Abstract
Small-molecules can control cell fate in vivo and may allow directed induction of desired cell types, providing an attractive alternative to transplant-based approaches in regenerative medicine. We have chemically induced functional oocytes in C. elegans adults that otherwise produced only sperm. These findings suggest that chemical approaches to therapeutic cell reprogramming may be feasible and provide a powerful platform for analyzing molecular mechanisms of in vivo cell reprogramming.
Cell fate reprogramming within organisms has the potential to revolutionize regenerative medicine1. By reprogramming endogenous cells into a desired cell type, major difficulties associated with transplant-based approaches (e.g. cell isolation, immune rejection) may be minimized. To date, most reprogramming has been limited to in vitro applications, although a recent breakthrough reported reprogramming of cells in mice with virally delivered transcription factors2. Small-molecules can modulate cell fates in vivo3, and chemical induction of a desired cell type could provide an attractive alternative to transplant- or viral-based cell replacement therapies. Notably, chemical modulation of prostaglandin E2 synthesis can regulate hematopoietic stem cell proliferation4 and retinoid-based “differentiation therapy” is used clinically to treat M3 acute myeloid leukemia (AML)5. However, to our knowledge, the chemical induction of functional cells that were absent prior to treatment has not been demonstrated in any organism. The ability to induce missing cells could have profound implications for the treatment of diseases of cellular deficiency.
The germline of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans provides a tractable system to study cellular reprogramming6. Normally, C. elegans hermaphrodites make sperm as larvae and oocytes as adults, yielding an adult gonad that uses stored sperm to fertilize its developing oocytes (Fig. 1a). Genetic screens for mutant hermaphrodites that make only sperm (masculinized germlines) or only oocytes (feminized germlines) have identified key regulators of sperm/oocyte cell fate6,7. Indeed, genetic manipulation of these fate regulators revealed that germ cells continuously make the sperm/oocyte decision, even in adults8. Such continued cell fate specification in adults is typical of many vertebrate tissues, including blood and intestinal epithelium. In C. elegans, one regulator that promotes the sperm fate is MPK-1, the ERK-1/2 MAPK homolog9,10 and terminal kinase of canonical Ras-ERK signaling. Yet, MPK-1/ERK hyperactivation, which occurs upon loss of the dual-specificity phosphatase LIP-1, fails to generate excess sperm11. However, we have found that a double mutant, lacking lip-1 and a second regulator (puf-8), produces only sperm (Fig. 1b). The puf-8 gene encodes a PUF [for Pumilio and FBF] RNA-binding protein that affects the sperm/oocyte decision redundantly with another PUF protein, FBF-112. Because PUF-8 targets are largely unknown, the mechanism underlying the interaction between PUF-8 and Ras-ERK signaling remains unclear. However, it is likely to involve parallel controls that impinge on the sperm/oocyte decision redundantly.
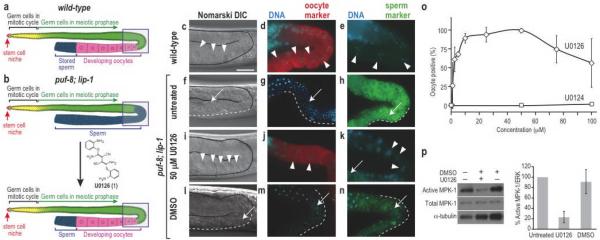
Figure 1. Small-molecule mediated reprogramming of sperm/oocyte fate.
(a) Organization of the wild-type hermaphrodite gonad. Boxed area indicates the region shown in panels. (b) The puf-8; lip-1 gonad produces only sperm, but oocytes can be induced chemically. (c–n) Genotypes and treatments are labelled in the figure. Oocytes are indicated with arrowheads. The extent of sperm is indicated with white dashed lines and representative single sperm with arrows. Scale bar, 10 μm. (c, f, i, l) DIC images reveal morphology of large granular oocytes (c, i) or small condensed sperm (f, l). (d, g, j, m) Germlines stained for DNA using DAPI (blue) and the RME-2 oocyte marker (red). (e, h, k, n) Germlines stained for DNA using DAPI (blue) and the SP56 sperm marker (green). (o) Dose-response analysis for oogenesis induction by U0126 (◊) and its inactive analog U0124 (□). Data are presented as mean +/− s.d., n=3–12 independent experiments with 3–149 (ave. 13) animals each. (p) Left, semi-quantitative Western blot analysis of activated MPK-1/ERK (top panel), total MPK-1/ERK (middle panel), and α-tubulin (bottom panel) in untreated, U0126-treated, and DMSO-treated animals. Right, graph generated with active MPK-1/ERK signals normalized to α-tubulin (n=3) and compared to untreated signal (set as 100% Active MPK-1/ERK).
We scored sperm and oocyte production in wild-type and puf-8(q725); lip-1(zh15) (hereafter referred to as “puf-8; lip-1” or “mutant”) adult germlines by morphology and staining for molecular markers (Fig. 1c–n). Wild-type oocytes are large cells with granular cytoplasm and their nuclei have progressed to diplotene or diakinesis of meiotic prophase13 (Fig. 1c). Moreover, oocytes stained with the oocyte marker RME-2 (Fig. 1d), but not with the sperm-specific marker SP56 (Fig. 1e). By contrast, mutant germlines lacked oocytes and instead made excess sperm. Sperm have compact nuclei (Fig. 1f–h) and fail to stain with oocyte marker (Fig. 1g), but stain strongly with the sperm marker (Fig. 1h). Indeed, all mutant germlines were masculinized (100%, n=199).
We used masculinized puf-8; lip-1 germlines to develop a small-molecule based method to switch germ cell fates. Specifically, we asked if inhibition of Ras-ERK signaling could reinstate oogenesis. To this end, we grew synchronized mutants on normal growth media until adulthood (to avoid effects on somatic development), and treated them with U0126 (1), a small-molecule MEK1/MEK2 inhibitor that blocks MPK-1/ERK activation14,15. After 24 hours of treatment,virtually all mutants made oocytes (99%; n=158). The induced oocytes had oocyte-specific cellular morphology (Fig. 1i), expressed the oocyte marker (Fig. 1j), and were negative for the sperm marker (Fig. 1k). These germlines with induced oocytes also contained sperm (Fig. 1k), so not all germ cells were reprogrammed. Induction of RME-2-positive oocytes was also observed when U0126 was solubilized in a different solvent (EtOH), while vehicle (DMSO or EtOH) treated control animals remained masculinized as assessed by morphology and markers (Fig. 1l–n and Supplementary Fig. 1).
One interpretation of the induced oocytes in the U0126-treated mutant germlines is that germ cells normally destined for sperm differentiation had been reprogrammed into the oocyte fate. Alternatively, germ cells destined for oogenesis might not be detected in the mutant due to differential proliferation or apoptosis of cells specified as oocytes. To compare proliferation, we determined the percentage of S-phase germ cells (see Methods) in spermatogenic and oogenic mutants and found 52±7.2% (n=3) and 57±1% (n=3) S-phase cells, respectively. Therefore, sex-specific differences in germline proliferation cannot explain the appearance of U0126-induced oocytes. We then asked if mutant germ cells undergo apoptosis instead of oocyte differentiation. To this end, we blocked apoptosis by RNAi of the Apaf-1 homolog ced-4, an essential regulator of programmed cell death16. However, no oocytes were observed in ced-4 RNAi-treated mutants (n=70). We conclude that U0126 induced oocytes by chemically reprogramming the germline, generating a cell type that was absent in untreated mutants.
We verified that U0126 inhibits Ras-ERK signaling to affect sperm/oocyte fate. U0126 induced oocytes in a dose-dependent manner with an in vivo EC50 of ~2 μM (Fig. 1o), consistent with the previously reported IC50 of ~1 μM for the effect of U0126 on AP-1 activity in tissue culture15. Moreover, high U0126 doses (75–100 μM) caused pachytene arrest, a defect diagnostic for loss of Ras-ERK signaling in C. elegans germlines17 (Fig. 1o). In Western blots, U0126 significantly reduced the abundance of activated MPK-1/ERK, compared to untreated and DMSO-treated controls (Fig. 1p, top panel), but levels of total MPK-1 were unchanged (Fig. 1p, middle panel). Therefore, U0126's effects on germline sex are likely to be the result of “tuning” ERK activity rather than complete inhibition. Taken together, our results show that U0126 inhibits MPK-1/ERK activity in the C. elegans mutant germline and confirms the role of MPK-1/ERK in sperm fate specification.
To rule out off-target effects of U0126 as the mechanism of reprogramming, we tested an inactive but structurally similar analog, U0124 (2) (Fig. 2a)14. U0124 failed to induce oogenesis (Fig. 1p, Supplementary Fig. 2b–d) or lower activated MPK-1/ERK (Supplementary Fig. 3 and Supplementary Table 1). Two structurally distinct small-molecule MEK-1/2 inhibitors, PD0325901 (3)18 and PD098059 (4)19,20, also induced oocytes in the mutants. 50 μM PD0325901 induced oocytes in 91% (n=35) of the mutants, assayed by cellular morphology and gamete-specific markers (Supplementary Fig. 2e–g and Supplementary Table 1). Consistent with this result, PD0325901 significantly decreased activated MPK-1/ERK (Supplementary Fig. 3). PD098059's induced oocytes in only 5.3% (n=75) at 100 μM (Supplementary Table 1), consistent with PD098059's poor bioavailability and ~100-fold lower affinity for MEK-1/214, relative to U012618. Thus, three structurally distinct inhibitors of Ras-ERK signaling elicited the same response, oocyte induction. These findings strongly suggest that the inhibitors elicit their effects via their common target, Ras-ERK signaling. We conclude that Ras-ERK inhibitors act as a chemical switch to reprogram germ cell fates in puf-8; lip-1 mutants.
Figure 2. Small-molecule induced oocytes are functional.
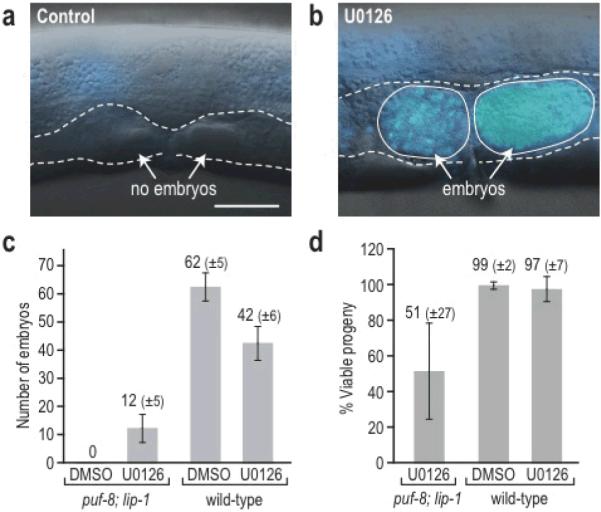
(a–b) Whole animals were imaged by DIC and DAPI (blue) staining after treatment with control (DMSO) or U0126. (a) DMSO-treated mutant lacking embryos (dashed outline indicating empty uterus). (b) U0126-treated mutant with embryos containing numerous DAPI-stained nuclei. (c) Number of embryos produced by mutants and wild type treated with DMSO or U0126. (d) Percentage of embryos that developed to adulthood after parents were treated with DMSO of U0126. Approximately half of the embryos from chemically-induced oocytes developed to adulthood. Data are presented as mean +/− s.d. Scale bar, 10 μm.
To confirm that MPK-1/ERK inhibition is sufficient for germ cell fate switching, we performed RNAi-mediated knockdown of the germline isoform of mpk-1, mpk-1b21. Mutants treated with mpk-1b RNAi made oocytes (99%; n=98), as assessed by morphology and gamete-specific markers (Supplementary Fig. 2h–j). By contrast, all animals treated with RNAi vector made sperm only (100%, n=63), by morphology and markers (Supplementary Fig. 2k–m). Therefore, inhibitors of Ras-ERK signaling can reprogram mutant germ cells. However, oogenesis was not induced by inhibition of several other major signaling pathways (Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Fig. 4). We conclude that germ cell fate switching does not occur by generalized perturbation, but specifically by inhibition of Ras-ERK signaling.
Finally, we asked if U0126-induced oocytes were functional gametes. To assess oocyte function, we examined their capacity to be fertilized, to make embryos, and to support embryo viability. Control DMSO-treated mutants were sterile and made no embryos (Fig. 2a) (n=23). By contrast, almost all U0126-treated mutants produced embryos (Fig. 2b) (96%, n=23), indicating that the oocytes were functional and that reprogramming was highly efficient. To examine this effect in more detail, we first scored embryo number. U0126-treated mutants made 11.5±4.8 embryos per animal (n=8), whereas DMSO-treated mutants made none (n=8) (Fig. 2c). For comparison, wild-type animals treated with DMSO or U0126 produced 62±5.3% or 41.5±5.7% embryos per animal, respectively (n=8 for each) (Fig. 2c). Therefore, embryo production by U0126-treated mutants reached ~30% of wild-type levels. We next assessed embryo viability. About half the embryos made from chemically-induced oocytes developed to adulthood (51%; n=92) (Fig. 2d). Much of their embryonic lethality could be secondary to mutant defects, since untreated puf-8 and lip-1 single mutants exhibit partial embryonic lethality22,23 and U0126 did not affect wild-type embryo viability. To assay embryonic lethality of the double mutants in the absence of U0126, we genetically induced oocytes by RNAi knockdown of fog-1, a terminal sperm fate regulator6. The fog-1 RNAi induced oocytes in all treated animals (100%, n=98), but those oocytes were small and did not support embryonic development. Therefore, U0126 treatment had additional positive effects, beyond inducing oogenesis. Among embryos from DMSO- and U0126-treated wild-type animals, 99.6±2.1 (n=497) and 96.6±6.6 (n=332) developed to adulthood, respectively (Fig. 2d). The puf-8; lip-1 progeny arising from chemically-induced oocytes were sterile as adults, because they made only sperm; yet oogenesis and fertility could be re-instated in these adults by U0126 treatment. Indeed, we expanded an initial population of homozygous mutants from 17 to ~15,000 animals in six generations by “pulsing” sterile adults with 50 μM U0126 and allowing their progeny to grow to adulthood prior to the next pulse. Therefore, a significant fraction of the U0126-induced oocytes are fully functional gametes.
In summary, we have shown that germ cell fate can be chemically reprogrammed within adult C. elegans and that reprogramming can induce a cell type that was absent without treatment. We speculate that the in vivo environment contributed significantly to the high efficiency and functionality of the reprogramming. We do not know whether the reprogramming occurs by lineage switching of progenitors or by direct conversion of spermatocytes to oocytes. C. elegans germlines have a stem cell reservoir that may provide a pool of cells with labile fate that can be efficiently reprogrammed. Indeed, the time required for reprogramming corresponds roughly to the time required for immature germ cells to enter meiosis and differentiate as sperm or oocyte. Some vertebrate tissues are similarly maintained in adults by a stem cell reservoir (e.g. blood), and some human diseases similarly lack differentiated cells while maintaining a progenitor pool (e.g. acute myelogenous leukemias24 and azoospermia25). Such disease cells may represent good targets for therapeutic chemical reprogramming efforts, a notion supported by the success of differentiation therapy in M3 AML5. Our results in nematodes strongly support the idea that pharmacological approaches to cell reprogramming will be therapeutically feasible more broadly. In addition, the reprogramming of germ cell fates in C. elegans provides a powerful model for analyzing molecular mechanisms of in vivo cell reprogramming. Therefore, our findings provide a paradigm that may facilitate pharmacological approaches to therapeutic cellular reprogramming in other organisms.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank S. Ward and B. Grant for providing reagents. We are grateful to Laura Vanderploeg, Adam Steinberg, and Anne Helsley-Marchbanks for help preparing the figures and manuscript. We thank the Kimble lab members for helpful discussions. This work was supported by NIH RO1 GM069454. J.K. is an investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Footnotes
Competing interests statement: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Note: Supplementary information and chemical compound information is available on the Nature Chemical Biology website.
References
- 1.Gurdon JB, Melton DA. Nuclear reprogramming in cells. Science. 2008;322:1811–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1160810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhou Q, Brown J, Kanarek A, Rajagopal J, Melton DA. In vivo reprogramming of adult pancreatic exocrine cells to beta-cells. Nature. 2008;455:627–32. doi: 10.1038/nature07314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Xu Y, Shi Y, Ding S. A chemical approach to stem-cell biology and regenerative medicine. Nature. 2008;453:338–44. doi: 10.1038/nature07042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.North TE, et al. Prostaglandin E2 regulates vertebrate haematopoietic stem cell homeostasis. Nature. 2007;447:1007–11. doi: 10.1038/nature05883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Castaigne S, et al. All-trans retinoic acid as a differentiation therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia. I. Clinical results. Blood. 1990;76:1704–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kimble J, Crittenden SL. Controls of germline stem cells, entry into meiosis, and the sperm/oocyte decision in Caenorhabditis elegans. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2007;23:405–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ellis R, Schedl T. Sex determination in the germ line. WormBook. 2006 doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.82.2. <www.wormbook.org>. doi:10.1895/wormbook.1.82.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Barton MK, Schedl TB, Kimble J. Gain-of-function mutations of fem-3, a sex-determination gene in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1987;115:107–119. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lee M-H, et al. Multiple functions and dynamic activation of MPK-1 extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans germline development. Genetics. 2007;177:2039–62. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.081356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sundaram MV. RTK/Ras/MAPK signaling. WormBook. 2006 <http://www.wormbook.org>. doi:10.1895/wormbook.1.80.1. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Berset T, Fröhli Hoier E, Battu G, Canevascini S, Hajnal A. Notch inhibition of RAS signaling through MAP kinase phosphatase LIP-1 during C. elegans vulval development. Science. 2001;291:1055–1058. doi: 10.1126/science.1055642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bachorik JL, Kimble J. Redundant control of the Caenorhabditis elegans sperm/oocyte switch by PUF-8 and FBF-1, two distinct PUF RNA-binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:10893–10897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504593102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Albertson DG, Rose AM, Villeneuve AM. Chromosome organization, mitosis, and meiosis. In: Riddle DL, Blumenthal T, Meyer BJ, Priess JR, editors. C. elegans II. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 1997. pp. 47–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Favata MF, et al. Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:18623–32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.29.18623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Duncia JV, et al. MEK inhibitors: the chemistry and biological activity of U0126, its analogs, and cyclization products. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1998;8:2839–44. doi: 10.1016/s0960-894x(98)00522-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gumienny TL, Lambie E, Hartwieg E, Horvitz HR, Hengartner MO. Genetic control of programmed cell death in the Caenorhabditis elegans hermaphrodite germline. Development. 1999;126:1011–1022. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.5.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Church DL, Guan K-L, Lambie EJ. Three genes of the MAP kinase cascade, mek-2, mpk-1/sur-1 and let-60 ras, are required for meiotic cell cycle progression in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development. 1995;121:2525–2535. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.8.2525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Barrett SD, et al. The discovery of the benzhydroxamate MEK inhibitors CI-1040 and PD 0325901. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008;18:6501–4. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.10.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:27489–94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.46.27489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dudley DT, Pang L, Decker SJ, Bridges AJ, Saltiel AR. A synthetic inhibitor of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1995;92:7686–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lee M-H, et al. Conserved regulation of MAP kinase expression by PUF RNA-binding proteins. PLoS Genet. 2007;3:e233. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Subramaniam K, Seydoux G. Dedifferentiation of primary spermatocytes into germ cell tumors in C. elegans lacking the Pumilio-like protein PUF-8. Curr. Biol. 2003;13:134–139. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hajnal A, Berset T. The C. elegans MAPK phosphatase LIP-1 is required for the G2/M meiotic arrest of developing oocytes. EMBO J. 2002;21:4317–4326. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tenen DG. Disruption of differentiation in human cancer: AML shows the way. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:89–101. doi: 10.1038/nrc989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.McLachlan RI, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Hoei-Hansen CE, de Kretser DM, Skakkebaek NE. Histological evaluation of the human testis--approaches to optimizing the clinical value of the assessment: mini review. Hum Reprod. 2007;22:2–16. doi: 10.1093/humrep/del279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.