Abstract
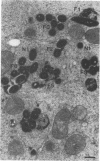
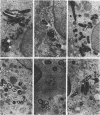
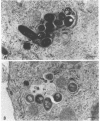
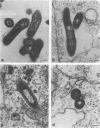
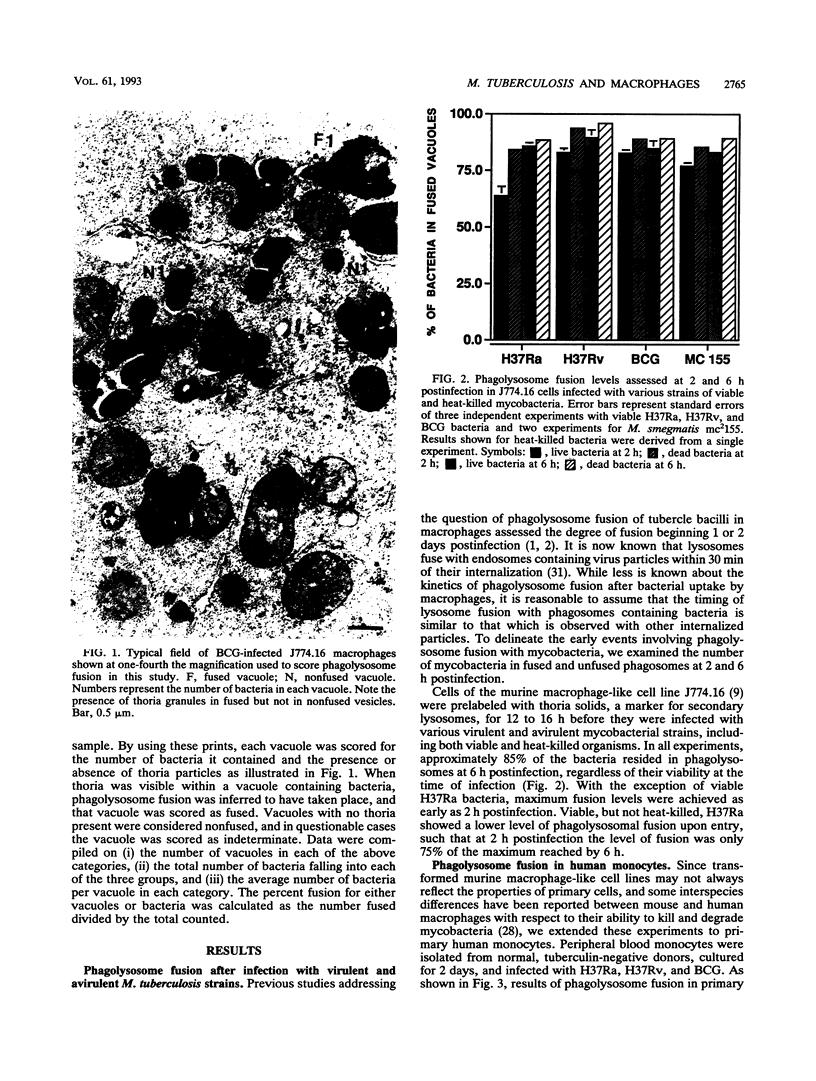
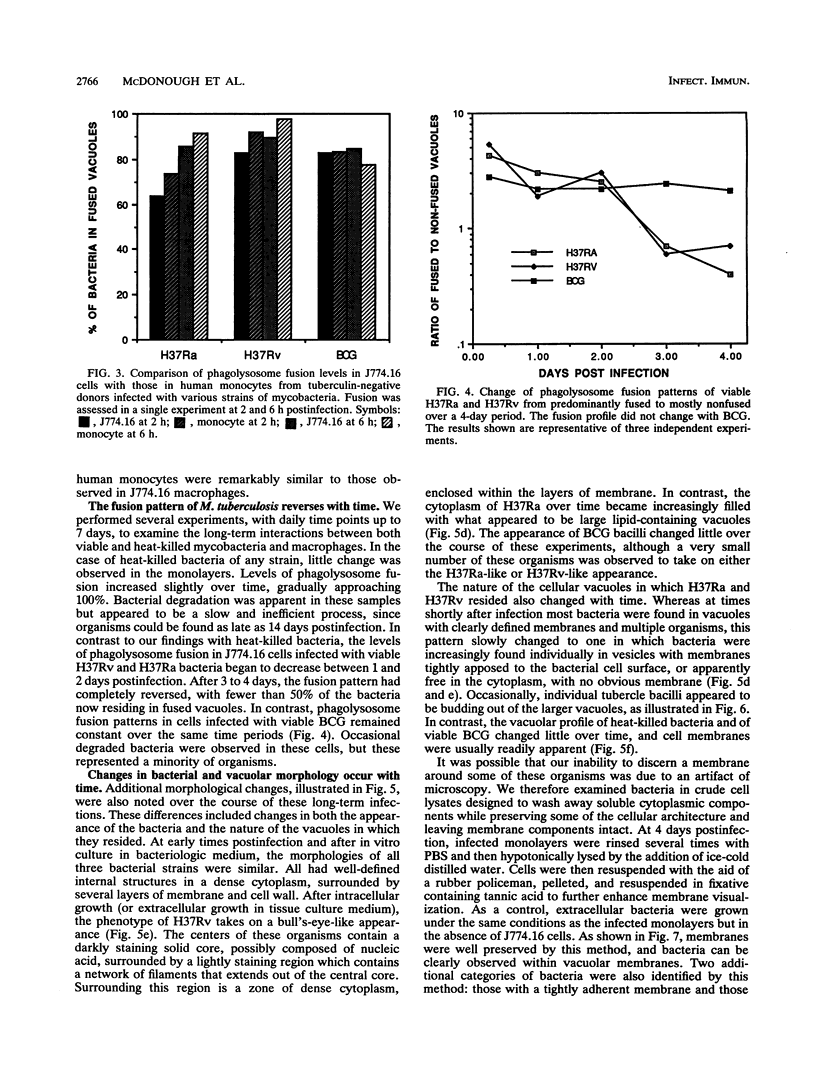
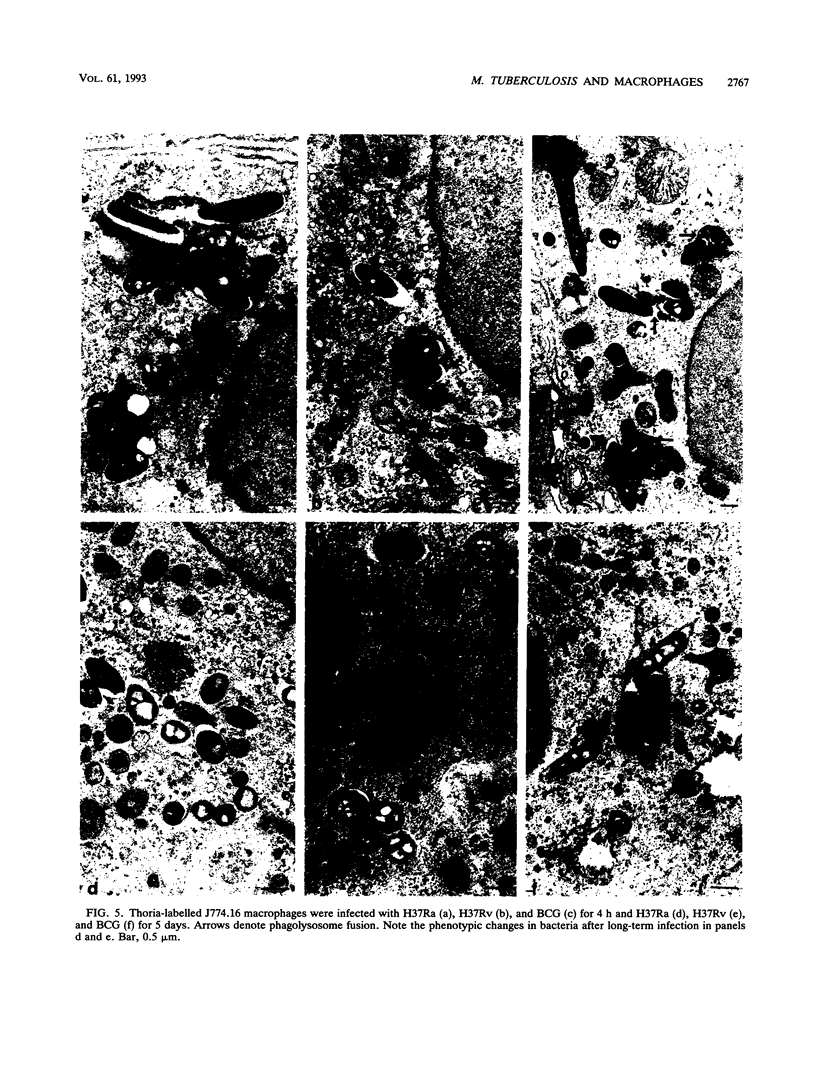
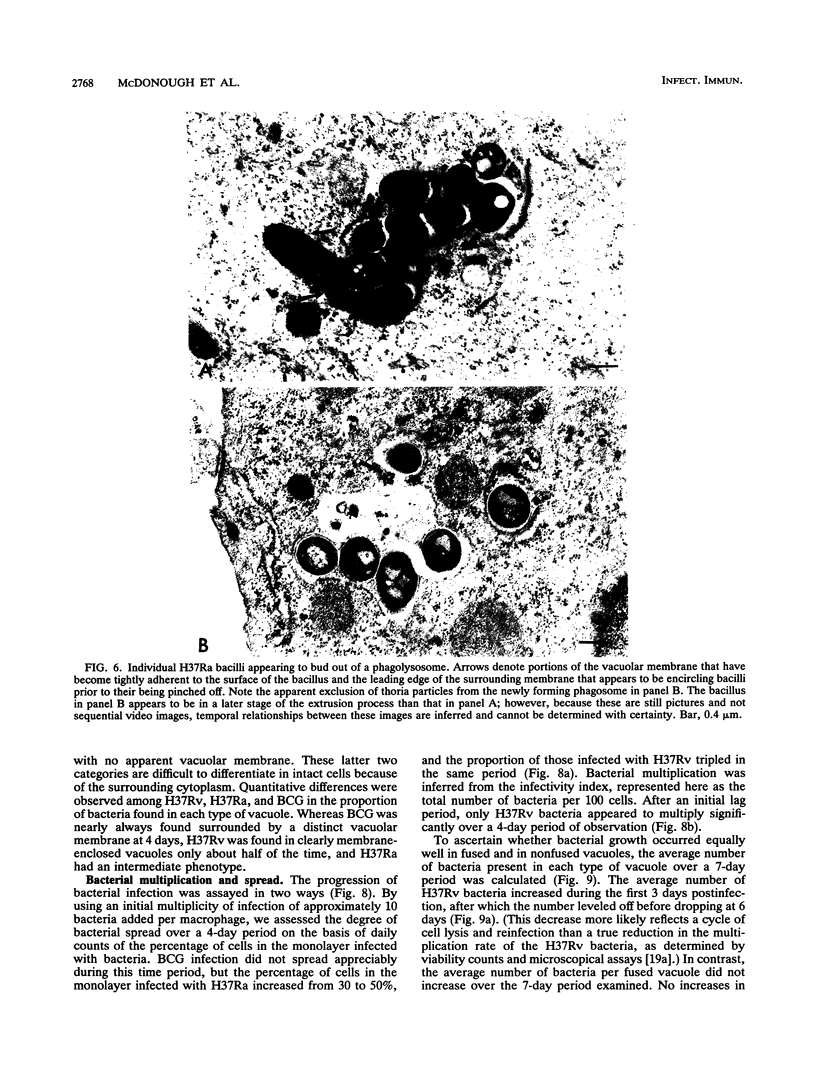
Central to understanding the pathogenesis of tuberculosis is the interaction between the pathogen and mononuclear phagocytes. A key question about that interaction is whether Mycobacterium tuberculosis exerts an effect on phagolysosome fusion. We have reexamined the dynamics of phagolysosome fusion and its effect on intracellular bacterial replication in M. tuberculosis-infected macrophages by performing an extensive study at the electron microscopic level. Thoria-labelled murine and human macrophages were infected with a virulent (H37Rv) or avirulent (H37Ra) strain of M. tuberculosis or with Mycobacterium bovis BCG vaccine for times ranging from 2 h to 7 days. In all cases, by 2 h postinfection, approximately 85% of the bacteria clearly resided in fused vacuoles. However, at 4 days postinfection, fusion levels for viable H37Rv and H37Ra were reduced by half, whereas the fusion profiles of BCG and of heat-killed H37Rv and H37Ra were unchanged. A comparison of the numbers of bacteria per fused and nonfused vacuoles suggests both a net transfer of bacteria out of fused vacuoles and preferential bacterial multiplication in nonfused vacuoles. H37Rv and H37Ra appeared to bud from the phagolysosomes into tightly apposed membrane vesicles that did not fuse with secondary lysosomes. In some cases, no such membrane was seen and the bacteria appeared to be free in the cytoplasm. Only viable H37Rv showed a significant increase in bacterial counts during the course of infection. Thus, both of the attenuated strains we examined differed from the virulent strain H37Rv in their abilities to replicate successfully within macrophages, but each diverged from H37Rv at a different point in the process. Viable tubercle bacilli H37Rv and H37Ra had the capacity to escape from fused vesicles as the infection progressed; BCG did not. After extrusion from the phagolysosome, H37Rv, but not H37Ra, was able to multiply. These results suggest a novel mechanism by which virulent M. tuberculosis eludes the microbicidal mechanisms of macrophages by escaping from fused phagolysosomes into nonfused vesicles or the cytoplasm.
Full text
PDF

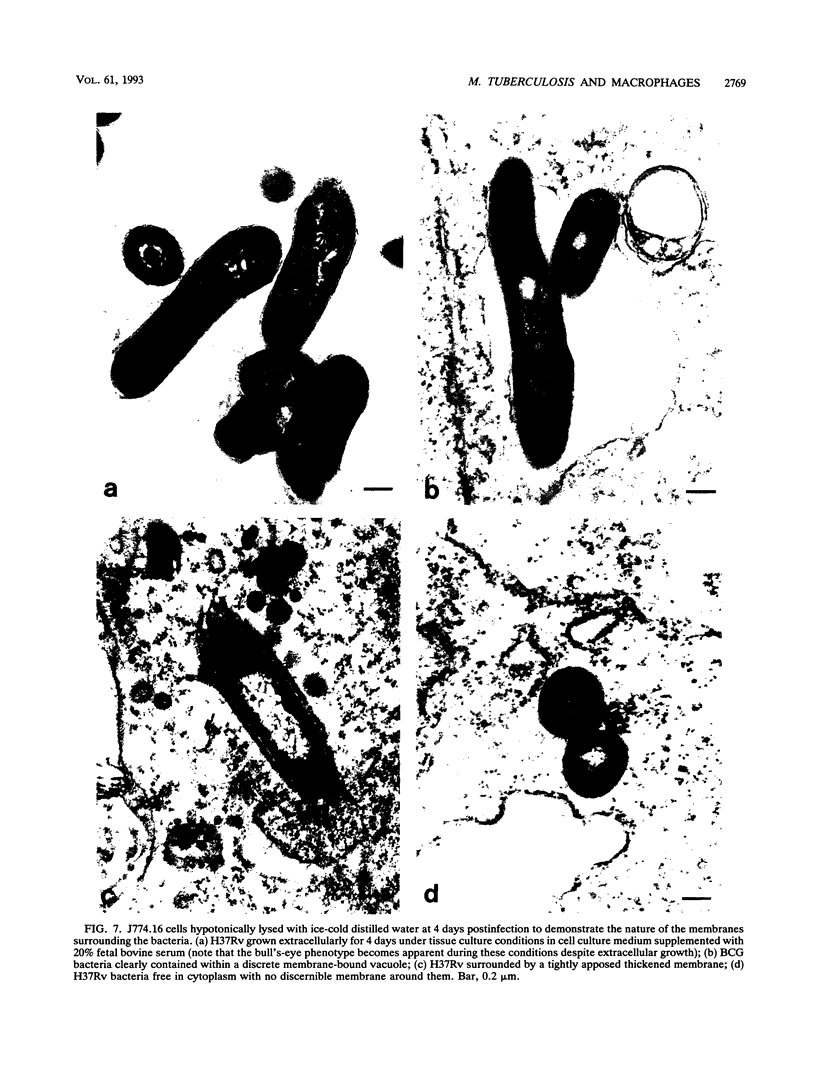
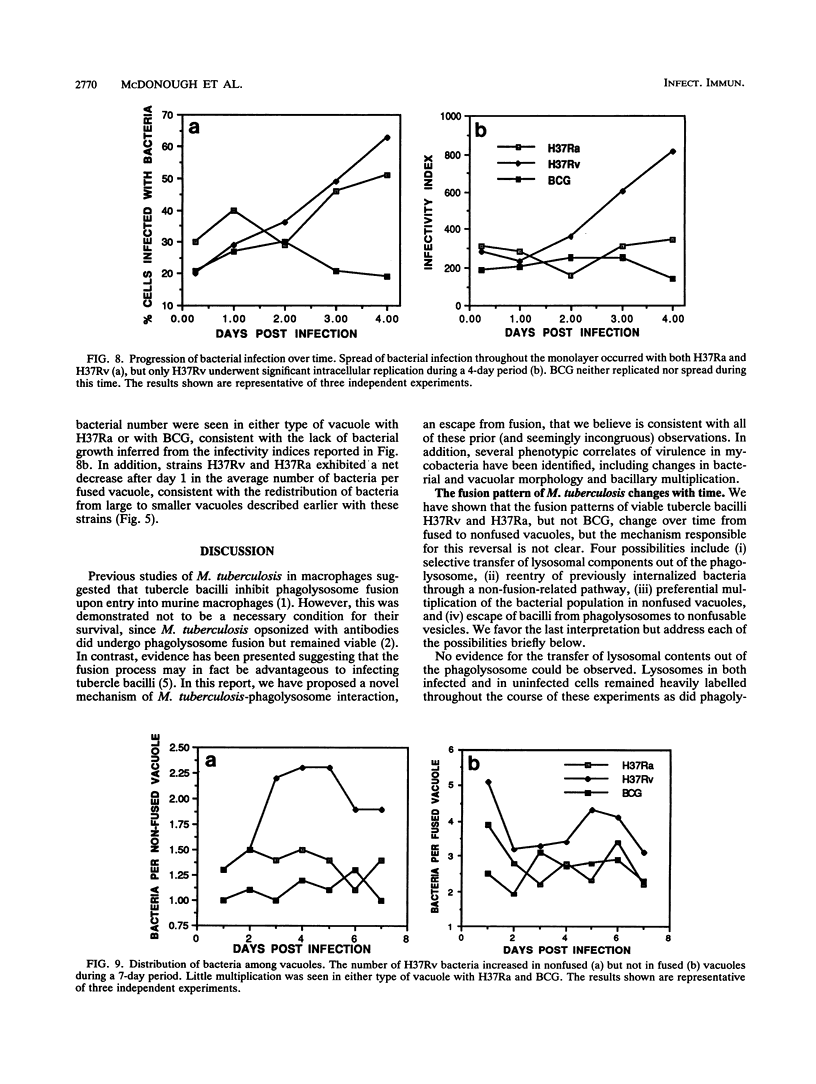



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A., Hart P. D. Phagosome-lysosome interactions in cultured macrophages infected with virulent tubercle bacilli. Reversal of the usual nonfusion pattern and observations on bacterial survival. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):1–16. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. A., Hart P. D. Response of cultured macrophages to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with observations on fusion of lysosomes with phagosomes. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):713–740. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry C. E., 3rd, Hayes S. F., Hackstadt T. Nucleoid condensation in Escherichia coli that express a chlamydial histone homolog. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):377–379. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Murray C. J. Tuberculosis: commentary on a reemergent killer. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1055–1064. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. A., Draper P., Hart P. D. Mycobacteria and lysosomes: a paradox. Nature. 1969 Feb 15;221(5181):658–660. doi: 10.1038/221658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canetti G. Present aspects of bacterial resistance in tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Nov;92(5):687–703. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.92.5.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J. Studies of antituberculosis chemotherapy with an in vitro model of human tuberculosis. Semin Respir Infect. 1986 Dec;1(4):262–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damiani G., Kiyotaki C., Soeller W., Sasada M., Peisach J., Bloom B. R. Macrophage variants in oxygen metabolism. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):808–822. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Libero G., Flesch I., Kaufmann S. H. Mycobacteria-reactive Lyt-2+ T cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):59–66. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douvas G. S., Berger E. M., Repine J. E., Crowle A. J. Natural mycobacteriostatic activity in human monocyte-derived adherent cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jul;134(1):44–48. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields P. I., Groisman E. A., Heffron F. A Salmonella locus that controls resistance to microbicidal proteins from phagocytic cells. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1059–1062. doi: 10.1126/science.2646710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn J. L., Goldstein M. M., Triebold K. J., Koller B., Bloom B. R. Major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted T cells are required for resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12013–12017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T., Baehr W., Ying Y. Chlamydia trachomatis developmentally regulated protein is homologous to eukaryotic histone H1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3937–3941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Armstrong J. A., Brown C. A., Draper P. Ultrastructural study of the behavior of macrophages toward parasitic mycobacteria. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):803–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.803-807.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Fuhrman S. A., Miettinen H. M., Kasper L. H., Mellman I. Toxoplasma gondii: fusion competence of parasitophorous vacuoles in Fc receptor-transfected fibroblasts. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):641–646. doi: 10.1126/science.2200126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Kim I. H., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G., Stadtman E. R. The isolation and purification of a specific "protector" protein which inhibits enzyme inactivation by a thiol/Fe(III)/O2 mixed-function oxidation system. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4704–4711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leake E. S., Ockers J. R., Myrvik Q. N. In vitro interactions of the BCG and Ravenel strains of Mycobacterium bovis with rabbit macrophages: adherence of the phagosomal membrane to the bacterial cell wall and the problem of the peribacillary space. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1977 Aug;22(2):129–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. J., Styblo K., Rouillon A. Tuberculosis in developing countries: burden, intervention and cost. Bull Int Union Tuberc Lung Dis. 1990 Mar;65(1):6–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrvik Q. N., Leake E. S., Wright M. J. Disruption of phagosomal membranes of normal alveolar macrophages by the H37Rv strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A correlate of virulence. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Feb;129(2):322–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce J. H. Early events in chlamydial infection. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 May-Jun;137A(3):325–332. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Steele J., Ainsworth M., Champion B. R. Activation of macrophages to inhibit proliferation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: comparison of the effects of recombinant gamma-interferon on human monocytes and murine peritoneal macrophages. Immunology. 1986 Nov;59(3):333–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD C. C. A comparison of the growth of selected mycobacteria in HeLa, monkey kidney, and human amnion cells in tissue culture. J Exp Med. 1958 Feb 1;107(2):237–246. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD C. C. Growth characteristics of tubercle bacilli and certain other mycobacteria in HeLa cells. J Exp Med. 1957 Jan 1;105(1):39–48. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger L. S., Bellinger-Kawahara C. G., Payne N. R., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors and complement component C3. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2771–2780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. L., Fuchs R., Male P., Mellman I. Two distinct subpopulations of endosomes involved in membrane recycling and transport to lysosomes. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90532-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibille Y., Reynolds H. Y. Macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils in lung defense and injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Feb;141(2):471–501. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.2.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Krahenbuhl J. L., Adams G. M., Weidner E. Toxoplasma modifies macrophage phagosomes by secretion of a vesicular network rich in surface proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):867–874. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Weidner E., Krahenbuhl J. L. Phagosome acidification blocked by intracellular Toxoplasma gondii. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):416–419. doi: 10.1038/315416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Harmon P. A. Yersinia pestis grows within phagolysosomes in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):655–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.655-659.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J. Host-pathogen relationships in respiratory tract infections. Clin Ther. 1991 Jan-Feb;13(1):172–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kielian M., Helenius A. Membrane fusion proteins of enveloped animal viruses. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 May;16(2):151–195. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Tsai V., Remington J. S. Failure to trigger the oxidative metabolic burst by normal macrophages: possible mechanism for survival of intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):328–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Bennink J. R. The binary logic of antigen processing and presentation to T cells. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90356-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeichner S. L. Isolation and characterization of macrophage phagosomes containing infectious and heat-inactivated Chlamydia psittaci: two phagosomes with different intracellular behaviors. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):956–966. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.956-966.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]