Abstract
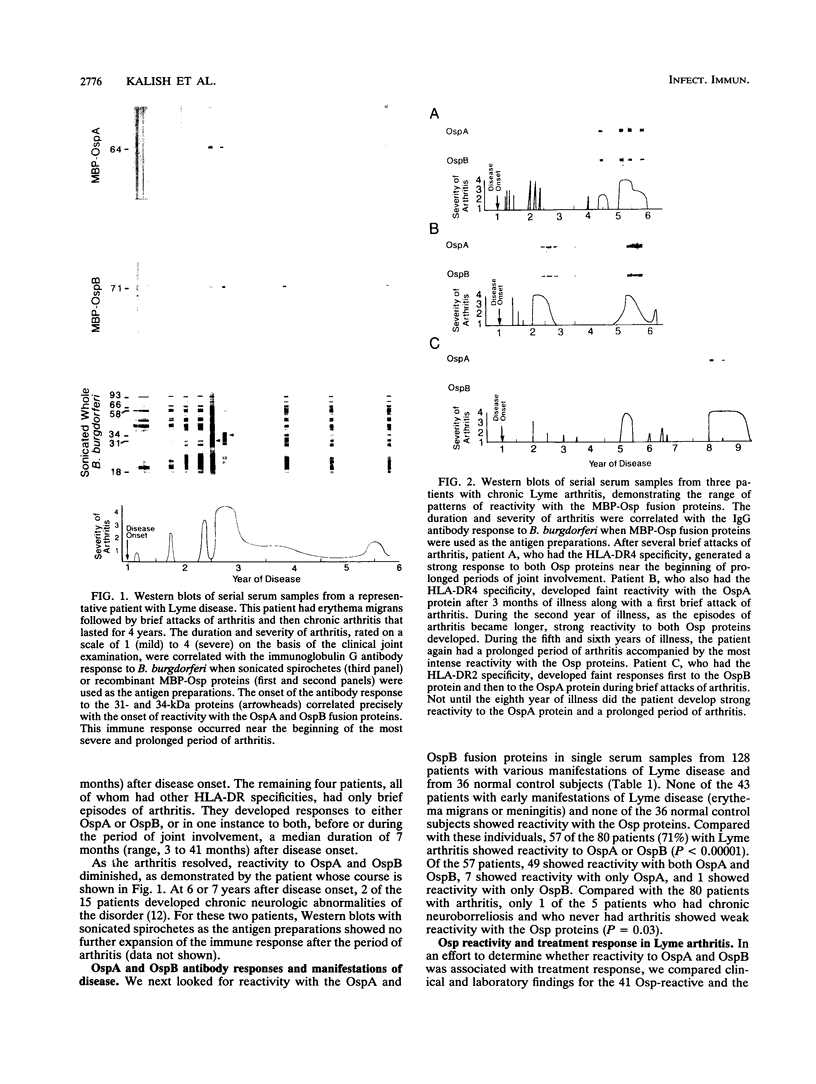
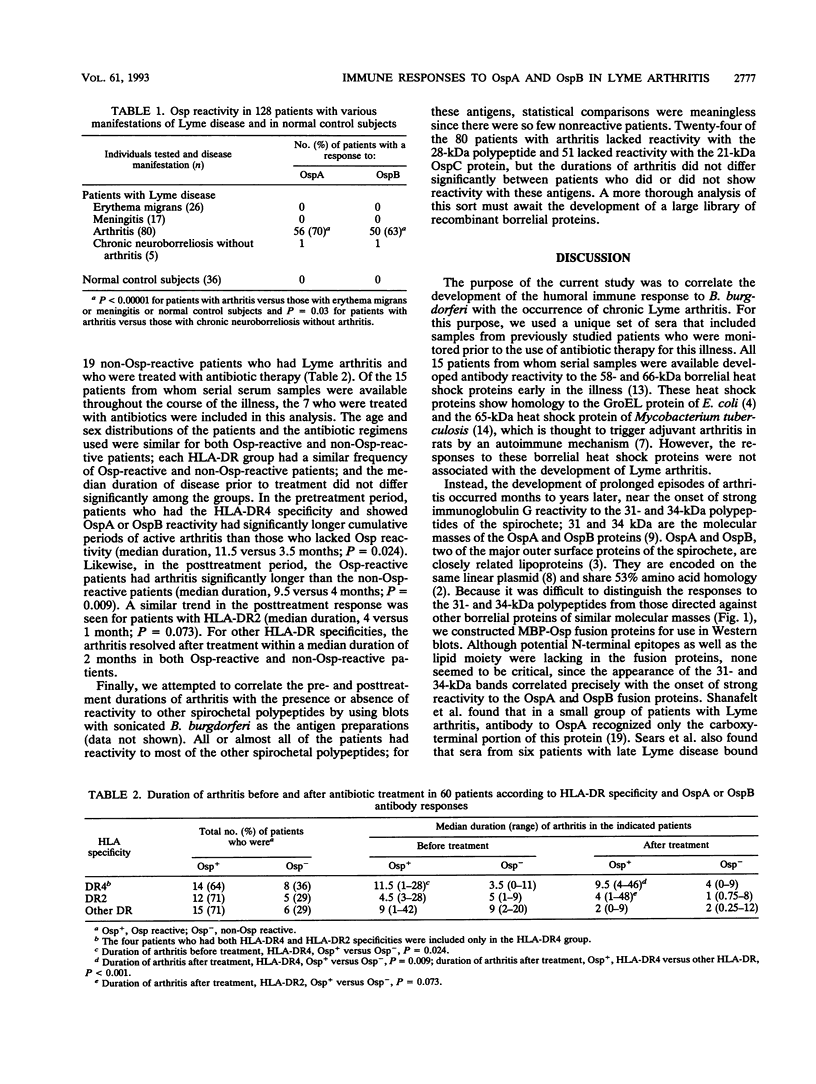
Chronic Lyme arthritis that is unresponsive to antibiotic therapy is associated with an increased frequency of the HLA-DR4 specificity. To determine whether the immune response to a particular polypeptide of Borrelia burgdorferi may be associated with treatment-resistant chronic Lyme arthritis, we correlated the clinical courses and HLA-DR specificities of 128 patients with Lyme disease with their antibody responses to spirochetal polypeptides. Antibody reactivity was determined by Western blotting (immunoblotting) with sonicated whole B. burgdorferi and recombinant forms of its outer surface proteins, OspA and OspB, as the antigen preparations. Of 15 patients monitored for 4 to 12 years, 11 (73%) developed strong immunoglobulin G responses to both OspA and OspB near the beginning of prolonged episodes of arthritis, from 5 months to 7 years after disease onset. When single serum samples from 80 patients with Lyme arthritis, were tested, 57 (71%) showed antibody reactivity to recombinant Osp proteins; in contrast, none of 43 patients who had erythema migrans or Lyme meningitis (P < 0.00001) and 1 of 5 patients who had chronic neuroborreliosis but who never had arthritis (P = 0.03) showed antibody reactivity to these proteins. Among the 60 antibiotic-treated patients with Lyme arthritis, those with the HLA-DR4 specificity and Osp reactivity had arthritis for a significantly longer time after treatment than those who lacked Osp reactivity (median duration, 9.5 versus 4 months; P = 0.009); a similar trend was found for the HLA-DR2 specificity. For other HLA-DR specificities, arthritis resolved within a median duration of 2 months in both Osp-reactive and nonreactive patients. We conclude that the combination of the HLA-DR4 specificity and OspA or OspB reactivity is associated with chronic arthritis and the lack of a response to antibiotic therapy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Grunwaldt E., Steere A. C. Antibodies of patients with Lyme disease to components of the Ixodes dammini spirochete. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):504–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI110998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Bundoc V. G., Barbour A. G. Molecular analysis of linear plasmid-encoded major surface proteins, OspA and OspB, of the Lyme disease spirochaete Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):479–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt M. E., Riley B. S., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Immunogenic integral membrane proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi are lipoproteins. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):983–991. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.983-991.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreiro M. M., Laux D. C., Nelson D. R. Characterization of the heat shock response and identification of heat shock protein antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2186–2191. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2186-2191.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler F., Whalen J. A., Reinhardt B. N., Steere A. C. Western blotting in the serodiagnosis of Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):392–400. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Naparstek Y., Ben-Nun A., Cohen I. R. Lines of T lymphocytes induce or vaccinate against autoimmune arthritis. Science. 1983 Jan 7;219(4580):56–58. doi: 10.1126/science.6336851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., LaQuier F. W., Barbour A. G. Organization of genes encoding two outer membrane proteins of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi within a single transcriptional unit. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):207–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.207-212.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., Mayer L. W., Barbour A. G. A single recombinant plasmid expressing two major outer surface proteins of the Lyme disease spirochete. Science. 1985 Feb 8;227(4687):645–646. doi: 10.1126/science.3969554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston Y. E., Duray P. H., Steere A. C., Kashgarian M., Buza J., Malawista S. E., Askenase P. W. Lyme arthritis. Spirochetes found in synovial microangiopathic lesions. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jan;118(1):26–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. M., Fournier R. S., Isberg R. R. Identification of the integrin binding domain of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis invasin protein. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1979–1989. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08326.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logigian E. L., Kaplan R. F., Steere A. C. Chronic neurologic manifestations of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1990 Nov 22;323(21):1438–1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011223232102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Gorevic P. D., Jiang W., Munoz P., Dattwyler R. J. Immunologic and structural characterization of the dominant 66- to 73-kDa antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2776–2782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maina C. V., Riggs P. D., Grandea A. G., 3rd, Slatko B. E., Moran L. S., Tagliamonte J. A., McReynolds L. A., Guan C. D. An Escherichia coli vector to express and purify foreign proteins by fusion to and separation from maltose-binding protein. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Winchester R., Lee S., Shookster L., Nunez-Roldan A. Identification of the DRw10 DR beta 1-chain allele as encoding a polymorphic class II major histocompatibility complex epitope otherwise restricted to DR beta 2 molecules of the DRw53 type. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):537–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez-Roldan A., Szer I., Toguchi T., Cuttner J., Winchester R. Association of certain Ia allotypes with the occurrence of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Recognition by a monoclonal anti-Ia reagent of a susceptibility determinant not in the DR series. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1872–1877. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberti G., Begovich A. B., Steere A. C., Klitz W., Erlich H. A., Fathman C. G. Molecular analysis of the role of the HLA class II genes DRB1, DQA1, DQB1, and DPB1 in susceptibility to Lyme arthritis. Hum Immunol. 1991 May;31(1):20–27. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(91)90044-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears J. E., Fikrig E., Nakagawa T. Y., Deponte K., Marcantonio N., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Molecular mapping of Osp-A mediated immunity against Borrelia burgdorferi, the agent of Lyme disease. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1995–2000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanafelt M. C., Anzola J., Soderberg C., Yssel H., Turck C. W., Peltz G. Epitopes on the outer surface protein A of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized by antibodies and T cells of patients with Lyme disease. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):218–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal L. H., Steere A. C., Freeman D. H., Dwyer J. M. Proliferative responses of mononuclear cells in Lyme disease. Reactivity to Borrelia burgdorferi antigens is greater in joint fluid than in blood. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Jun;29(6):761–769. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Bartenhagen N. H., Craft J. E., Hutchinson G. J., Newman J. H., Rahn D. W., Sigal L. H., Spieler P. N., Stenn K. S., Malawista S. E. The early clinical manifestations of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):76–82. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Duray P. H., Butcher E. C. Spirochetal antigens and lymphoid cell surface markers in Lyme synovitis. Comparison with rheumatoid synovium and tonsillar lymphoid tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Apr;31(4):487–495. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Gibofsky A., Patarroyo M. E., Winchester R. J., Hardin J. A., Malawista S. E. Chronic Lyme arthritis. Clinical and immunogenetic differentiation from rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jun;90(6):896–901. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-6-896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Schoen R. T., Taylor E. The clinical evolution of Lyme arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Nov;107(5):725–731. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-5-725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Gregersen P. K. The molecular basis of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis: the conformational equivalence hypothesis. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1988;10(2-3):119–139. doi: 10.1007/BF01857219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinari N. H., Reinhardt B. N., Steere A. C. T cell responses to polypeptide fractions of Borrelia burgdorferi in patients with Lyme arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jun;34(6):707–713. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]