Abstract
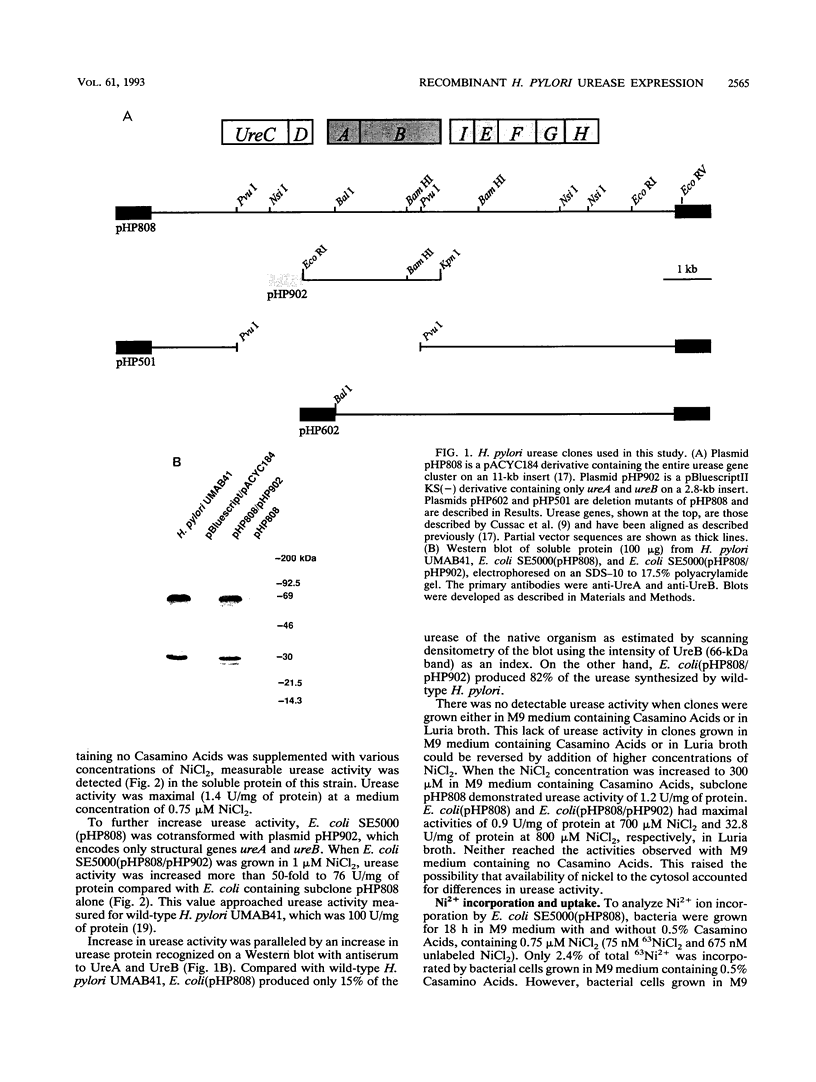
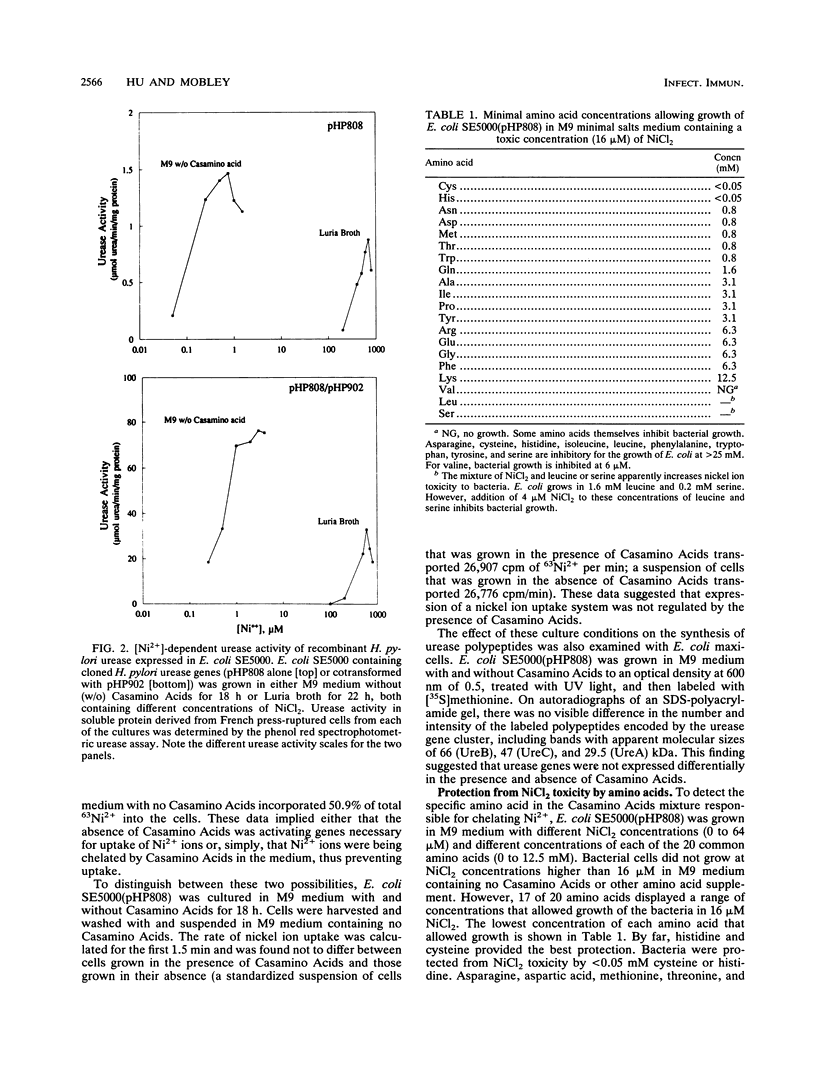
The genes encoding Helicobacter pylori urease, a nickel metalloenzyme, have been cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. Enzymatic activity, however, has been very weak compared with that in clinical isolates of H. pylori. Conditions under which near wild-type urease activity was achieved were developed. E. coli. SE5000 containing recombinant H. pylori urease genes was grown in minimal medium containing no amino acids, NiCl2 was added to 0.75 microM, and structural genes ureA and ureB (pHP902) were overexpressed in trans to the complete urease gene cluster (pHP808). Under these conditions, E. coli SE5000 pHP808/pHP902) expressed a urease activity up to 87 mumol of urea per min per mg of protein (87 U/mg of protein), a level approaching that of wild-type H. pylori UMAB41 (100 U/mg of protein), from which the genes were cloned. Poor catalytic activity of recombinant clones grown in Luria broth or M9 medium containing 0.5% Casamino Acids was due to chelation of nickel ions by medium components, particularly histidine and cysteine. In cultures containing these amino acids, 63Ni2+ was prevented from being transported into cells and was not incorporated into urease protein. As a consequence, M9 minimal medium cultures containing histidine or cysteine produced only 0.05 and 0.9%, respectively, of active urease produced by control cultures containing no amino acids. We conclude that recombinant H. pylori urease is optimally expressed when Ni2+ transport is not inhibited and when sufficient synthesis of urease subunits UreA and UreB is provided.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alagna L., Hasnain S. S., Piggott B., Williams D. J. The nickel ion environment in jack bean urease. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):591–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2200591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassford P. J., Jr, Silhavy T. J., Beckwith J. R. Use of gene fusion to study secretion of maltose-binding protein into Escherichia coli periplasm. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):19–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.19-31.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. D., Weil J., Harrison G., Morden A., Jones P. H., Gant P. W., Trowell J. E., Yoong A. K., Daneshmend T. K., Logan R. F. 14C-urea breath analysis, a non-invasive test for Campylobacter pylori in the stomach. Lancet. 1987 Jun 13;1(8546):1367–1368. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90664-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard A. Ureaplasma urealyticum urease genes; use of a UGA tryptophan codon. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):669–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. L., Pallen M. J., Kleanthous H., Wren B. W., Tabaqchali S. Nucleotide sequence of two genes from Helicobacter pylori encoding for urease subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):362–362. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. M., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of an Escherichia coli urease locus: evidence of DNA rearrangement. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1041–1045. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1041-1045.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cussac V., Ferrero R. L., Labigne A. Expression of Helicobacter pylori urease genes in Escherichia coli grown under nitrogen-limiting conditions. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2466–2473. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2466-2473.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. C., McNulty C. A., Uff J. S., Gear M. W., Wilkinson S. P. Campylobacter pylori urease: a new serological test. Lancet. 1988 Apr 30;1(8592):1002–1002. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91827-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton K. A., Brooks C. L., Morgan D. R., Krakowka S. Essential role of urease in pathogenesis of gastritis induced by Helicobacter pylori in gnotobiotic piglets. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2470–2475. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2470-2475.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherardini F. C., Hobbs M. M., Stamm L. V., Bassford P. J., Jr Complementation of an Escherichia coli proC mutation by a gene cloned from Treponema pallidum. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2996–3002. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2996-3002.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. Y., Klein P. D., Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Alpert L. C., Opekun A. R., Boutton T. W. Campylobacter pylori detected noninvasively by the 13C-urea breath test. Lancet. 1987 May 23;1(8543):1174–1177. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M., Gargan R. A. Rapid screening for urease inhibitors. Invest Urol. 1979 Mar;16(5):327–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasnain S. S., Piggott B. An EXAFS study of jack bean urease, a nickel metalloenzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 15;112(1):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91827-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawtin P. R., Delves H. T., Newell D. G. The demonstration of nickel in the urease of Helicobacter pylori by atomic absorption spectroscopy. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jan 1;61(1):51–54. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90012-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L. T., Foxall P. A., Russell R., Mobley H. L. Purification of recombinant Helicobacter pylori urease apoenzyme encoded by ureA and ureB. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2657–2666. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2657-2666.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L. T., Mobley H. L. Purification and N-terminal analysis of urease from Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):992–998. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.992-998.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L. T., Nicholson E. B., Jones B. D., Lynch M. J., Mobley H. L. Morganella morganii urease: purification, characterization, and isolation of gene sequences. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3073–3080. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3073-3080.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Mobley H. L. Proteus mirabilis urease: genetic organization, regulation, and expression of structural genes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3342–3349. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3342-3349.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Mobley H. L. Proteus mirabilis urease: nucleotide sequence determination and comparison with jack bean urease. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6414–6422. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6414-6422.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne A., Cussac V., Courcoux P. Shuttle cloning and nucleotide sequences of Helicobacter pylori genes responsible for urease activity. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):1920–1931. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.1920-1931.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. H., Mulrooney S. B., Renner M. J., Markowicz Y., Hausinger R. P. Klebsiella aerogenes urease gene cluster: sequence of ureD and demonstration that four accessory genes (ureD, ureE, ureF, and ureG) are involved in nickel metallocenter biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4324–4330. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4324-4330.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Cortesia M. J., Rosenthal L. E., Jones B. D. Characterization of urease from Campylobacter pylori. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):831–836. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.831-836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Hausinger R. P. Microbial ureases: significance, regulation, and molecular characterization. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):85–108. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.85-108.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Jones B. D., Jerse A. E. Cloning of urease gene sequences from Providencia stuartii. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):161–169. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.161-169.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Buck M. In vivo studies on the interaction of RNA polymerase-sigma 54 with the Klebsiella pneumoniae and Rhizobium meliloti nifH promoters. The role of NifA in the formation of an open promoter complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulrooney S. B., Hausinger R. P. Sequence of the Klebsiella aerogenes urease genes and evidence for accessory proteins facilitating nickel incorporation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5837–5843. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5837-5843.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulrooney S. B., Pankratz H. S., Hausinger R. P. Regulation of gene expression and cellular localization of cloned Klebsiella aerogenes (K. pneumoniae) urease. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jun;135(6):1769–1776. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-6-1769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mörsdorf G., Kaltwasser H. Cloning of the genes encoding urease from Proteus vulgaris and sequencing of the structural genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 1;54(1-3):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90260-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G., Stacey A. Antigens for the serodiagnosis of Campylobacter pylori infections. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1989;13(1 Pt 1):37B–41B. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Kerner T. C., Jr, Bankaitis V. A., Bassford P. J., Jr Identification and preliminary characterization of Treponema pallidum protein antigens expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):709–721. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.709-721.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takishima K., Suga T., Mamiya G. The structure of jack bean urease. The complete amino acid sequence, limited proteolysis and reactive cysteine residues. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 15;175(1):151–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd M. J., Hausinger R. P. Identification of the essential cysteine residue in Klebsiella aerogenes urease. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24327–24331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd M. J., Hausinger R. P. Reactivity of the essential thiol of Klebsiella aerogenes urease. Effect of pH and ligands on thiol modification. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10260–10267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]