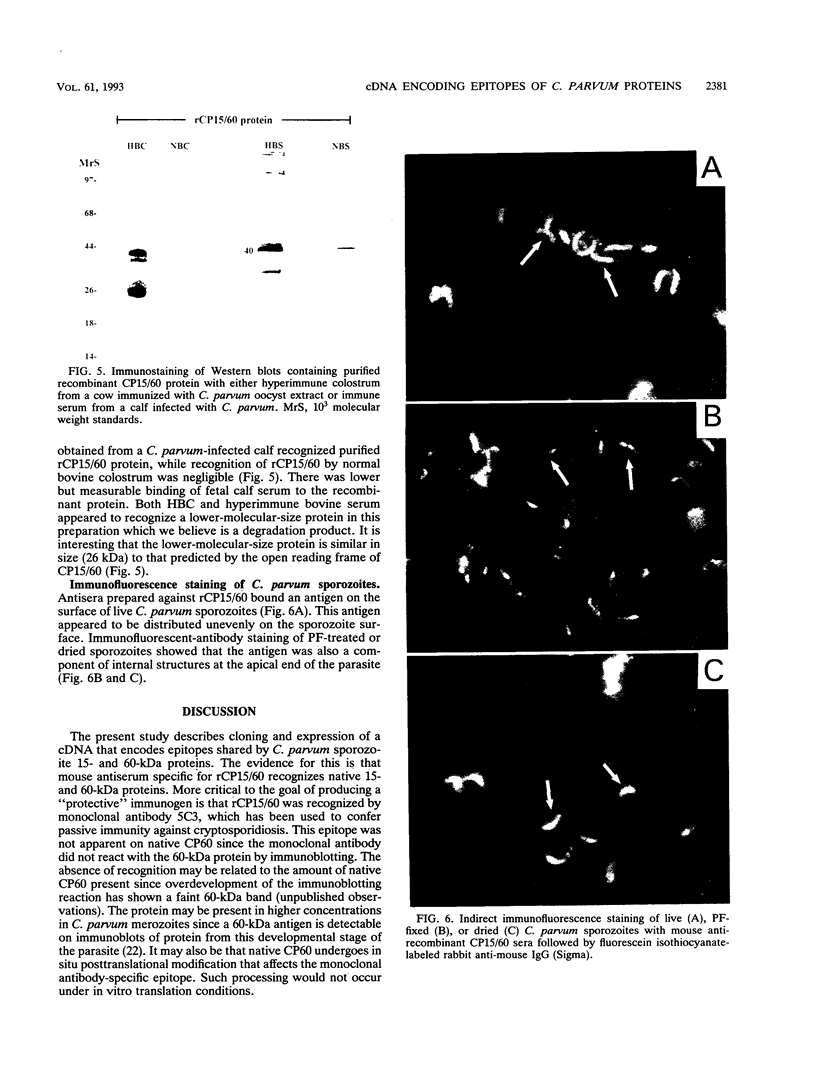
A cDNA (CP15/60) encoding epitopes of Cryptosporidium parvum 15- and 60-kDa sporozoite proteins was isolated and expressed in Escherichia coli toward the goal of developing an immunogen for producing high-titer anticryptosporidial colostrum. Antisera prepared in rats to native C. parvum 15-kDa protein and used to identify the CP15/60 bacteriophage clone recognized both 15- and 60-kDa in vitro translation products derived from sporozoite RNA. Antisera specific for recombinant CP15/60 antigen recognized native 15- and 60-kDa C. parvum sporozoite proteins by immunoblotting and identified both surface and internal antigens on C. parvum sporozoites by immunofluorescence staining. Northern (RNA) and Southern blot hybridization experiments using sporozoite RNA and DNA indicated that CP15/60 DNA is transcribed as a single 1.4-kb RNA species from a single-copy gene. Recombinant CP15/60 antigen was recognized by hyperimmune colostrum from cows immunized with C. parvum oocyst-sporozoite protein and by convalescent-phase sera from C. parvum-infected calves.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorneby J. M., Hunsaker B. D., Riggs M. W., Perryman L. E. Monoclonal antibody immunotherapy in nude mice persistently infected with Cryptosporidium parvum. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1172–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1172-1176.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorneby J. M., Riggs M. W., Perryman L. E. Cryptosporidium parvum merozoites share neutralization-sensitive epitopes with sporozoites. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):298–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayer R., Andrews C., Ungar B. L., Blagburn B. Efficacy of hyperimmune bovine colostrum for prophylaxis of cryptosporidiosis in neonatal calves. J Parasitol. 1989 Jun;75(3):393–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayer R., Guidry A., Blagburn B. L. Immunotherapeutic efficacy of bovine colostral immunoglobulins from a hyperimmunized cow against cryptosporidiosis in neonatal mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2962–2965. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2962-2965.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayer R., Perryman L. E., Riggs M. W. Hyperimmune bovine colostrum neutralizes Cryptosporidium sporozoites and protects mice against oocyst challenge. J Parasitol. 1989 Feb;75(1):151–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayer R., Ungar B. L. Cryptosporidium spp. and cryptosporidiosis. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):458–483. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.458-483.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner A. L., Roche J. K., Weikel C. S., Guerrant R. L. Intestinal cryptosporidiosis: pathophysiologic alterations and specific cellular and humoral immune responses in rnu/+ and rnu/rnu (athymic) rats. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Jan;44(1):49–62. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1991.44.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. C., Dame J. B. Identification of immunodominant surface antigens of Eimeria acervulina sporozoites and merozoites. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Sep;25(2):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. C., Lillehoj H. S., Dame J. B. Eimeria acervulina: DNA cloning and characterization of recombinant sporozoite and merozoite antigens. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Jun;66(1):96–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilani R. T., Sekla L. Purification of Cryptosporidium oocysts and sporozoites by cesium chloride and Percoll gradients. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 May;36(3):505–508. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Goozé L., Petersen C., Gut J., Nelson R. G. Isolation, sequence and molecular karyotype analysis of the actin gene of Cryptosporidium parvum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Jan;50(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90248-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeGendre N. Immobilon-P transfer membrane: applications and utility in protein biochemical analysis. Biotechniques. 1990 Dec;9(6 Suppl):788–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald V., Deer R., Uni S., Iseki M., Bancroft G. J. Immune responses to Cryptosporidium muris and Cryptosporidium parvum in adult immunocompetent or immunocompromised (nude and SCID) mice. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3325–3331. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3325-3331.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J. R., Arrowood M. J., Sidwell R. W., Healey M. C. Chronic Cryptosporidium parvum infections in congenitally immunodeficient SCID and nude mice. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1297–1304. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord J., Ma P., DiJohn D., Tzipori S., Tacket C. O. Treatment with bovine hyperimmune colostrum of cryptosporidial diarrhea in AIDS patients. AIDS. 1990 Jun;4(6):581–584. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199006000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Borman P. A rapid biochemical method for purifying high molecular weight bacterial chromosomal DNA for restriction enzyme analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3631–3631. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perryman L. E., Riggs M. W., Mason P. H., Fayer R. Kinetics of Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoite neutralization by monoclonal antibodies, immune bovine serum, and immune bovine colostrum. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):257–259. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.257-259.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs M. W., Perryman L. E. Infectivity and neutralization of Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2081–2087. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2081-2087.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley M., Upton S. J., Fayer R., Barta J. R., Chrisp C. E., Freed P. S., Blagburn B. L., Anderson B. C., Barnard S. M. Identification of a 15-kilodalton surface glycoprotein on sporozoites of Cryptosporidium parvum. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1002–1007. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1002-1007.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley M., Upton S. J. Sporozoites and merozoites of Cryptosporidium parvum share a common epitope recognized by a monoclonal antibody and two-dimensional electrophoresis. J Protozool. 1991 Nov-Dec;38(6):48S–49S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Roberton D., Chapman C. Remission of diarrhoea due to cryptosporidiosis in an immunodeficient child treated with hyperimmune bovine colostrum. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Nov 15;293(6557):1276–1277. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6557.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar B. L., Kao T. C., Burris J. A., Finkelman F. D. Cryptosporidium infection in an adult mouse model. Independent roles for IFN-gamma and CD4+ T lymphocytes in protective immunity. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):1014–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar B. L., Ward D. J., Fayer R., Quinn C. A. Cessation of Cryptosporidium-associated diarrhea in an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patient after treatment with hyperimmune bovine colostrum. Gastroenterology. 1990 Feb;98(2):486–489. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90842-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. M., Weber D. K., Johnson T., Sakaguchi A. Y. Supercoil sequencing using unpurified templates produced by rapid boiling. Biotechniques. 1988 Oct;6(9):839, 841-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W. Q., Rothblum L. I. Rapid, small-scale RNA isolation from tissue culture cells. Biotechniques. 1991 Sep;11(3):324, 326-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Transcending the impenetrable: how proteins come to terms with membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 9;947(2):307–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]