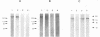Abstract
The binding of bacteria or bacterial products to host proteins of tissue extracellular matrix may be a mechanism of tissue adherence. We investigated interactions of the plasmid-encoded outer membrane protein YadA, which confers pathogenic functions on enteropathogenic yersiniae, with fibronectin. Attachment of YadA-positive and YadA-negative recombinant Yersinia enterocolitica strains to cartilage-derived human cellular fibronectin and human plasma fibronectin in the solid phase revealed that YadA mediates binding of yersiniae to cellular fibronectin in a saturable, concentration-dependent manner. The interaction could be inhibited by an anti-YadA-specific anti-serum. An anti-beta 1-integrin antibody and the synthetic peptide G-R-G-D-S-P, representing the binding site for alpha 5 beta 1-integrin on fibronectin, did not block attachment of YadA-positive yersiniae to cellular fibronectin, indicating a binding site for YadA on cellular fibronectin independent of the R-G-D-S-containing site. By contrast, YadA failed to mediate binding to plasma fibronectin immobilized on nitrocellulose or plastic surfaces. These observations provide evidence for the hypothesis that the binding region for YadA in cellular fibronectin is not present in plasma fibronectin. This study is the first report on differential binding of bacteria to splicing variants of fibronectin. Further experiments might answer the question whether binding of YadA to cellular fibronectin contributes to the pathogenesis of yersiniae, both to the initial adhesion of the bacteria to the matrices of the host and to the arthritogenic potential of enteropathogenic yersiniae.
Full text
PDF
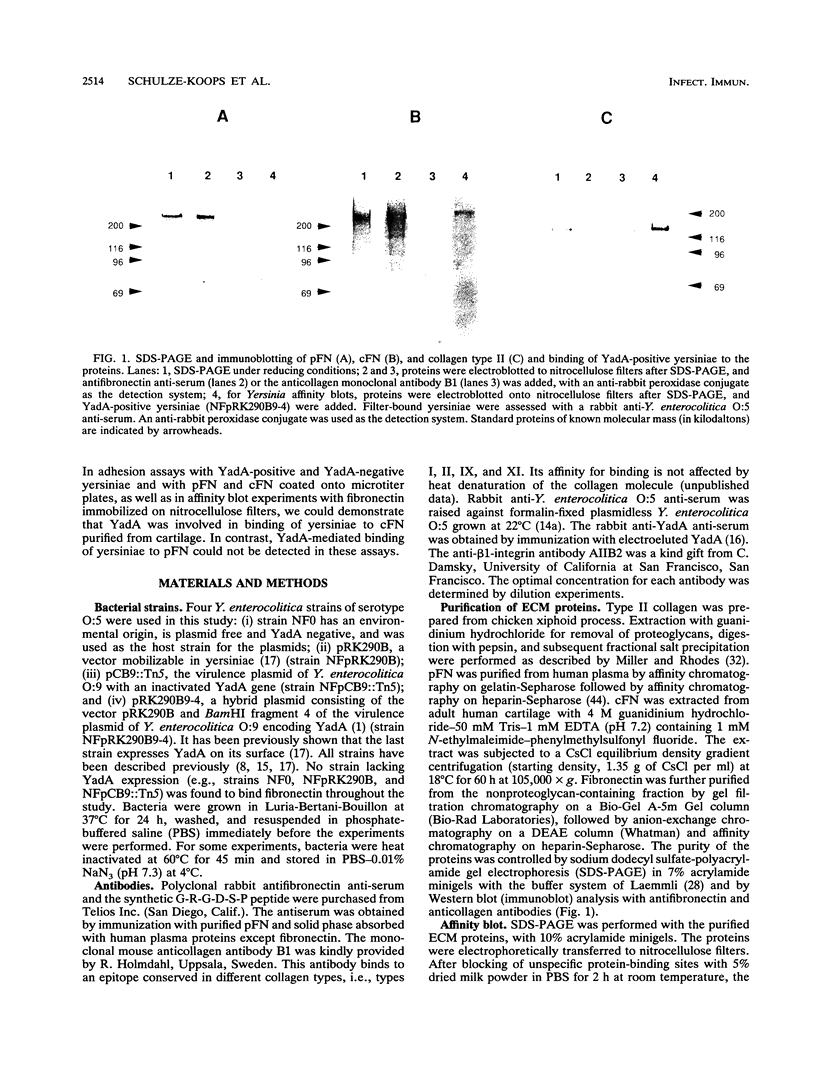

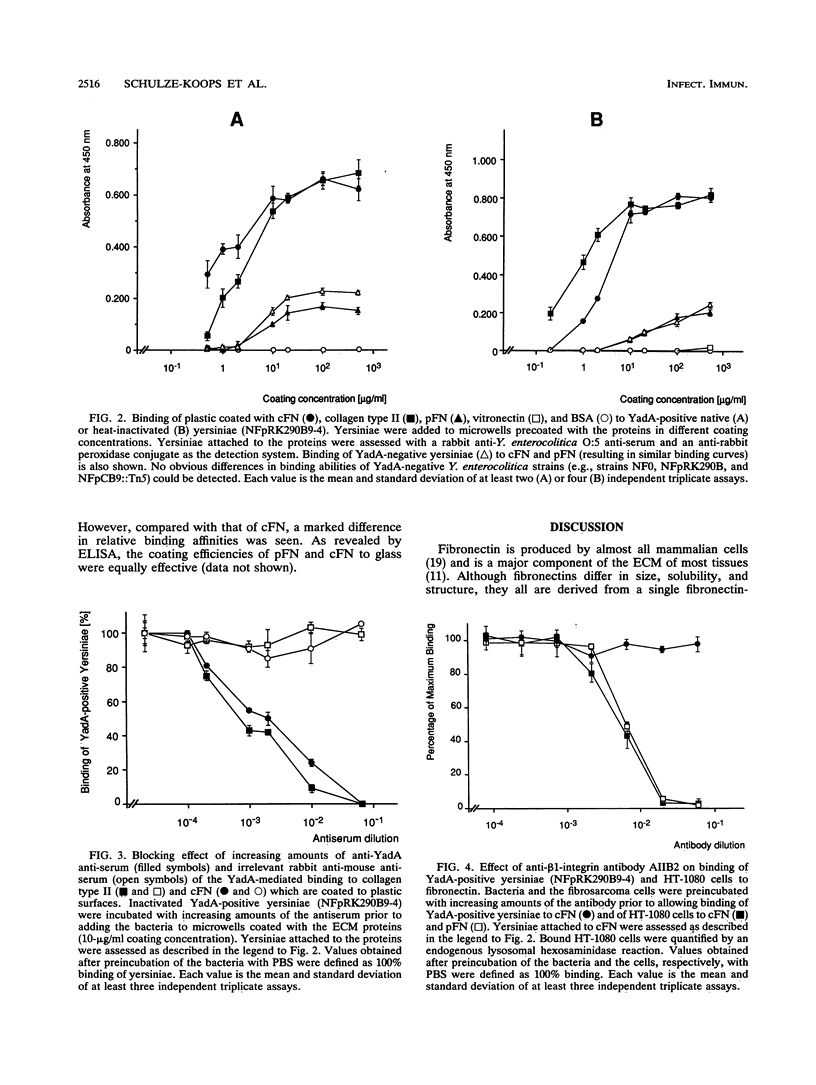
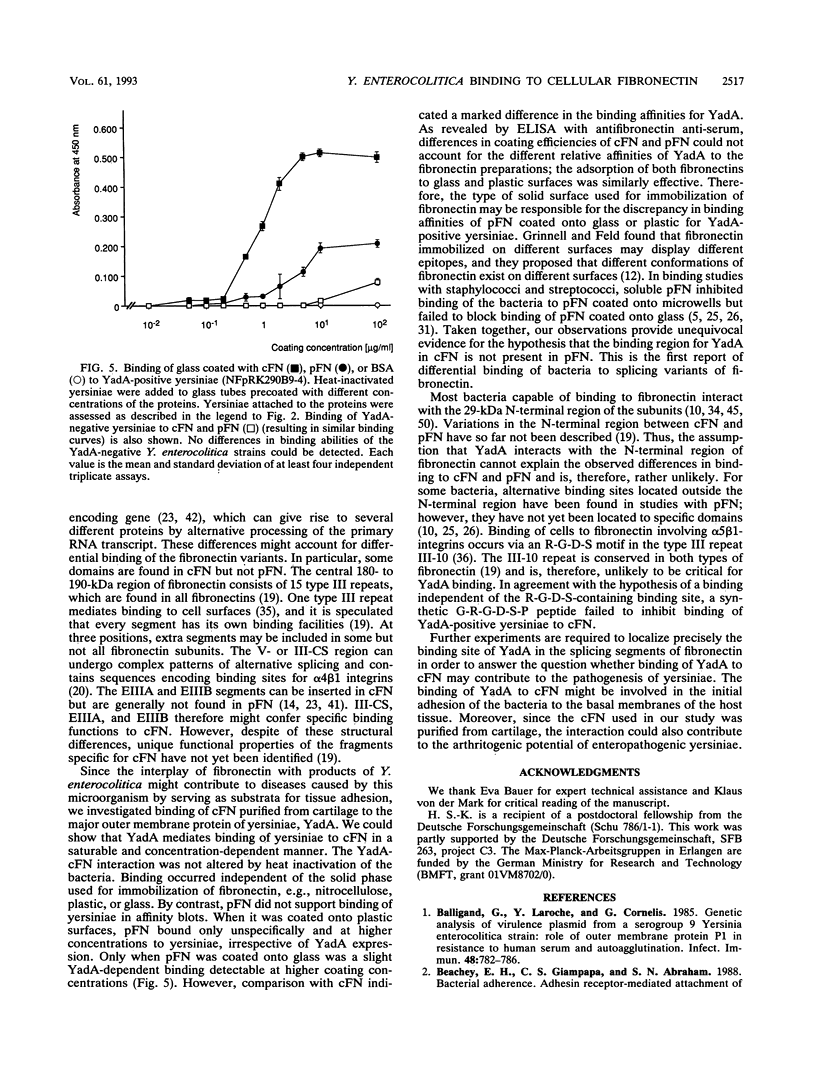


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balligand G., Laroche Y., Cornelis G. Genetic analysis of virulence plasmid from a serogroup 9 Yersinia enterocolitica strain: role of outer membrane protein P1 in resistance to human serum and autoagglutination. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):782–786. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.782-786.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H. Expression of the temperature-inducible outer membrane proteins of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):234–240. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.234-240.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G. R., Biot T., Lambert de Rouvroit C., Michiels T., Mulder B., Sluiters C., Sory M. P., Van Bouchaute M., Vanooteghem J. C. The Yersinia yop regulon. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1455–1459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney H. S., Ofek I., Simpson W. A., Hasty D. L., Beachey E. H. Binding of Streptococcus pyogenes to soluble and insoluble fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):454–459. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.454-459.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Aber R. C. Yersinia enterocolitica. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 6;321(1):16–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907063210104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessau W., Sasse J., Timpl R., Jilek F., von der Mark K. Synthesis and extracellular deposition of fibronectin in chondrocyte cultures. Response to the removal of extracellular cartilage matrix. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):342–355. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emödy L., Heesemann J., Wolf-Watz H., Skurnik M., Kapperud G., O'Toole P., Wadström T. Binding to collagen by Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis: evidence for yopA-mediated and chromosomally encoded mechanisms. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6674–6679. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6674-6679.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröman G., Switalski L. M., Faris A., Wadström T., Hök M. Binding of Escherichia coli to fibronectin. A mechanism of tissue adherence. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14899–14905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J. M., Hynes R. O., Davidson E. A., Bainton D. F. The location of proteins labeled by the 125I-lactoperoxidase system in the NIL 8 hamster fibroblast. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):353–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell F., Feld M. K. Fibronectin adsorption on hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces detected by antibody binding and analyzed during cell adhesion in serum-containing medium. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4888–4893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity of an essential virulence determinant in Yersinia. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2166336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Kornblihtt A. R. Identification of a third region of cell-specific alternative splicing in human fibronectin mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7179–7182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Algermissen B., Laufs R. Genetically manipulated virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):105–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.105-110.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Gross U., Grüter L. Genetic manipulation of virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1987;9:312–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Discrimination between intracellular uptake and surface adhesion of bacterial pathogens. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):934–938. doi: 10.1126/science.1674624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Namork E., Skurnik M., Nesbakken T. Plasmid-mediated surface fibrillae of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica: relationship to the outer membrane protein YOP1 and possible importance for pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2247–2254. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2247-2254.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Human fibronectin: molecular cloning evidence for two mRNA species differing by an internal segment coding for a structural domain. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):221–226. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P. Fibronectin binds to Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):718–720. doi: 10.1038/276718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Vartio T., Vuento M., Myhre E. B. Attachment of staphylococci and streptococci on fibronectin, fibronectin fragments, and fibrinogen bound to a solid phase. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.77-81.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Vartio T., Vuento M., Myhre E. B. Binding sites for streptococci and staphylococci in fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):433–436. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.433-436.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Zink D. L., Ferris W. R. Association of fibril structure formation with cell surface properties of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):272–275. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.272-275.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landegren U. Measurement of cell numbers by means of the endogenous enzyme hexosaminidase. Applications to detection of lymphokines and cell surface antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 16;67(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J. D., dos Reis M., Brentani R. R. Presence of laminin receptors in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.3160113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxe I., Rydén C., Wadström T., Rubin K. Specific attachment of Staphylococcus aureus to immobilized fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):695–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.695-704.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Rhodes R. K. Preparation and characterization of the different types of collagen. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):33–64. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Umfleet R. A. The cold-insoluble globulin of human plasma. I. Purification, primary characterization, and relationship to fibrinogen and other cold-insoluble fraction components. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5728–5736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Proctor R. A. Binding and factor XIIIa-mediated cross-linking of a 27-kilodalton fragment of fibronectin to Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):927–929. doi: 10.1126/science.7403857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Hayman E. G., Ruoslahti E. Location of the cell-attachment site in fibronectin with monoclonal antibodies and proteolytic fragments of the molecule. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90308-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):30–33. doi: 10.1038/309030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilz D., Vocke T., Heesemann J., Brade V. Mechanism of YadA-mediated serum resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O3. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):189–195. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.189-195.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Martinez R. J. Role of a plasmid in the pathogenicity of Yersinia species. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:29–51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T. Structure and biological role of vitronectin. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:275–310. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Koops H., Burkhardt H., Heesemann J., von der Mark K., Emmrich F. Plasmid-encoded outer membrane protein YadA mediates specific binding of enteropathogenic yersiniae to various types of collagen. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2153–2159. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2153-2159.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Patel R. S., Fonda D., Hynes R. O. Multiple sites of alternative splicing of the rat fibronectin gene transcript. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2573–2580. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Lemischka I. R., Hynes R. O. Three different fibronectin mRNAs arise by alternative splicing within the coding region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerl K. G., Calderone R. A., Segal E., Sreevalsan T., Scheld W. M. In vitro binding of Candida albicans yeast cells to human fibronectin. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Feb;30(2):221–227. doi: 10.1139/m84-033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skrha J., Richter H., Hörmann H. Evidence for the presence of a free N-terminal fibronectin 30-kDa domain in human plasma by quantitative determination with an indirect immunosorbent assay. Anal Biochem. 1988 Sep;173(2):228–234. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale P., Hök M., Switalski L. M., Wadström T. Fibronectin binding to a Streptococcus pyogenes strain. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):420–427. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.420-427.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale P., Hök M., Wadström T., Timpl R. Binding of the basement membrane protein laminin to Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80704-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale P., Raucci G., Visai L., Switalski L. M., Timpl R., Hök M. Binding of collagen to Staphylococcus aureus Cowan 1. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.77-81.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Speziale P., Hök M., Wadström T., Timpl R. Binding of Streptococcus pyogenes to laminin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3734–3738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tertti R., Skurnik M., Vartio T., Kuusela P. Adhesion protein YadA of Yersinia species mediates binding of bacteria to fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):3021–3024. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.3021-3024.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Water L., Destree A. T., Hynes R. O. Fibronectin binds to some bacteria but does not promote their uptake by phagocytic cells. Science. 1983 Apr 8;220(4593):201–204. doi: 10.1126/science.6338594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartio T., Vaheri A., Von Essen R., Isomäki H., Stenman S. Fibronectin in synovial fluid and tissue in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;11(3):207–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1981.tb01842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M. Cell surface interactions with extracellular materials. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:761–799. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark H., Dürr J., Sonnenberg A., von der Mark K., Deutzmann R., Goodman S. L. Skeletal myoblasts utilize a novel beta 1-series integrin and not alpha 6 beta 1 for binding to the E8 and T8 fragments of laminin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23593–23601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]