Abstract
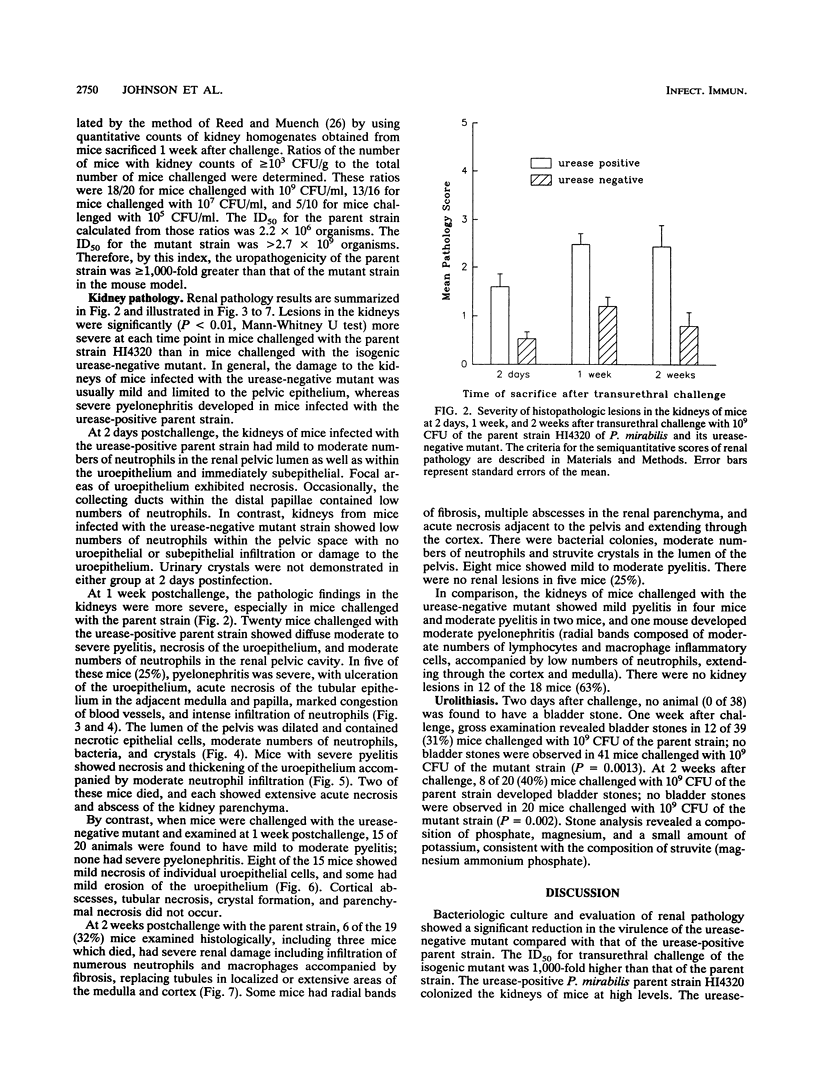
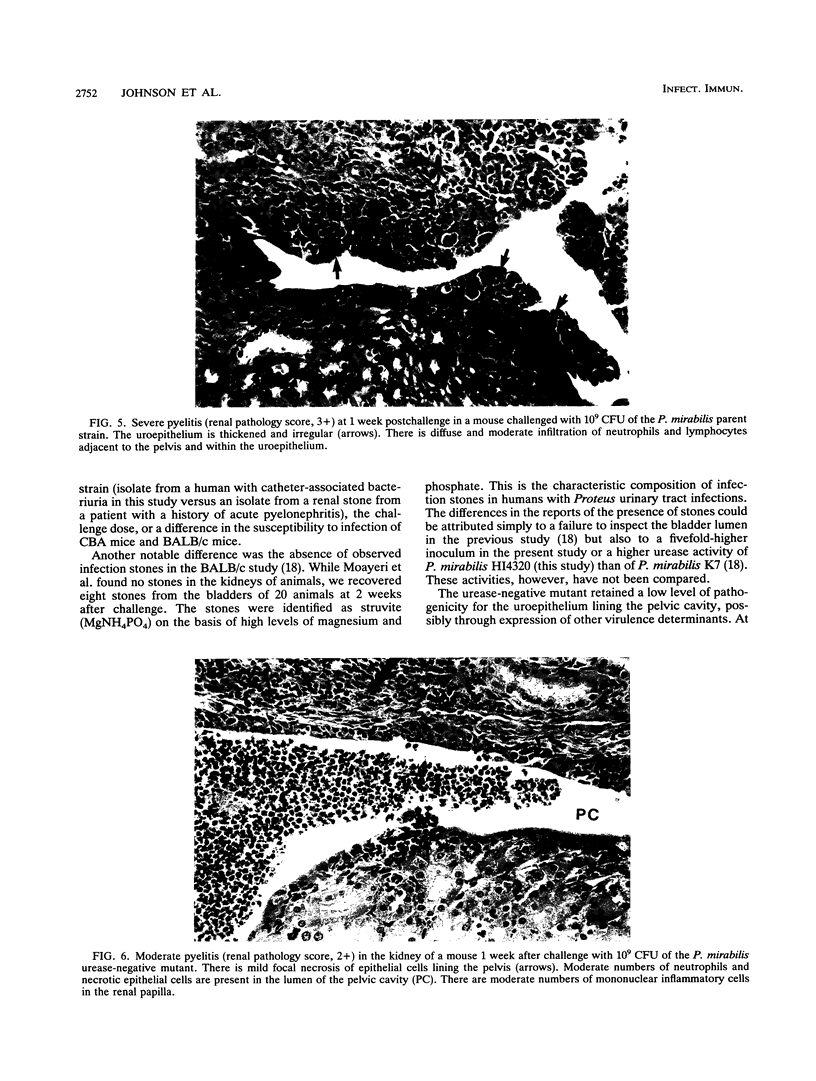
Proteus mirabilis, a significant cause of bacteriuria and acute pyelonephritis in humans, produces urease. This high-molecular-weight, multimeric, cytoplasmic enzyme hydrolyzes urea to ammonia and carbon dioxide. To assess the role of urease in colonization, urolithiasis, and acute pyelonephritis in an animal model of ascending urinary tract infection, we compared a uropathogenic strain of P. mirabilis with its isogenic urease-negative mutant, containing an insertion mutation within ureC, the gene encoding the large subunit of the enzyme. Mice challenged transurethrally with the parent strain developed significant bacteriuria and urinary stones. The urease-negative mutant had a 50% infective dose of 2.7 x 10(9) CFU, a value more than 1,000-fold greater than that of the parent strain (2.2 x 10(6) CFU). The urease-positive parent strain reached significantly higher concentrations and persisted significantly longer in the bladder and kidney than did the mutant. Indeed, in the kidney, the parent strain increased in concentration while the mutant concentration fell so that, by 1 week, the parent strain concentration was 10(6) times that of the mutant. Similarly, the urease-positive parent produced significantly more severe renal pathology than the mutant. The initial abnormalities were in and around the pelvis and consisted of acute inflammation and epithelial necrosis. By 1 week, pyelitis was more severe, crystals were seen in the pelvis, and acute pyelonephritis, with acute interstitial inflammation, tubular epithelial cell necrosis, and in some cases abscesses, had developed. By 2 weeks, more animals had renal abscesses and radial bands of fibrosis. We conclude that the urease of P. mirabilis is a critical virulence determinant for colonization, urolithiasis, and severe acute pyelonephritis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson M., Medalia O., Griffel B. Prevention of ascending pyelonephritis in mice by urease inhibitors. Nephron. 1974;12(2):94–104. doi: 10.1159/000180271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I., SHAPIRO A. P., SIEMIENSKI J. Hematogenous pyelonephritis in rats. III. Relationship of bacterial species to the pathogenesis of acute pyeionephritis. J Bacteriol. 1959 Mar;77(3):270–280. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.3.270-280.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I., SIEMIENSKI J. Role of bacterial urease in experimental pyelonephritis. J Bacteriol. 1960 Aug;80:171–179. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.2.171-179.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas R., Erskine D., Flaherty D. Transposon mutagenesis in Proteus mirabilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6289–6293. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6289-6293.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatermann S., Marre R. Cloning and expression of Staphylococcus saprophyticus urease gene sequences in Staphylococcus carnosus and contribution of the enzyme to virulence. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):2998–3002. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.2998-3002.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith D. P., Musher D. M., Itin C. Urease. The primary cause of infection-induced urinary stones. Invest Urol. 1976 Mar;13(5):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Engberg I., Freter R., Lam J., Olling S., Svanborg Edén C. Ascending, unobstructed urinary tract infection in mice caused by pyelonephritogenic Escherichia coli of human origin. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):273–283. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.273-283.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Lockatell C. V., Hall-Craggs M., Warren J. W. Mouse models of short- and long-term foreign body in the urinary bladder: analogies to the bladder segment of urinary catheters. Lab Anim Sci. 1991 Oct;41(5):451–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Lockatell C. V., Hall-Craigs M., Mobley H. L., Warren J. W. Uropathogenicity in rats and mice of Providencia stuartii from long-term catheterized patients. J Urol. 1987 Sep;138(3):632–635. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)43287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Lockatell C. V., Johnson D. E., Warren J. W., Mobley H. L. Construction of a urease-negative mutant of Proteus mirabilis: analysis of virulence in a mouse model of ascending urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1120–1123. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1120-1123.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Mobley H. L. Genetic and biochemical diversity of ureases of Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella species isolated from urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2198–2203. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2198-2203.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Mobley H. L. Proteus mirabilis urease: genetic organization, regulation, and expression of structural genes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3342–3349. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3342-3349.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLaren D. M. The significance of urease in proteus pyelonephritis: a bacteriological study. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):45–56. doi: 10.1002/path.1700960106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLaren D. M. The significance of urease in proteus pyelonephritis: a histological and biochemical study. J Pathol. 1969 Jan;97(1):43–49. doi: 10.1002/path.1710970107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclaren D. M. The influence of acetohydroxamic acid on experimental proteus pyelonephritis. Invest Urol. 1974 Sep;12(2):146–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moayeri N., Collins C. M., O'Hanley P. Efficacy of a Proteus mirabilis outer membrane protein vaccine in preventing experimental Proteus pyelonephritis in a BALB/c mouse model. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3778–3786. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3778-3786.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Chippendale G. R. Hemagglutinin, urease, and hemolysin production by Proteus mirabilis from clinical sources. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):525–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Chippendale G. R., Swihart K. G., Welch R. A. Cytotoxicity of the HpmA hemolysin and urease of Proteus mirabilis and Proteus vulgaris against cultured human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2036–2042. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2036-2042.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Green D. M., Trifillis A. L., Johnson D. E., Chippendale G. R., Lockatell C. V., Jones B. D., Warren J. W. Pyelonephritogenic Escherichia coli and killing of cultured human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells: role of hemolysin in some strains. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1281–1289. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1281-1289.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Hausinger R. P. Microbial ureases: significance, regulation, and molecular characterization. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):85–108. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.85-108.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Warren J. W. Urease-positive bacteriuria and obstruction of long-term urinary catheters. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2216–2217. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2216-2217.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Griffith D. P., Yawn D., Rossen R. D. Role of urease in pyelonephritis resulting from urinary tract infection with Proteus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):177–181. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemoy N. J., Staney T. A. Surgical, bacteriological, and biochemical management of "infection stones". JAMA. 1971 Mar 1;215(9):1470–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J. Host-parasite interaction in the rat renal pelvis: a possible role for pili in the pathogenesis of pyelonephritis. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1696–1711. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi H., Takayama H., Konishi T., Tomoyoshi T. Scanning electron microscopy detects bacteria within infection stones. J Urol. 1984 Jul;132(1):67–69. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)49466-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. W., Damron D., Tenney J. H., Hoopes J. M., Deforge B., Muncie H. L., Jr Fever, bacteremia, and death as complications of bacteriuria in women with long-term urethral catheters. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1151–1158. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







