Abstract
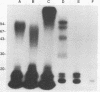
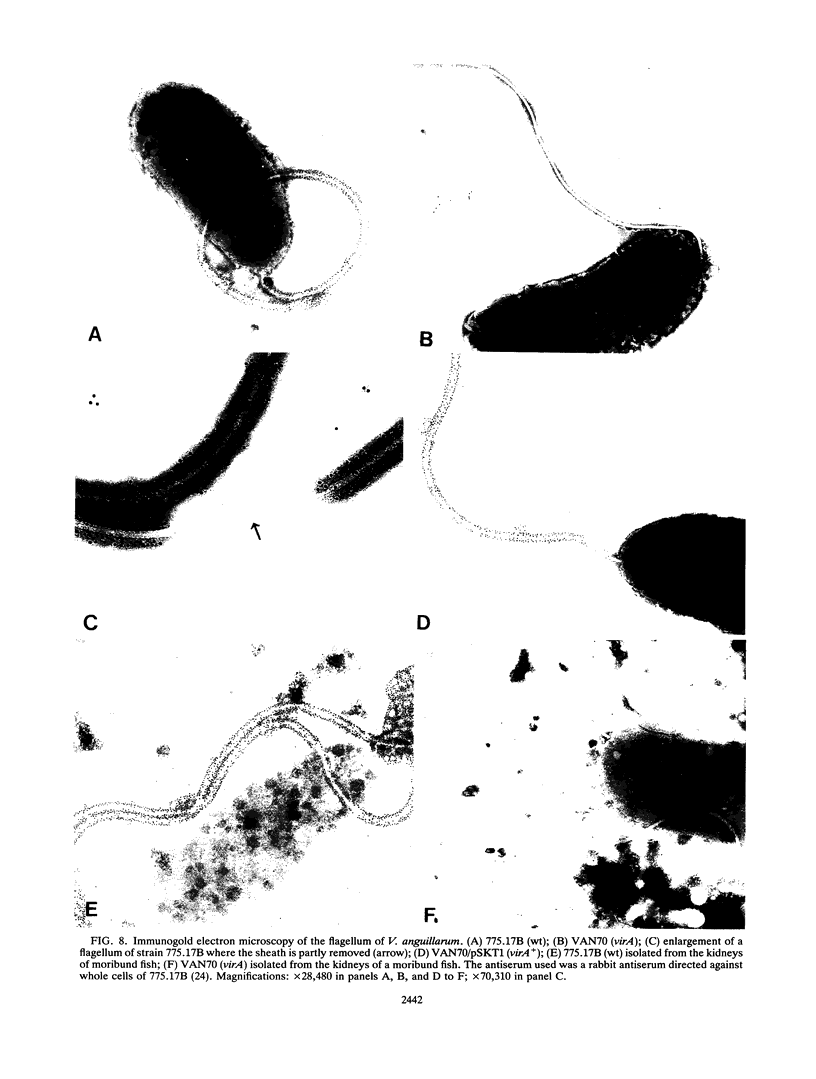
The fish pathogenic bacterium Vibrio anguillarum 775.17B was mutated by the use of transposon Tn5-132. Two hundred independent exconjugants were isolated and screened for a reduction of virulence in experimental infections of rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss). Two of these exconjugants, VAN20 and VAN70, showed a significant reduction in virulence after both intraperitoneal and immersion infections. The avirulent mutants showed no loss of any previously suggested virulence determinants of V. anguillarum. One of the mutants (VAN70) was further characterized. DNA sequence analysis revealed two open reading frames, the gene into which Tn5-132 had been inserted (virA) and a closely linked upstream gene (virB). A virB mutant of 775.17B, NQ706, was isolated and also shown to be avirulent. The deduced amino acid sequences of virA and virB correspond to proteins with molecular weights of 36,000 and 42,000, respectively. Insertional mutagenesis of the corresponding virA and virB genes of a clinical isolate of V. anguillarum, serotype O1, also resulted in avirulence. In immunoblot experiments, the total cell lysates of VAN70 (virA) and NQ706 (virB) did not respond to a rabbit polyclonal antiserum directed against whole cells of 775.17B (wild type). This suggests that virA and virB are involved in the biosynthesis of a major surface antigen important for the virulence of V. anguillarum. Immunogold electron microscopy showed that a constituent of the flagellar sheath was expressed by 775.17B (wild type) but not by VAN70 (virA) and NQ706 (virB), suggesting that the major surface antigen lacking in VAN70 and NQ706 is located on the outer sheath of the flagellum. Analysis of this major surface antigen revealed it likely to be lipopolysaccharide. Further analysis showed that the flagellum and the major surface antigen were expressed in vivo during fish infections.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Actis L. A., Tolmasky M. E., Farrell D. H., Crosa J. H. Genetic and molecular characterization of essential components of the Vibrio anguillarum plasmid-mediated iron-transport system. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2853–2860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alm R. A., Manning P. A. Characterization of the hlyB gene and its role in the production of the El Tor haemolysin of Vibrio cholerae O1. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Mar;4(3):413–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alm R. A., Stroeher U. H., Manning P. A. Extracellular proteins of Vibrio cholerae: nucleotide sequence of the structural gene (hlyA) for the haemolysin of the haemolytic El Tor strain 017 and characterization of the hlyA mutation in the non-haemolytic classical strain 569B. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jul;2(4):481–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banoub J. H., Shaw D. H. Isolation and characterization of 3-acetamido-3,6-dideoxy-L-glucose from the core oligosaccharides obtained from the aquatic gram-negative bacteria Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio anguillarum. Can J Biochem. 1981 Nov-Dec;59(11-12):877–879. doi: 10.1139/o81-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H. Multiflagellate variants of Vibrio anguillarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2193–2197. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. A plasmid associated with virulence in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum specifies an iron-sequestering system. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):566–568. doi: 10.1038/284566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Hodges L. L., Schiewe M. H. Curing of a plasmid is correlated with an attenuation of virulence in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):897–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.897-902.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eguchi H., Kaya S., Araki Y. Occurrence of 2,4-dihydroxy-3,3,4-trimethylpyroglutamic acid as an N-acyl substituent in the O-polysaccharide chain of the lipopolysaccharide of Vibrio anguillarum V-123. Carbohydr Res. 1992 Jul 2;231:147–158. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(92)84015-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B. Vectors for transposon mutagenesis of non-enteric bacteria. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(2):302–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00425440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLLETT E. A., GORDON J. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF VIBRIO FLAGELLA. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Aug;32:235–239. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell D. H., Mikesell P., Actis L. A., Crosa J. H. A regulatory gene, angR, of the iron uptake system of Vibrio anguillarum: similarity with phage P22 cro and regulation by iron. Gene. 1990 Jan 31;86(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geis G., Leying H., Suerbaum S., Mai U., Opferkuch W. Ultrastructure and chemical analysis of Campylobacter pylori flagella. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):436–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.436-441.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helander I. M., Hurme R., Haikara A., Moran A. P. Separation and characterization of two chemically distinct lipopolysaccharides in two Pectinatus species. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3348–3354. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3348-3354.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hranitzky K. W., Mulholland A., Larson A. D., Eubanks E. R., Hart L. T. Characterization of a flagellar sheath protein of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):597–603. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.597-603.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama H., Moustafa M., Mikami T., Izawa H. Characterization of extracellular substance of Vibrio anguillarum toxic for rainbow trout and mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1985;29(10):909–920. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1985.tb02956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Inuzuka M., Helinski D. R. Trans-complementation-dependent replication of a low molecular weight origin fragment from plasmid R6K. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1199–1208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norqvist A., Hagström A., Wolf-Watz H. Protection of rainbow trout against vibriosis and furunculosis by the use of attenuated strains of Vibrio anguillarum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1400–1405. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1400-1405.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norqvist A., Norrman B., Wolf-Watz H. Identification and characterization of a zinc metalloprotease associated with invasion by the fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3731–3736. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3731-3736.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg G., Strömberg N., Jonsson A., Karlsson K. A., Normark S. Erythrocyte gangliosides act as receptors for Neisseria subflava: identification of the Sia-1 adhesin. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2555–2563. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2555-2563.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai D. K. Loss of virulence in a protease-deficient mutant of Aeromonas salmonicida. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):146–152. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.146-152.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinas P. C., Tolmasky M. E., Crosa J. H. Regulation of the iron uptake system in Vibrio anguillarum: evidence for a cooperative effect between two transcriptional activators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3529–3533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J. T., Schmidt K. A., Reno P. W. Polypeptides p40, pOM2, and pAngR are required for iron uptake and for virulence of the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum 775. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1347–1352. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1347-1352.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Mayer L. W., Tam M. R. Antigenicity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae outer membrane protein(s) III detected by immunoprecipitation and Western blot transfer with a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):668–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.668-672.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen U. B., Larsen J. L. Serotyping of Vibrio anguillarum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Mar;51(3):593–597. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.3.593-597.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trust T. J., Courtice I. D., Khouri A. G., Crosa J. H., Schiewe M. H. Serum resistance and hemagglutination ability of marine vibrios pathogenic for fish. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):702–707. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.702-707.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter M. A., Potter S. A., Crosa J. H. Iron uptake system medicated by Vibrio anguillarum plasmid pJM1. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):880–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.880-887.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M. K., Crosa J. H. Evidence for the role of a siderophore in promoting Vibrio anguillarum infections. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Oct;132(10):2949–2952. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-10-2949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]