Abstract
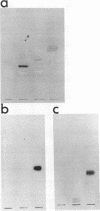
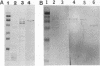
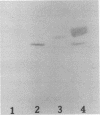
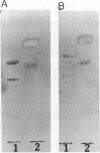
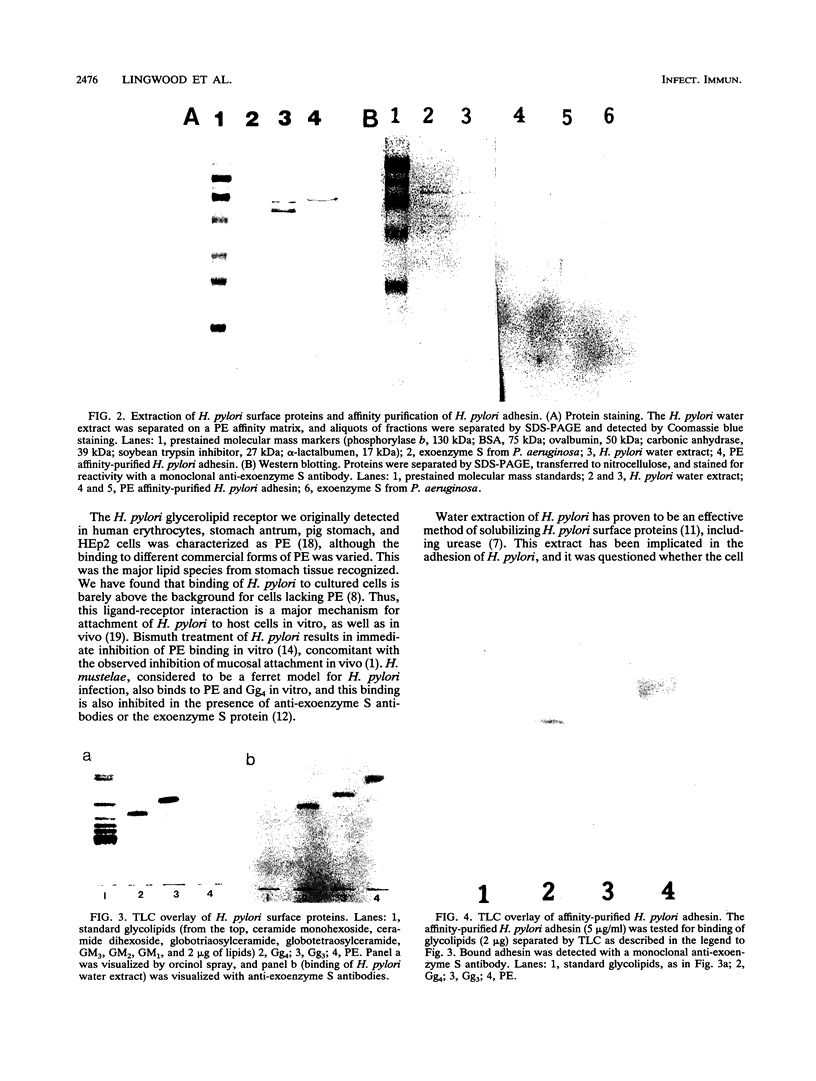
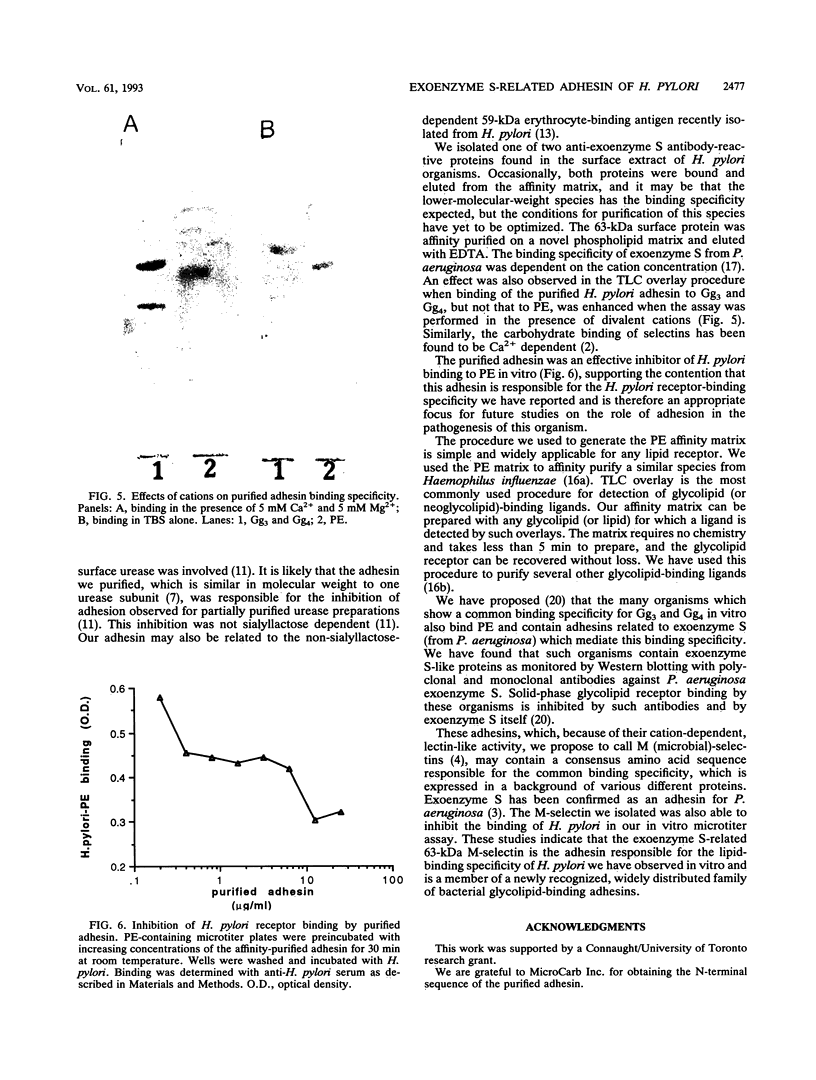
Our previous work has shown that Helicobacter pylori specifically recognizes gangliotetraosylceramide, gangliotriaosylceramide, and phosphatidylethanolamine in vitro. This binding specificity is shared by exoenzyme S from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and monoclonal antibodies against this adhesin prevent the attachment of H. pylori to its lipid receptors. We now report the use of a novel, versatile affinity matrix to purify a 63-kDa exoenzyme S-like adhesin from H. pylori which is responsible for the lipid-binding specificity of this organism.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A., Wee S. H., Goodwin C. S., Wilson D. H. Response of Campylobacter pyloridis to antibiotics, bismuth and an acid-reducing agent in vitro--an ultrastructural study. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Dec;24(4):343–350. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-4-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asa D., Gant T., Oda Y., Brandley B. K. Evidence for two classes of carbohydrate binding sites on selectins. Glycobiology. 1992 Oct;2(5):395–399. doi: 10.1093/glycob/2.5.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker N. R., Minor V., Deal C., Shahrabadi M. S., Simpson D. A., Woods D. E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S is an adhesion. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2859–2863. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2859-2863.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M., Butcher E., Furie B., Furie B., Gallatin M., Gimbrone M., Harlan J., Kishimoto K., Lasky L., McEver R. Selectins: a family of adhesion receptors. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):233–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90174-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J. Helicobacter pylori and the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal inflammation. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):626–633. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick J. D. Helicobacter (Campylobacter) pylori: a new twist to an old disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:249–269. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.001341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. E., Campbell G. P., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Purification and characterization of urease from Helicobacter pylori. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9464–9469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dytoc M., Gold B., Louie M., Huesca M., Fedorko L., Crowe S., Lingwood C., Brunton J., Sherman P. Comparison of Helicobacter pylori and attaching-effacing Escherichia coli adhesion to eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):448–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.448-456.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Moulds J. J., Graham D. Y. N-acetylneuraminyllactose-binding fibrillar hemagglutinin of Campylobacter pylori: a putative colonization factor antigen. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2896–2906. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2896-2906.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Karjalainen T. K., Evans D. J., Jr, Graham D. Y., Lee C. H. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a gene encoding an adhesin subunit protein of Helicobacter pylori. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):674–683. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.674-683.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauchère J. L., Blaser M. J. Adherence of Helicobacter pylori cells and their surface components to HeLa cell membranes. Microb Pathog. 1990 Dec;9(6):427–439. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90061-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold B. D., Huesca M., Sherman P. M., Lingwood C. A. Helicobacter mustelae and Helicobacter pylori bind to common lipid receptors in vitro. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2632–2638. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2632-2638.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J., Keeling P. W., Smyth C. J. Identification of erythrocyte-binding antigens in Helicobacter pylori. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jul;138(7):1503–1513. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-7-1503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivan H. C., Ginsburg V., Roberts D. D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas cepacia isolated from cystic fibrosis patients bind specifically to gangliotetraosylceramide (asialo GM1) and gangliotriaosylceramide (asialo GM2). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jan;260(1):493–496. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivan H. C., Roberts D. D., Ginsburg V. Many pulmonary pathogenic bacteria bind specifically to the carbohydrate sequence GalNAc beta 1-4Gal found in some glycolipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6157–6161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A., Cheng M., Krivan H. C., Woods D. Glycolipid receptor binding specificity of exoenzyme S from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 29;175(3):1076–1081. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91675-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A., Huesca M., Kuksis A. The glycerolipid receptor for Helicobacter pylori (and exoenzyme S) is phosphatidylethanolamine. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2470–2474. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2470-2474.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A., Law H., Pellizzari A., Sherman P., Drumm B. Gastric glycerolipid as a receptor for Campylobacter pylori. Lancet. 1989 Jul 29;2(8657):238–241. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90428-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura A., Stemmermann G. N., Chyou P. H., Kato I., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinoma among Japanese Americans in Hawaii. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 17;325(16):1132–1136. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110173251604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Friedman G. D., Vandersteen D. P., Chang Y., Vogelman J. H., Orentreich N., Sibley R. K. Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 17;325(16):1127–1131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110173251603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Vandersteen D., Goates J., Sibley R. K., Pritikin J., Chang Y. Helicobacter pylori infection in intestinal- and diffuse-type gastric adenocarcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991 May 1;83(9):640–643. doi: 10.1093/jnci/83.9.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei Z., Ellison R. T., 3rd, Lewis R. V., Blaser M. J. Purification and characterization of a family of high molecular weight surface-array proteins from Campylobacter fetus. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6416–6420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Natomi H., Zhao W. L., Okuzumi K., Sugano K., Iwamori M., Nagai Y. Identification of glycolipid receptors for Helicobacter pylori by TLC-immunostaining. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 6;282(2):385–387. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Que J. U. Purification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):579–586. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.579-586.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yiu S. C., Lingwood C. A. Polyisobutylmethacrylate modifies glycolipid binding specificity of verotoxin 1 in thin-layer chromatogram overlay procedures. Anal Biochem. 1992 Apr;202(1):188–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90226-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]