Abstract
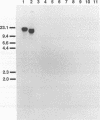
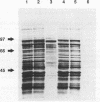
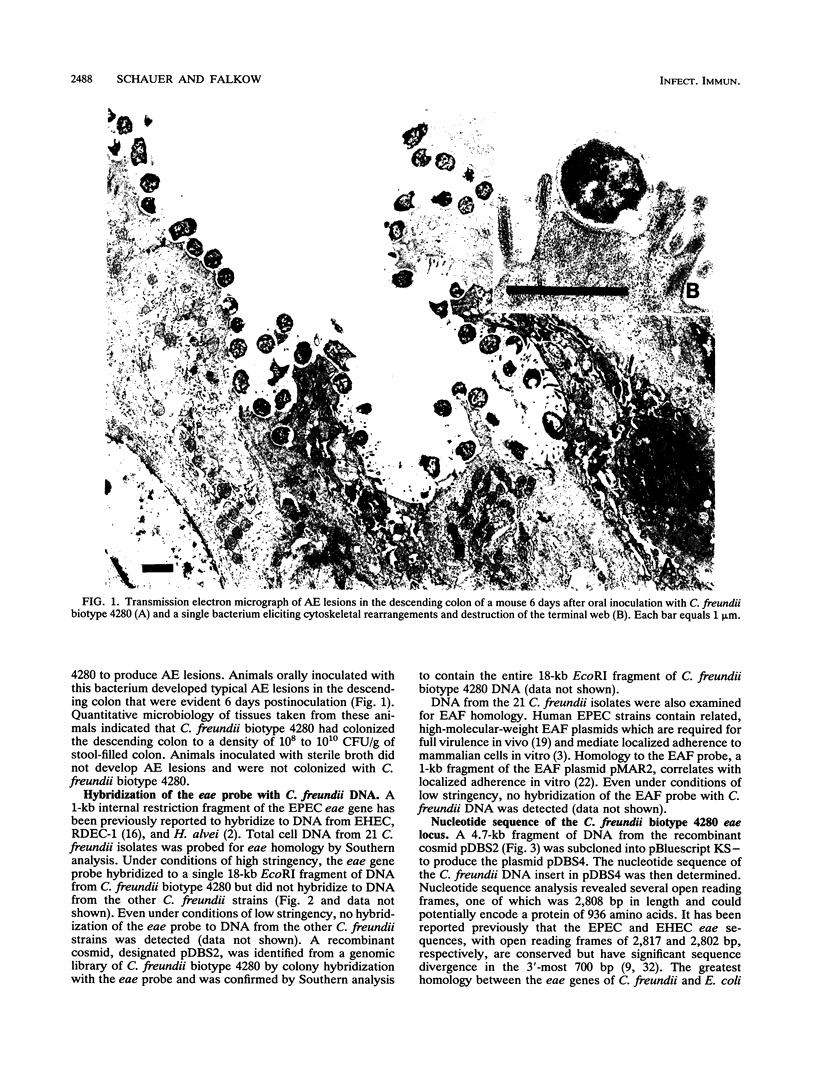
Citrobacter freundii biotype 4280 produces attaching and effacing (AE) lesions in the large intestine of laboratory mice and is the causative agent of transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia. AE lesions are also produced by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in humans. Southern analysis revealed that biotype 4280, but not 20 other strains of C. freundii, contained DNA homologous to the eae (E. coli attaching and effacing) gene which is necessary for AE activity by enteropathogenic E. coli in vitro. We have cloned and determined the nucleotide sequence of the C. freundii eae homolog. Our findings suggest that the eae locus of C. freundii biotype 4280 is necessary for AE activity and has a role in the pathogenesis of transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert M. J., Alam K., Islam M., Montanaro J., Rahaman A. S., Haider K., Hossain M. A., Kibriya A. K., Tzipori S. Hafnia alvei, a probable cause of diarrhea in humans. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1507–1513. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1507-1513.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert M. J., Faruque S. M., Ansaruzzaman M., Islam M. M., Haider K., Alam K., Kabir I., Robins-Browne R. Sharing of virulence-associated properties at the phenotypic and genetic levels between enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Hafnia alvei. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Nov;37(5):310–314. doi: 10.1099/00222615-37-5-310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRENNAN P. C., FRITZ T. E., FLYNN R. J., POOLE C. M. CITROBACTER FREUNDII ASSOCIATED WITH DIARRHEA IN A LABORATORY MICE. Lab Anim Care. 1965 Aug;15:266–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini M. M., Nataro J. P., Kaper J. B. Localization of a determinant for HEp-2 adherence by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.334-336.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W. Autoradiographic cytokinetics of colonic mucosal hyperplasia in mice. Cancer Res. 1979 Jan;39(1):24–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Coleman G. L., Bhatt P. N., Osbaldiston G. W., Jonas A. M. The etiology of transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia. Lab Anim Sci. 1976 Dec;26(6 Pt 1):889–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Coleman G. L., Jacoby R. O., Livestone E. M., Jonas A. M. Transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia. Vet Pathol. 1978 Mar;15(2):223–236. doi: 10.1177/030098587801500209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Jonas A. M. Morphogenesis of early 1, 2-dimethylhydrazine-induced lesions and latent period reduction of colon carcinogenesis in mice by a variant of Citrobacter freundii. Cancer Res. 1977 Dec;37(12):4352–4360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Osbaldiston G. W., Jonas A. M. Dietary, bacterial, and host genetic interactions in the pathogenesis of transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia. Lab Anim Sci. 1977 Dec;27(6):938–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. M., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of Escherichia coli urease genes: evidence for two distinct loci. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7138–7144. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7138-7144.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Leong J. M. Multiple beta 1 chain integrins are receptors for invasin, a protein that promotes bacterial penetration into mammalian cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90099-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Kaper J. B. The eae gene of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli encodes a 94-kilodalton membrane protein, the expression of which is influenced by the EAF plasmid. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4302–4309. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4302-4309.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Yu J., Tall B. D., Kaper J. B. A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7839–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E., Barthold S. W. The ultrastructure of transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia. Am J Pathol. 1979 Nov;97(2):291–313. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nataro J. P., Karch H., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L., O'Brien A. D. The diarrheal response of humans to some classic serotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is dependent on a plasmid encoding an enteroadhesiveness factor. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):550–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Argenzio R. A., Levine M. M., Giannella R. A. Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1340–1351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1340-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nataro J. P., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Bravo N., Levine M. M. Detection of an adherence factor of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with a DNA probe. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):560–565. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Kelly J. K., Meyers G. L. Experimental infection of infant rabbits with verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):16–23. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.16-23.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenshine I., Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B., Finlay B. B. Signal transduction between enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) and epithelial cells: EPEC induces tyrosine phosphorylation of host cell proteins to initiate cytoskeletal rearrangement and bacterial uptake. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3551–3560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H., Montag M., Bockemühl J., Heesemann J., Karch H. Shiga-like toxin II-related cytotoxins in Citrobacter freundii strains from humans and beef samples. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):534–543. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.534-543.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P., Cockerill F., 3rd, Soni R., Brunton J. Outer membranes are competitive inhibitors of Escherichia coli O157:H7 adherence to epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):890–899. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.890-899.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Inman L. R., O'Hanley P. D., Cantey J. R., Lushbaugh W. B. Scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of Escherichia coli O15 (RDEC-1) enteric infection in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):686–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.686-694.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Kaper J. B. Cloning and characterization of the eae gene of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(3):411–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]