Abstract
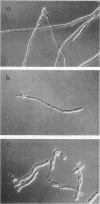
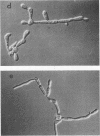
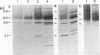
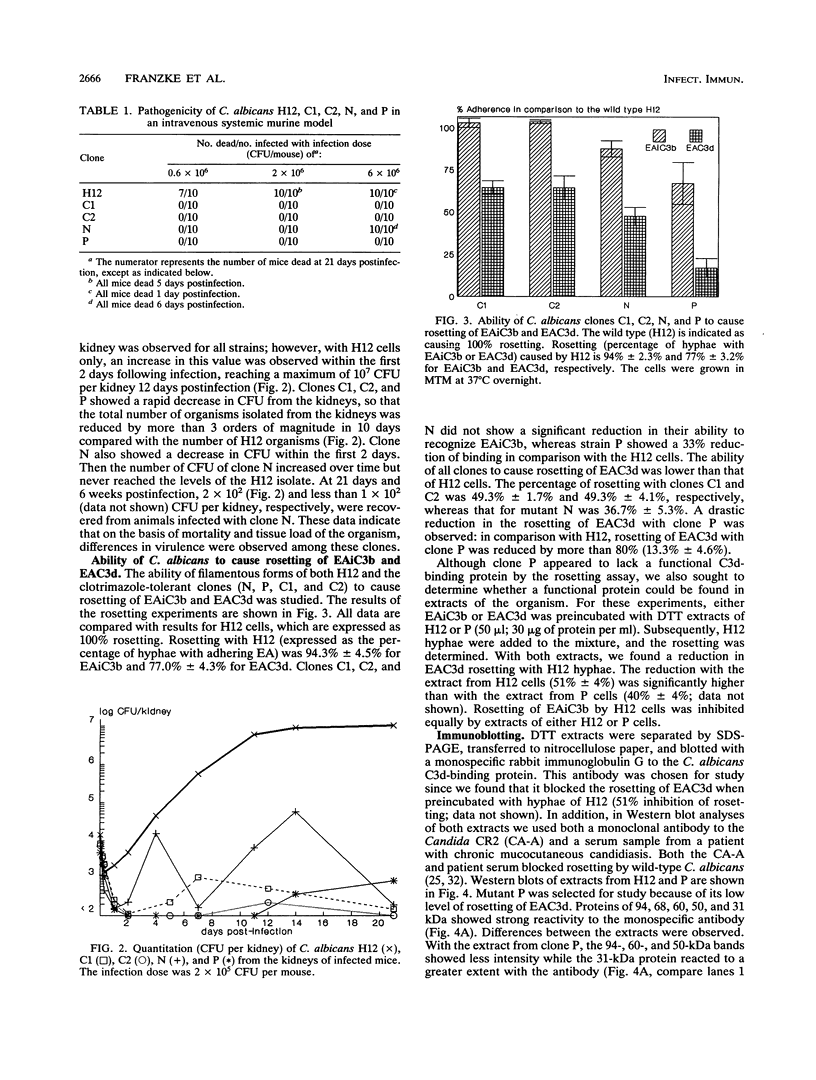
Four clones of the yeast Candida albicans, isolated on the basis of their tolerance to clotrimazole, were compared with their parental strains in terms of growth, morphology, virulence, and cell surface complement receptor activity. In a newly described synthetic medium, these clones, designated C1, C2, N, and P, produced germ tubes or pseudohyphae, but no true hyphae, in a pattern which was specific for each strain. The growth of each clone at 37 degrees C, under conditions which favor the filamentous growth form of the organism, was equal to that of the parental strain (H12). The pathogenicity of each clone was tested in an intravenous mouse model. None of the mice infected with the tolerant clones but all of the mice infected with H12 developed severe renal candidiasis after infection with 1.4 x 10(6) to 2.0 x 10(6) CFU/ml. The number of CFU of each clone from the mouse kidney was reduced about 3 or 4 orders of magnitude in comparison with the wild type. As a correlate, we measured the complement receptor activity (CR2 and CR3) of each clone. The C3 ligands, iC3b and C3d, were conjugated to sheep erythrocytes (E) sensitized with antibody (A) to the erythrocytes (EA). We found that all tolerant clones showed reduced recognition of C3d-bearing sheep erythrocytes (EAC3d) in rosetting assays. Clone P showed more than an 80% reduction in rosetting of EAC3d in comparison with H12 cells. In contrast, recognition of iC3b (EAiC3b) by each of the clones was similar to that by H12 cells. When dithiothreitol extracts of clone P and H12 were compared by immunoblot, both quantitative and qualitative differences in reactivities were observed with antibodies specific for the Candida C3d receptor and with antiserum from a patient with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borg M., Rüchel R. Expression of extracellular acid proteinase by proteolytic Candida spp. during experimental infection of oral mucosa. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):626–631. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.626-631.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buffo J., Herman M. A., Soll D. R. A characterization of pH-regulated dimorphism in Candida albicans. Mycopathologia. 1984 Mar 15;85(1-2):21–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00436698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Braun P. C. Adherence and receptor relationships of Candida albicans. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):1–20. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.1-20.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Cihlar R. L., Lee D. D., Hoberg K., Scheld W. M. Yeast adhesion in the pathogenesis of endocarditis due to Candida albicans: studies with adherence-negative mutants. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):710–715. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Linehan L., Wadsworth E., Sandberg A. L. Identification of C3d receptors on Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):252–258. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.252-258.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova M., Gil M. L., Cardeñoso L., Martinez J. P., Sentandreu R. Identification of wall-specific antigens synthesized during germ tube formation by Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):262–271. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.262-271.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Putative virulence factors of Candida albicans. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:187–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. E., Jr, Gaither T. A., O'Shea J. J., Rotrosen D., Lawley T. J., Wright S. A., Frank M. M., Green I. Expression of specific binding sites on Candida with functional and antigenic characteristics of human complement receptors. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3577–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigentler A., Schulz T. F., Larcher C., Breitwieser E. M., Myones B. L., Petzer A. L., Dierich M. P. C3bi-binding protein on Candida albicans: temperature-dependent expression and relationship to human complement receptor type 3. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):616–622. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.616-622.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukayama M., Wadsworth E., Calderone R. Expression of the C3d-binding protein (CR2) from Candida albicans during experimental candidiasis as measured by lymphoblastogenesis. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):8–12. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.8-12.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum M. A. Candida albicans antifungal-resistant strains: studies on adherence and other pathogenicity related characteristics. Mycoses. 1992 May-Jun;35(5-6):131–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1992.tb00833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore B. J., Retsinas E. M., Lorenz J. S., Hostetter M. K. An iC3b receptor on Candida albicans: structure, function, and correlates for pathogenicity. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):38–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson K. S., Vercellotti G. M., Bendel C. M., Hostetter M. K. Molecular mimicry in Candida albicans. Role of an integrin analogue in adhesion of the yeast to human endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1896–1902. doi: 10.1172/JCI115214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen B. W., Hazen K. C. Dynamic expression of cell surface hydrophobicity during initial yeast cell growth and before germ tube formation of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2521–2525. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2521-2525.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich F., Dierich M. P. Candida albicans and Candida stellatoidea, in contrast to other Candida species, bind iC3b and C3d but not C3b. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):598–600. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.598-600.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanbe T., Li R. K., Wadsworth E., Calderone R. A., Cutler J. E. Evidence for expression of the C3d receptor of Candida albicans in vitro and in vivo obtained by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1832–1838. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1832-1838.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. J., Calderone R. A., Cutler J. E., Kanabe T., Riesselman M. H., Robert R., Senet J. M., Annaix V., Bouali A., Mahaza C. Molecular basis of Candida albicans adhesion. J Med Vet Mycol. 1992;30 (Suppl 1):95–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A. Fungal adherence to the vascular compartment: a critical step in the pathogenesis of disseminated candidiasis. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):340–347. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Lehman D., Good C., Magee P. T. Genetic evidence for role of extracellular proteinase in virulence of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):571–575. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.571-575.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. L., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. An amino acid liquid synthetic medium for the development of mycelial and yeast forms of Candida Albicans. Sabouraudia. 1975 Jul;13(2):148–153. doi: 10.1080/00362177585190271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer N., Segal E., Cihlar R. L., Calderone R. A. Pathogenesis of vaginal candidiasis: studies with a mutant which has reduced ability to adhere in vitro. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Apr;24(2):127–131. doi: 10.1080/02681218680000191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linehan L., Wadsworth E., Calderone R. Candida albicans C3d receptor, isolated by using a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1981–1986. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1981-1986.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald F., Odds F. C. Virulence for mice of a proteinase-secreting strain of Candida albicans and a proteinase-deficient mutant. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Feb;129(2):431–438. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-2-431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattia E., Carruba G., Angiolella L., Cassone A. Induction of germ tube formation by N-acetyl-D-glucosamine in Candida albicans: uptake of inducer and germinative response. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):555–562. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.555-562.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., Moore M. D., Cooper N. R. Structure and function of the B-lymphocyte Epstein-Barr virus/C3d receptor. Adv Cancer Res. 1990;54:273–300. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60814-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Candida albicans proteinase as a virulence factor in the pathogenesis of Candida infections. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Dec;260(4):539–542. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Cockayne A., Hayward J., Abbott A. B. Effects of imidazole- and triazole-derivative antifungal compounds on the growth and morphological development of Candida albicans hyphae. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Oct;131(10):2581–2589. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-10-2581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Morphogenesis in Candida albicans. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;12(1):45–93. doi: 10.3109/10408418509104425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollert M. W., Wadsworth E., Calderone R. A. Reduced expression of the functionally active complement receptor for iC3b but not for C3d on an avirulent mutant of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):909–913. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.909-913.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryley J. F., Ryley N. G. Candida albicans--do mycelia matter? J Med Vet Mycol. 1990;28(3):225–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena A., Calderone R. Purification and characterization of the extracellular C3d-binding protein of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):309–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.309-314.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd M. G. Pathogenicity of morphological and auxotrophic mutants of Candida albicans in experimental infections. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):541–544. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.541-544.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smail E. H., Jones J. M. Demonstration and solubilization of antigens expressed primarily on the surfaces of Candida albicans germ tubes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.74-81.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosh F. D., Douglas L. J. Characterization of a fucoside-binding adhesin of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4734–4739. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4734-4739.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin G., Bouchara J. P., Robert R. Dynamic changes of the cell wall surface of Candida albicans associated with germination and adherence. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;50(2):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan W. L., Delga J. M., Wadsworth E., Walsh T. J., Kwon-Chung K. J., Calderone R., Lipke P. N. Isolation and characterization of cell surface mutants of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1552–1557. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1552-1557.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]