Abstract
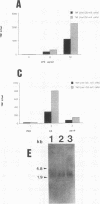
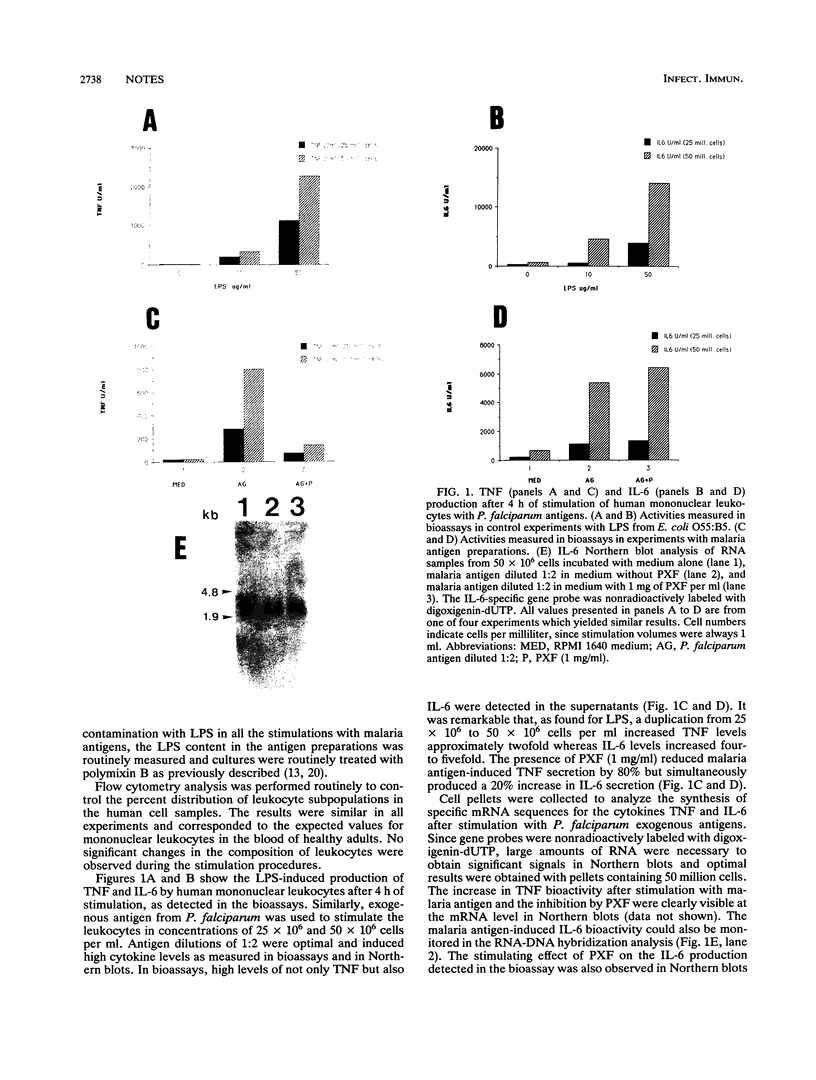
When pentoxifylline was present during stimulation of human mononuclear leukocytes with Plasmodium falciparum exogenous antigens, an increase in interleukin-6 production was observed simultaneously with a reduction of tumor necrosis factor secretion. Similar results were obtained in murine macrophages stimulated with P. vinckei antigens. This indicates the independence of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor secretion in response to malaria antigens.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarden L. A., De Groot E. R., Schaap O. L., Lansdorp P. M. Production of hybridoma growth factor by human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Oct;17(10):1411–1416. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. A., Taverne J., Karunaweera N. D., Mendis K. N., Kwiatkowski D., Playfair J. H. Serological relationship of tumor necrosis factor-inducing exoantigens of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1241–1243. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1241-1243.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. A., Taverne J., Playfair J. H. Soluble malarial antigens are toxic and induce the production of tumour necrosis factor in vivo. Immunology. 1989 Apr;66(4):600–605. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Cate R. L., Perlmutter A. P. Precise location of two promoters for the beta-lactamase gene of pBR322. S1 mapping of ribonucleic acid isolated from Escherichia coli or synthesized in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9205–9210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., MacMicking J. D., Gray K. M., Rockett K. A., Cowden W. B. Malaria mimicry with tumor necrosis factor. Contrasts between species of murine malaria and Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Pathol. 1992 Feb;140(2):325–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graninger W., Thalhammer F., Locker G. Pentoxifylline in cerebral malaria. J Infect Dis. 1991 Oct;164(4):829–829. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.4.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Fajardo L. F., Piguet P. F., Allet B., Lambert P. H., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) as an essential mediator in murine cerebral malaria. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1210–1212. doi: 10.1126/science.3306918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Frei K., Piguet P. F., Fontana A., Heremans H., Billiau A., Vassalli P., Lambert P. H. Interleukin 6 production in experimental cerebral malaria: modulation by anticytokine antibodies and possible role in hypergammaglobulinemia. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1505–1508. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Taylor T. E., Molyneux M. E., Wirima J. J., Vassalli P., Hommel M., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and disease severity in children with falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 15;320(24):1586–1591. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906153202404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern P., Hemmer C. J., Van Damme J., Gruss H. J., Dietrich M. Elevated tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 serum levels as markers for complicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Am J Med. 1989 Aug;87(2):139–143. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80688-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremsner P. G., Feldmeier H., Zotter G. M., Jansen-Rosseck R., Graninger W., Rocha R. M., Bienzle U. Immunological alterations in uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Relationship between parasitaemia and indicators of macrophage activation. Acta Trop. 1989 Oct;46(5-6):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0001-706x(89)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremsner P. G., Grundmann H., Neifer S., Sliwa K., Sahlmüller G., Hegenscheid B., Bienzle U. Pentoxifylline prevents murine cerebral malaria. J Infect Dis. 1991 Sep;164(3):605–608. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.3.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neifer S., Kremsner P. G., Bienzle U. Application of anti-TNF to Plasmodium vinckei-infected mice is followed by an increase of parasitaemia. Acta Trop. 1989 Jul;46(4):273–275. doi: 10.1016/0001-706x(89)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schandené L., Vandenbussche P., Crusiaux A., Alègre M. L., Abramowicz D., Dupont E., Content J., Goldman M. Differential effects of pentoxifylline on the production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) by monocytes and T cells. Immunology. 1992 May;76(1):30–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Waage A., Aarden L., Espevik T. Endotoxin, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1 induce interleukin 6 production in vivo. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Dec;53(3):488–498. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliwa K., Grundmann H. J., Neifer S., Chaves M. F., Sahlmüller G., Blitstein-Willinger E., Bienzle U., Kremsner P. G. Prevention of murine cerebral malaria by a stable prostacyclin analog. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3846–3848. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3846-3848.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Remick D. G., Ward P. A., Spengler R. N., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Larrick J., Kunkel S. L. Cellular and molecular regulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by pentoxifylline. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 30;155(3):1230–1236. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81271-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabone M. D., Muanza K., Lyagoubi M., Jardel C., Pied S., Amedee-Manesme O., Grau G. E., Mazier D. The role of interleukin-6 in vitamin A deficiency during Plasmodium falciparum malaria and possible consequences for vitamin A supplementation. Immunology. 1992 Mar;75(3):553–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverne J., Bate C. A., Kwiatkowski D., Jakobsen P. H., Playfair J. H. Two soluble antigens of Plasmodium falciparum induce tumor necrosis factor release from macrophages. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2923–2928. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2923-2928.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverne J., Bate C. A., Playfair J. H. Malaria exoantigens induce TNF, are toxic and are blocked by T-independent antibody. Immunol Lett. 1990 Aug;25(1-3):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverne J., Bate C. A., Sarkar D. A., Meager A., Rook G. A., Playfair J. H. Human and murine macrophages produce TNF in response to soluble antigens of Plasmodium falciparum. Parasite Immunol. 1990 Jan;12(1):33–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1990.tb00934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Sørensen M., Størdal B. Differential effect of oxpentifylline on tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-6 production. Lancet. 1990 Mar 3;335(8688):543–543. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90779-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel P., Wolter D. T., Schönharting M. M., Schade U. F. Oxpentifylline in endotoxaemia. Lancet. 1989 Dec 23;2(8678-8679):1474–1477. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92929-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]