Abstract
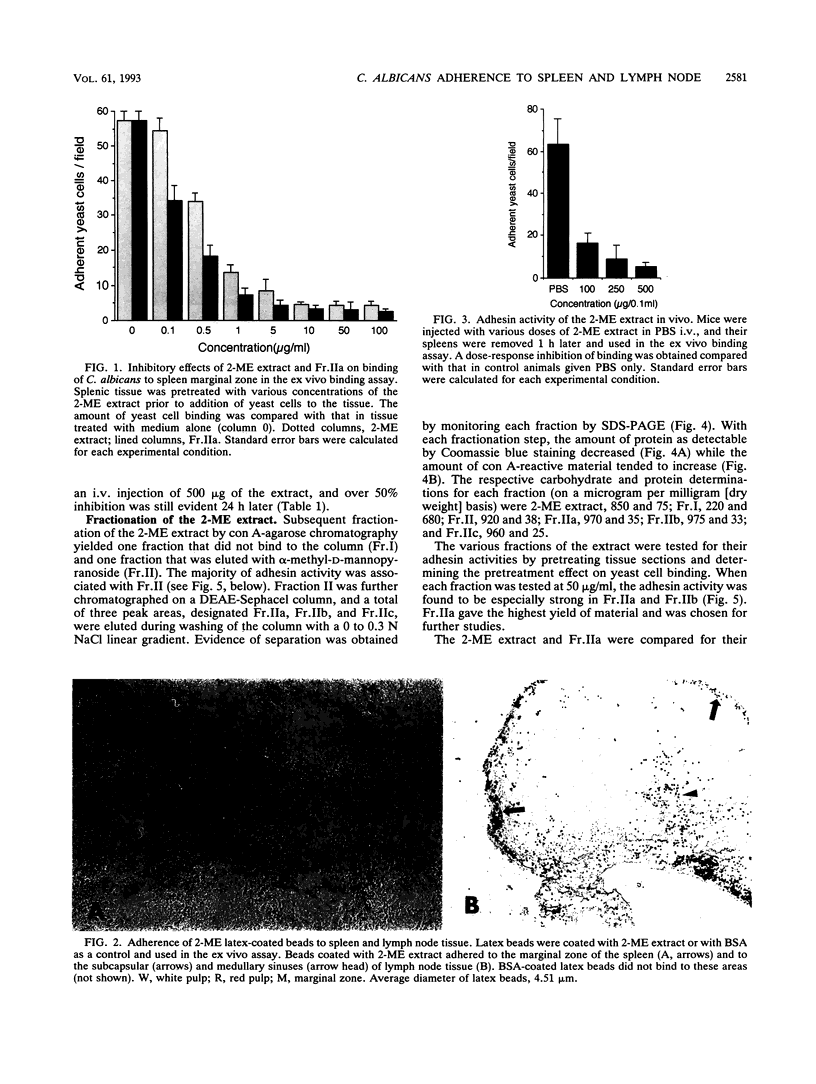
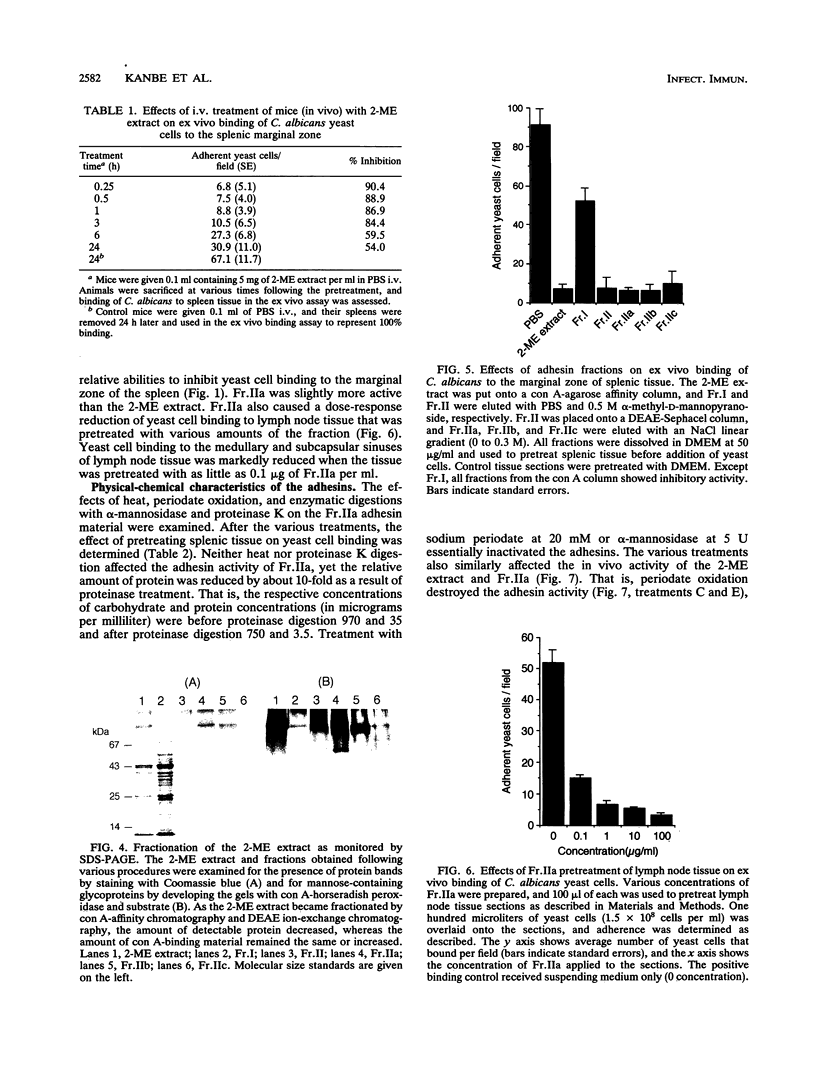
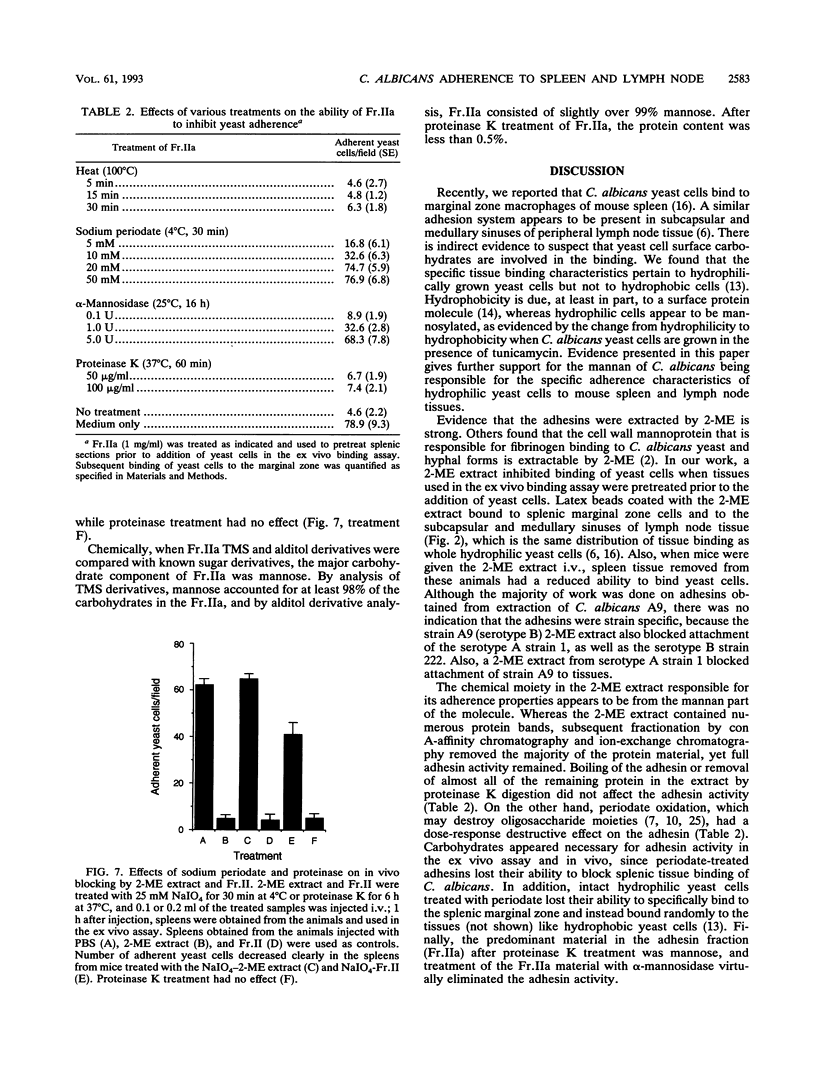
We have described a unique binding system between Candida albicans yeast-form cells and the marginal zone of mouse spleen (16). The chemical nature of the fungal adhesin(s) involved in this binding phenomenon was examined. A fraction obtained by 2-mercaptoethanol extraction (2-ME extract) of fungal cells caused a dose-response inhibition of yeast cell adherence to splenic marginal zone sites and also to subcapsular and medullary sinuses of mouse popliteal lymph nodes. Latex beads coated with the 2-ME extract showed a pattern of spleen and lymph node tissue binding identical to that observed with yeast cells. The extracted adhesins retained their binding activity in vivo. When 0.5 mg of the 2-ME extract was given intravenously to mice, spleen tissue removed up to 3 h later showed over 80% inhibition of yeast cell binding to the spleen marginal zone, and over 50% inhibition was retained for at least 24 h. The adhesins bound to a concanavalin A affinity column and were eluted by 0.5 M alpha-methyl-D-mannopyranoside, and the eluted adhesins were designated Fr.II. Fr.II was further fractioned by DEAE-Sephacel ion-exchange column chromatography, and one especially active and abundant fraction was designated Fr.IIa. The adhesin moiety appeared to be carbohydrate, because the activity of Fr.IIa was destroyed by 20 mM sodium periodate or by 5 U of alpha-mannosidase, but boiling (30 min) or proteinase K (100 micrograms/ml) treatments had no effect. Chemically, whereas the 2-ME extract contained significant amounts of protein and mannose, Fr.IIa consisted of over 98% mannose and less than 0.5% protein. These data strongly suggest that the mannan portion within a mannoprotein is responsible for the binding of yeast cells to splenic marginal zone and to subcapsular and medullary sinuses of mouse lymph node tissue.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butcher E. C., Scollay R. G., Weissman I. L. Lymphocyte adherence to high endothelial venules: characterization of a modified in vitro assay, and examination of the binding of syngeneic and allogeneic lymphocyte populations. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):1996–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova M., Lopez-Ribot J. L., Monteagudo C., Llombart-Bosch A., Sentandreu R., Martinez J. P. Identification of a 58-kilodalton cell surface fibrinogen-binding mannoprotein from Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4221–4229. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4221-4229.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassone A. Cell wall of Candida albicans: its functions and its impact on the host. Curr Top Med Mycol. 1989;3:248–314. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-3624-5_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley I. A., Douglas L. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an adhesin from Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):629–636. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E., Brawner D. L., Hazen K. C., Jutila M. A. Characteristics of Candida albicans adherence to mouse tissues. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1902–1908. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1902-1908.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Putative virulence factors of Candida albicans. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:187–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth A. J. Methods for assaying nonenzymatic glycosylation. Anal Biochem. 1988 Dec;175(2):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum M. A., Abu-Elteen K. H. Pathogenicity determinants of Candida. Mycoses. 1990 Jun;33(6):265–282. doi: 10.1111/myc.1990.33.6.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum M. A., Burns G. R., Elteen K. A., Radwan S. S. Experimental evidence for the role of lipids in adherence of Candida spp. to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):189–193. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.189-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopal P., Sullivan P. A., Shepherd M. G. Isolation and structure of glucan from regenerating spheroplasts of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 May;130(5):1217–1225. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-5-1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson K. S., Vercellotti G. M., Bendel C. M., Hostetter M. K. Molecular mimicry in Candida albicans. Role of an integrin analogue in adhesion of the yeast to human endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1896–1902. doi: 10.1172/JCI115214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen K. C., Brawner D. L., Riesselman M. H., Jutila M. A., Cutler J. E. Differential adherence of hydrophobic and hydrophilic Candida albicans yeast cells to mouse tissues. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):907–912. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.907-912.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen K. C., Hazen B. W. Hydrophobic surface protein masking by the opportunistic fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1499–1508. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1499-1508.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jutila M. A., Rott L., Berg E. L., Butcher E. C. Function and regulation of the neutrophil MEL-14 antigen in vivo: comparison with LFA-1 and MAC-1. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3318–3324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanbe T., Jutila M. A., Cutler J. E. Evidence that Candida albicans binds via a unique adhesion system on phagocytic cells in the marginal zone of the mouse spleen. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1972–1978. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1972-1978.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanbe T., Li R. K., Wadsworth E., Calderone R. A., Cutler J. E. Evidence for expression of the C3d receptor of Candida albicans in vitro and in vivo obtained by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1832–1838. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1832-1838.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitany R. A., Zebrowski E. J. A high resolution PAS stain for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A. Fungal adherence to the vascular compartment: a critical step in the pathogenesis of disseminated candidiasis. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):340–347. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A., Smith R. L., Stewart B. W. Effect of an arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-containing peptide on hematogenous candidal infections in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jan;36(1):132–136. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.1.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer N., Segal E., Lis H., Gov Y. Effect of Candida albicans cell wall components on the adhesion of the fungus to human and murine vaginal mucosa. Mycopathologia. 1988 May;102(2):115–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00437448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R. K., Cutler J. E. A cell surface/plasma membrane antigen of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Mar;137(3):455–464. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcantonio E. E., Hynes R. O. Antibodies to the conserved cytoplasmic domain of the integrin beta 1 subunit react with proteins in vertebrates, invertebrates, and fungi. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1765–1772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCourtie J., Douglas L. J. Extracellular polymer of Candida albicans: isolation, analysis and role in adhesion. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Mar;131(3):495–503. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-3-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa Y., Kuribayashi T., Kagaya K., Suzuki M., Nakase T., Fukazawa Y. Role of specific determinants in mannan of Candida albicans serotype A in adherence to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2493–2499. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2493-2499.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. L., Payne C. D., Morrow B. J. Candida albicans acid proteinase: characterization and role in candidiasis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;306:173–183. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-6012-4_22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesselman M. H., Kanbe T., Cutler J. E. Improvements and important considerations of an ex vivo assay to study Candida albicans-splenic tissue interactions. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Dec 15;145(1-2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R. T., Garner R. E., Hudson J. A. Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptides alter hepatic killing of Candida albicans in the isolated perfused mouse liver model. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):213–218. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.213-218.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamper H. B., Jr, Woodruff J. J. Lymphocyte homing into lymph nodes: in vitro demonstration of the selective affinity of recirculating lymphocytes for high-endothelial venules. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):828–833. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosh F. D., Douglas L. J. Characterization of a fucoside-binding adhesin of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4734–4739. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4734-4739.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]