Abstract
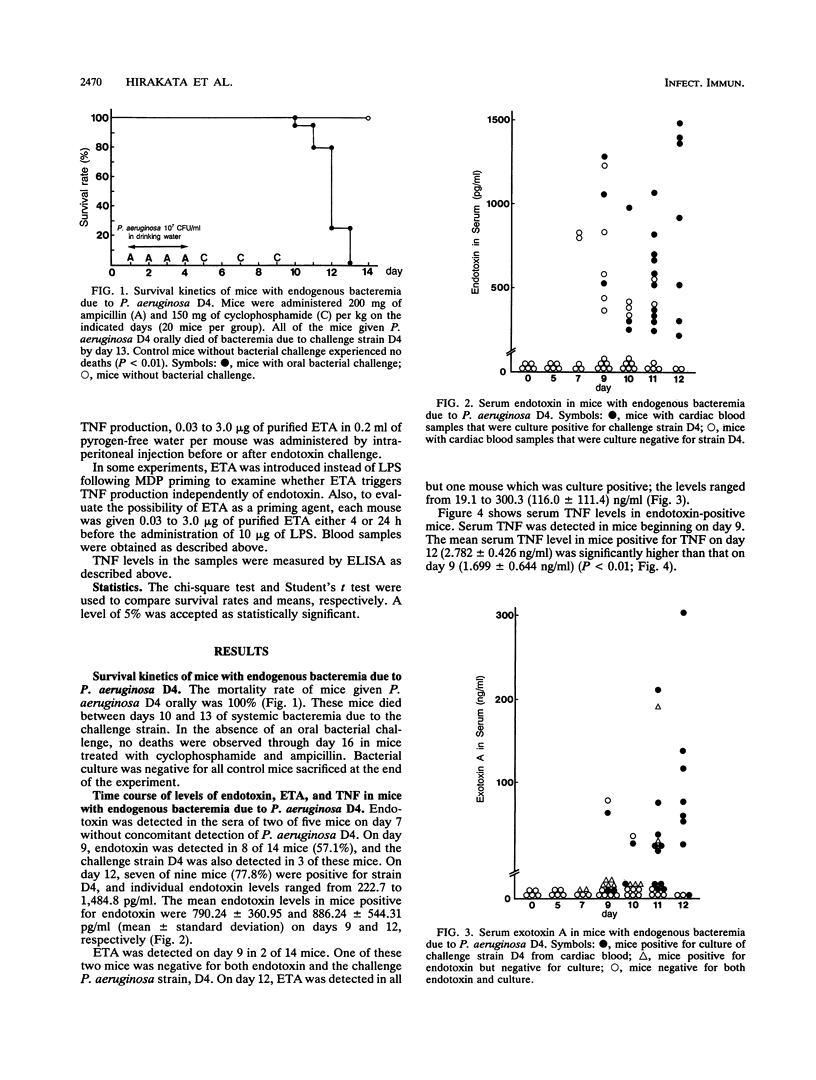
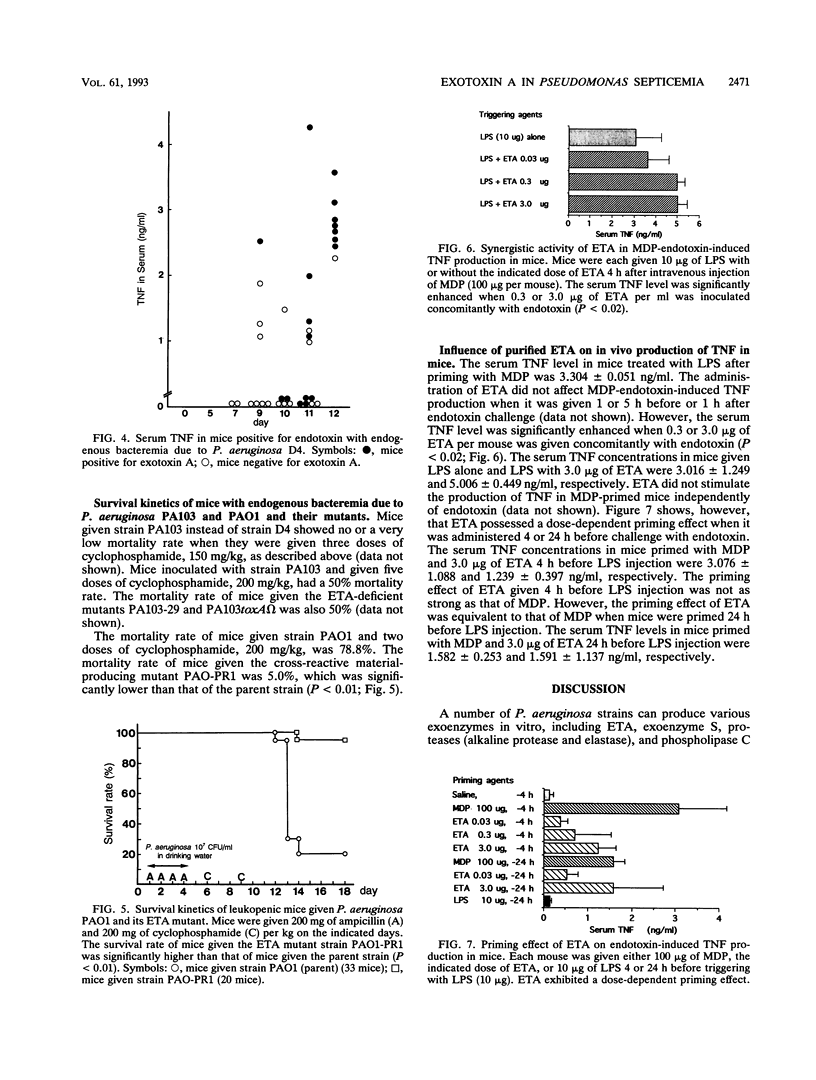
We have examined the production of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A (ETA) and its role in endogenous bacteremia in mice. Mice given P. aeruginosa D4 orally died of bacteremia between days 10 and 13 following cyclophosphamide-induced leukocytopenia. In this model, serum endotoxin was detected beginning on day 7 by the Limulus assay and P. aeruginosa was cultured from blood beginning on day 9. ETA and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) were also detected in serum by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay beginning on day 9. Purified ETA did not stimulate the production of TNF in normal mice primed with a synthetic derivative of muramyl dipeptide in the absence of endotoxin. However, ETA enhanced and primed endotoxin-induced TNF production in mice. The mortality rate of mice given ETA mutant PAO-PRI (5.0%) was significantly lower than that of mice given the parent strain (78.8%). These data indicate that ETA may be an important factor in the occurrence of P. aeruginosa bacteremia and/or the death of mice. Also, ETA may be responsible for enhancing the production of a lethal dose of TNF in the presence of endotoxin in P. aeruginosa bacteremia.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorn M. J., Pavlovskis O. R., Thompson M. R., Iglewski B. H. Production of exoenzyme S during Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections of burned mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):837–842. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.837-842.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan C. S., Reynolds K. L., Brenner E. R. Analysis of 1,186 episodes of gram-negative bacteremia in non-university hospitals: the effects of antimicrobial therapy. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):629–638. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H., Sokol P. A. Evidence for the role of toxin A in the pathogenesis of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in humans. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):538–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant producing a nontoxic, immunologically crossreactive toxin A protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7199–7203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick J. D., Shull V., Karp J. E., Valentine J. Bacterial and host factors affecting Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonization versus bacteremia in granulocytopenic patients. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1988;24 (Suppl 1):S47–S54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. J., Schlievert P. M., Nelson R. D. Toxic shock syndrome-associated staphylococcal and streptococcal pyrogenic toxins are potent inducers of tumor necrosis factor production. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):291–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.291-294.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. R., Hedstrom R. C., McGowan J. L., Kessler S. P., Wozniak D. J. Biochemical analysis of CRM 66. A nonfunctional Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14869–14873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauser M. P., Zanetti G., Baumgartner J. D., Cohen J. Septic shock: pathogenesis. Lancet. 1991 Sep 21;338(8769):732–736. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91452-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henne E., Campbell W. H., Carlson E. Toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 enhances synthesis of endotoxin-induced tumor necrosis factor in mice. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2929–2933. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2929-2933.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirakata Y., Kaku M., Mizukane R., Ishida K., Furuya N., Matsumoto T., Tateda K., Yamaguchi K. Potential effects of erythromycin on host defense systems and virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Sep;36(9):1922–1927. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.9.1922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirakata Y., Kaku M., Tomono K., Tateda K., Furuya N., Matsumoto T., Araki R., Yamaguchi K. Efficacy of erythromycin lactobionate for treating Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jun;36(6):1198–1203. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.6.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirakata Y., Tomono K., Tateda K., Matsumoto T., Furuya N., Shimoguchi K., Kaku M., Yamaguchi K. Role of bacterial association with Kupffer cells in occurrence of endogenous systemic bacteremia. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):289–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.289-294.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. S., Misfeldt M. L. Alteration of murine immune response by Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):227–233. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.227-233.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Sadoff J. C. Toxin inhibitors of protein synthesis: production, purification, and assay of Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:780–793. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Extracellular toxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S94–S99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Response of cultured mammalian cells to the exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Corynebacterium diphtheriae: differential cytotoxicity. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Feb;23(2):183–189. doi: 10.1139/m77-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miethke T., Wahl C., Heeg K., Echtenacher B., Krammer P. H., Wagner H. T cell-mediated lethal shock triggered in mice by the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: critical role of tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):91–98. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt M. L., Legaard P. K., Howell S. E., Fornella M. H., LeGrand R. D. Induction of interleukin-1 from murine peritoneal macrophages by Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):978–982. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.978-982.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. The role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 May;11 (Suppl B):1–13. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.suppl_b.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Iglewski B. H. The contribution of exoproducts to virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Apr;31(4):387–392. doi: 10.1139/m85-074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Burns R. P., Iglewski B. H. Corneal infections in mice with toxin A and elastase mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):547–555. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H. Toxin A-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):899–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.899-908.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Iglewski B. H., Pollack M. Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A in experimental mouse infections: adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of elongation factor 2. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):29–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.29-33.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Anderson S. E., Jr Toxicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A for human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1092–1096. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1092-1096.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Young L. S. Protective activity of antibodies to exotoxin A and lipopolysaccharide at the onset of Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):276–286. doi: 10.1172/JCI109300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell K., Holder I. A., Leppla S. A., Saelinger C. B. Role of exotoxin and protease as possible virulence factors in experimental infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):839–845. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.839-845.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staugas R. E., Harvey D. P., Ferrante A., Nandoskar M., Allison A. C. Induction of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and exotoxin A-induced suppression of lymphoproliferation and TNF, lymphotoxin, gamma interferon, and IL-1 production in human leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3162–3168. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3162-3168.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart R. K., Pollack M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A inhibits proliferation of human bone marrow progenitor cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):206–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.206-211.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick M. J., Cook J. M., Iglewski B. H. Structure-function analysis of exotoxin A proteins with mutations at histidine 426. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1128–1139. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1128-1139.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Schaffer M. S., Rabin H. R., Campbell G. D., Sokol P. A. Phenotypic comparison of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from a variety of clinical sites. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):260–264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.260-264.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Stevens P., Kaijser B. Gram-negative pathogens in septicaemic infections. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;31:78–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehavi-Willner T. Induction of murine cytolytic T lymphocytes by Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):213–218. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.213-218.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


