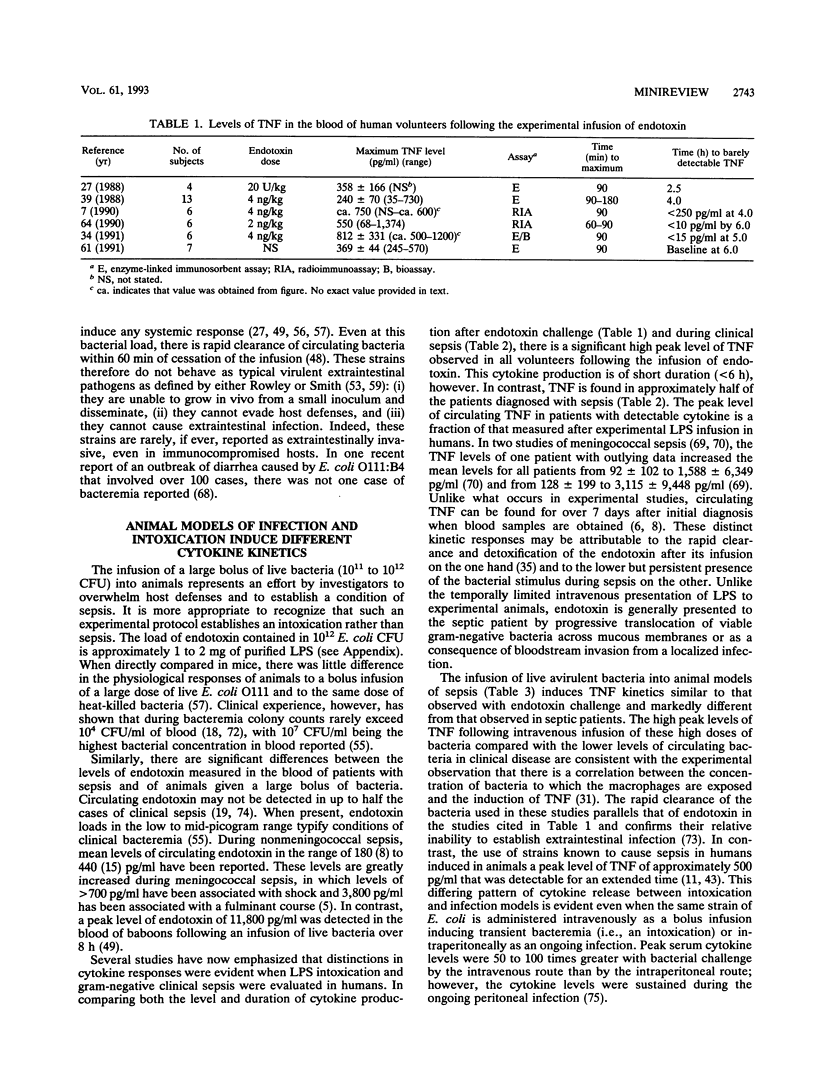
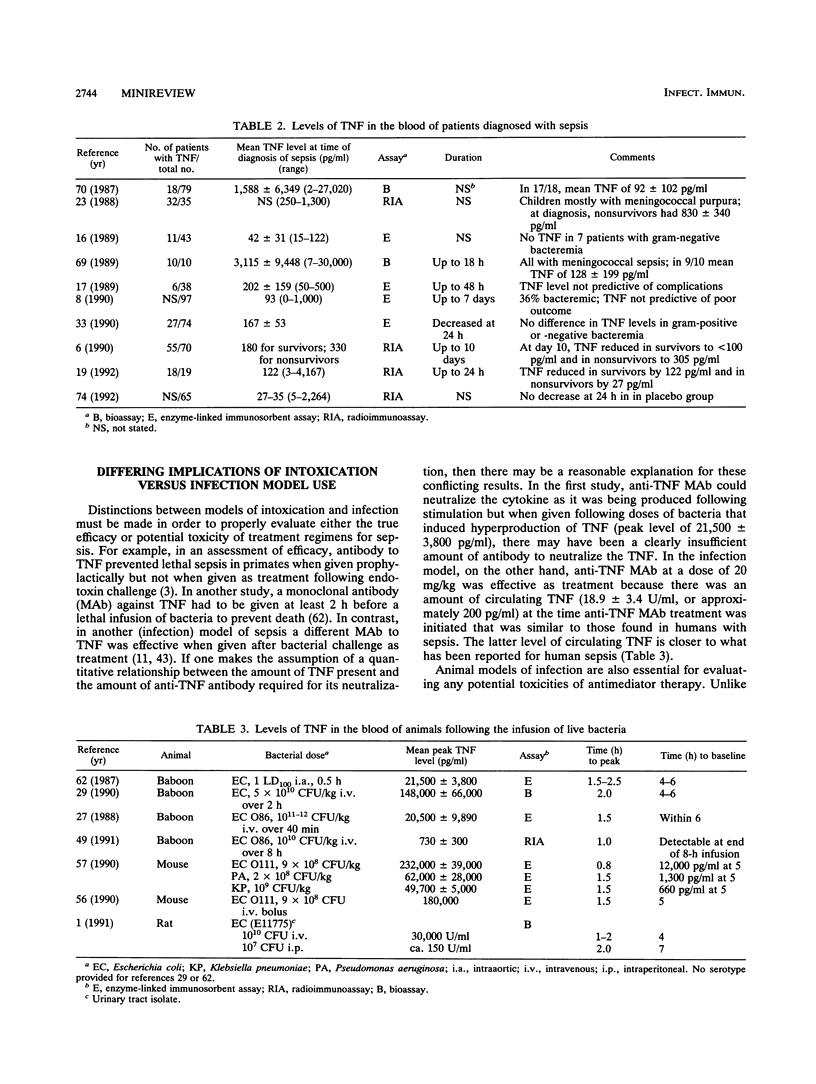
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagby G. J., Plessala K. J., Wilson L. A., Thompson J. J., Nelson S. Divergent efficacy of antibody to tumor necrosis factor-alpha in intravascular and peritonitis models of sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):83–88. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin W. H., Jr, Posey B. S., Briles D. E. Effects of in vitro growth phase on the pathogenesis of Salmonella typhimurium in mice. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 May;132(5):1283–1295. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-5-1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C., Fisher C. J., Jr, Clemmer T. P., Slotman G. J., Metz C. A., Balk R. A. A controlled clinical trial of high-dose methylprednisolone in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 10;317(11):653–658. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709103171101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Kierulf P., Gaustad P., Skulberg A., Bruun J. N., Halvorsen S., Sørensen E. Plasma endotoxin as a predictor of multiple organ failure and death in systemic meningococcal disease. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):195–204. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra T., Baumgartner J. D., Grau G. E., Wu M. M., Lambert P. H., Schellekens J., Verhoef J., Glauser M. P. Prognostic values of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin, interleukin-1, interferon-alpha, and interferon-gamma in the serum of patients with septic shock. Swiss-Dutch J5 Immunoglobulin Study Group. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):982–987. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Tompkins R. G., Gelfand J. A., Michie H. R., Stanford G. G., van der Meer J. W., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Corsetti J., Chernow B. Circulating interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor in septic shock and experimental endotoxin fever. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):79–84. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Levin B. R., Orskov I., Orskov F., Svanborg Eden C., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity in relation to serotype in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):407–413. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.407-413.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Gemski P., Sadoff J. C., Orskov F., Orskov I. The importance of the K1 capsule in invasive infections caused by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):184–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Opal S. M., Palardy J. E., Bodmer M. W., Sadoff J. C. The efficacy of combination immunotherapy in experimental Pseudomonas sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;167(1):112–118. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Kelly N., Bernton E., Gemski P. Pretreatment with recombinant murine tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin and murine interleukin 1 alpha protects mice from lethal bacterial infection. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2021–2027. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Zollinger W., Mandrell R., Gemski P., Sadoff J. Evaluation of immunotherapeutic approaches for the potential treatment of infections caused by K1-positive Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):68–76. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F. Recombinant murine interleukin-1 alpha enhancement of nonspecific antibacterial resistance. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2061–2065. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2061-2065.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner R. L., Elin R. J., Hosseini J. M., Wesley R. A., Reilly J. M., Parillo J. E. Endotoxemia in human septic shock. Chest. 1991 Jan;99(1):169–175. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.1.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debets J. M., Kampmeijer R., van der Linden M. P., Buurman W. A., van der Linden C. J. Plasma tumor necrosis factor and mortality in critically ill septic patients. Crit Care Med. 1989 Jun;17(6):489–494. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198906000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzman D. E., Fischer G. W., Schoenknecht F. D. Neonatal Escherichia coli septicemia--bacterial counts in blood. J Pediatr. 1974 Jul;85(1):128–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80308-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dofferhoff A. S., Bom V. J., de Vries-Hospers H. G., van Ingen J., vd Meer J., Hazenberg B. P., Mulder P. O., Weits J. Patterns of cytokines, plasma endotoxin, plasminogen activator inhibitor, and acute-phase proteins during the treatment of severe sepsis in humans. Crit Care Med. 1992 Feb;20(2):185–192. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199202000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON W. W., JUNE R. C. Experiments on feeding adult volunteers with Escherichia coli 111, B4, a coliform organism associated with infant diarrhea. Am J Hyg. 1952 Mar;55(2):155–169. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Regulation by membrane sialic acid of beta1H-dependent decay-dissociation of amplification C3 convertase of the alternative complement pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1971–1975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Tracey K. J., Moldawer L. L., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. B., Kenney J. S., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Allison A. C., Lowry S. F. Antibodies to cachectin/tumor necrosis factor reduce interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 6 appearance during lethal bacteremia. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1627–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardin E., Grau G. E., Dayer J. M., Roux-Lombard P., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in the serum of children with severe infectious purpura. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 18;319(7):397–400. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808183190703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Howard C. J. The sensitivity to complement of strains of Escherichia coli related to their K antigens. Immunology. 1970 Mar;18(3):331–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenman R. L., Schein R. M., Martin M. A., Wenzel R. P., MacIntyre N. R., Emmanuel G., Chmel H., Kohler R. B., McCarthy M., Plouffe J. A controlled clinical trial of E5 murine monoclonal IgM antibody to endotoxin in the treatment of gram-negative sepsis. The XOMA Sepsis Study Group. JAMA. 1991 Aug 28;266(8):1097–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. J., Rowe B. Escherichia coli diarrhoea. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Dec;95(3):531–550. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse D. G., Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Manogue K. R., Palladino M. A., Jr, Cerami A., Shires G. T., Lowry S. F. Cytokine appearance in human endotoxemia and primate bacteremia. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1988 Feb;166(2):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw L. B., Benjamin B., Holmes D. D., Beller B., Archer L. T., Coalson J. J., Whitsett T. Responses of the baboon to live Escherichia coli organisms and endotoxin. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1977 Jul;145(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw L. B., Tekamp-Olson P., Chang A. C., Lee P. A., Taylor F. B., Jr, Murray C. K., Peer G. T., Emerson T. E., Jr, Passey R. B., Kuo G. C. Survival of primates in LD100 septic shock following therapy with antibody to tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha). Circ Shock. 1990 Mar;30(3):279–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Glynn A. A. The virulence for mice of strains of Escherichia coli related to the effects of K antigens on their resistance to phagocytosis and killing by complement. Immunology. 1971 May;20(5):767–777. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly N. M., Young L., Cross A. S. Differential induction of tumor necrosis factor by bacteria expressing rough and smooth lipopolysaccharide phenotypes. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4491–4496. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4491-4496.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger B. E., Craven D. E., Carling P. C., McCabe W. R. Gram-negative bacteremia. III. Reassessment of etiology, epidemiology and ecology in 612 patients. Am J Med. 1980 Mar;68(3):332–343. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H. Bactericidal activity of normal serum against bacterial cultures. II. Activity against Eschericha coli strains. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Mar;103:632–636. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. D., Marks C. B., Luce J. M., Montgomery A. B., Turner J., Metz C. A., Murray J. F. Plasma tumor necrosis factor in patients with septic shock. Mortality rate, incidence of adult respiratory distress syndrome, and effects of methylprednisolone administration. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Jan;141(1):94–97. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martich G. D., Danner R. L., Ceska M., Suffredini A. F. Detection of interleukin 8 and tumor necrosis factor in normal humans after intravenous endotoxin: the effect of antiinflammatory agents. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):1021–1024. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Ulevitch R. J. The clearance, tissue distribution, and cellular localization of intravenously injected lipopolysaccharide in rabbits. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2133–2143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R., Kaijser B., Olling S., Uwaydah M., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli in bacteremia: K and O antigens and serum sensitivity of strains from adults and neonates. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):33–41. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Sarff L. D., Glode M. P., Mize S. G., Schiffer M. S., Robbins J. B., Gotschlich E. C., Orskov I., Orskov F. Relation between Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide antigen and clinical outcome in neonatal meningitis. Lancet. 1974 Aug 3;2(7875):246–250. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91413-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medearis D. N., Jr, Camitta B. M., Heath E. C. Cell wall composition and virulence in Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):399–414. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medearis D. N., Jr, Kenny J. F. Observations concerning the pathogenesis of E. coli infections in mice. J Immunol. 1968 Sep;101(3):534–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Manogue K. R., Spriggs D. R., Revhaug A., O'Dwyer S., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Wolff S. M., Wilmore D. W. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1481–1486. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel L. H., Larsen L. J. The sensitivity of smooth and rough gram-negative bacteria to the immune bactericidal reaction. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jan;133(1):345–348. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kato K. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is essential to host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2563–2569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2563-2569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opal S. M., Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Collins H. H., Kelly N. M., Victor G. H., Palardy J. E., Bodmer M. W. Efficacy of antilipopolysaccharide and anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibodies in a neutropenic rat model of Pseudomonas sepsis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):885–890. doi: 10.1172/JCI115390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I. Escherichia coli O:H serotypes isolated from human blood. Prevalence of the K1 antigen with technical details of O and H antigenic determination. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1975 Dec;83(6):595–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F. Escherichia coli in extra-intestinal infections. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Dec;95(3):551–575. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porat R., Mosseri R., Kaplan E., Johns M. A., Shibolet S. Distribution of polysaccharide side chains of lipopolysaccharide determine resistance of Escherichia coli to the bactericidal activity of serum. J Infect Dis. 1992 May;165(5):953–956. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.5.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel J., Schloerb P. R., Furtado D. Pathophysiologic alterations during bacterial infusions for the study of bacteremic shock. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1975 Nov;141(5):683–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROANTREE R. J., PAPPAS N. C. The survival of strains of enteric bacilli in the blood stream as related to their sensitivity to the bactericidal effect of serum. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39:82–88. doi: 10.1172/JCI104031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D. The virulence of strains of Bacterium coli for mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Dec;35(6):528–538. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redl H., Schlag G., Bahrami S., Schade U., Ceska M., Stütz P. Plasma neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin-8 and neutrophil elastase in a primate bacteremia model. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):383–388. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J., Rantz L. A. A STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP OF THE NORMAL BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY OF HUMAN SERUM TO BACTERIAL INFECTION. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39(1):72–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI104029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J. Salmonella O antigens and virulence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:443–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. Sensitivity of rough gram-negative bacteria to the bactericidal action of serum. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1647–1650. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1647-1650.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenep J. L., Flynn P. M., Barrett F. F., Stidham G. L., Westenkirchner D. F. Serial quantitation of endotoxemia and bacteremia during therapy for gram-negative bacterial sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):565–568. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva A. T., Appelmelk B. J., Buurman W. A., Bayston K. F., Cohen J. Monoclonal antibody to endotoxin core protects mice from Escherichia coli sepsis by a mechanism independent of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):454–459. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva A. T., Bayston K. F., Cohen J. Prophylactic and therapeutic effects of a monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor-alpha in experimental gram-negative shock. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):421–427. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Pathogenicity and the microbe in vivo. The 1989 Fred Griffith Review Lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Mar;136(3):377–393. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-3-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinas G. A., Bloesch D., Keller U., Zimmerli W., Cammisuli S. Pretreatment with ibuprofen augments circulating tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and elastase during acute endotoxinemia. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):89–95. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen C., Cross A., Byrne W. R., Zollinger W. Quantitative relationship between capsular content and killing of K1-encapsulated Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2723–2730. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2723-2730.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljanen M. K., Peltola T., Junnila S. Y., Olkkonen L., Järvinen H., Kuistila M., Huovinen P. Outbreak of diarrhoea due to Escherichia coli O111:B4 in schoolchildren and adults: association of Vi antigen-like reactivity. Lancet. 1990 Oct 6;336(8719):831–834. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92337-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Brandtzaeg P., Halstensen A., Kierulf P., Espevik T. The complex pattern of cytokines in serum from patients with meningococcal septic shock. Association between interleukin 6, interleukin 1, and fatal outcome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Espevik T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels B. C., Wells M. T., Gaffin S. L., Brock-Utne J. G., Gathiram P., Hinshaw L. B. Plasma endotoxin concentration in healthy primates and during E. coli-induced shock. Crit Care Med. 1988 Jun;16(6):601–605. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198806000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wortel C. H., von der Möhlen M. A., van Deventer S. J., Sprung C. L., Jastremski M., Lubbers M. J., Smith C. R., Allen I. E., ten Cate J. W. Effectiveness of a human monoclonal anti-endotoxin antibody (HA-1A) in gram-negative sepsis: relationship to endotoxin and cytokine levels. J Infect Dis. 1992 Dec;166(6):1367–1374. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.6.1367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti G., Heumann D., Gérain J., Kohler J., Abbet P., Barras C., Lucas R., Glauser M. P., Baumgartner J. D. Cytokine production after intravenous or peritoneal gram-negative bacterial challenge in mice. Comparative protective efficacy of antibodies to tumor necrosis factor-alpha and to lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1890–1897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., Fisher C. J., Jr, Sprung C. L., Straube R. C., Sadoff J. C., Foulke G. E., Wortel C. H., Fink M. P., Dellinger R. P., Teng N. N. Treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and septic shock with HA-1A human monoclonal antibody against endotoxin. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The HA-1A Sepsis Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1991 Feb 14;324(7):429–436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102143240701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groote M. A., Martin M. A., Densen P., Pfaller M. A., Wenzel R. P. Plasma tumor necrosis factor levels in patients with presumed sepsis. Results in those treated with antilipid A antibody vs placebo. JAMA. 1989 Jul 14;262(2):249–251. doi: 10.1001/jama.262.2.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deventer S. J., Buller H. R., ten Cate J. W., Sturk A., Pauw W. Endotoxaemia: an early predictor of septicaemia in febrile patients. Lancet. 1988 Mar 19;1(8586):605–609. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91412-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deventer S. J., Büller H. R., ten Cate J. W., Aarden L. A., Hack C. E., Sturk A. Experimental endotoxemia in humans: analysis of cytokine release and coagulation, fibrinolytic, and complement pathways. Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2520–2526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



