Abstract
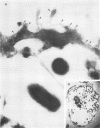
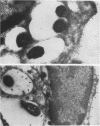
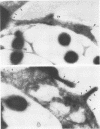
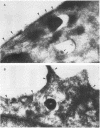
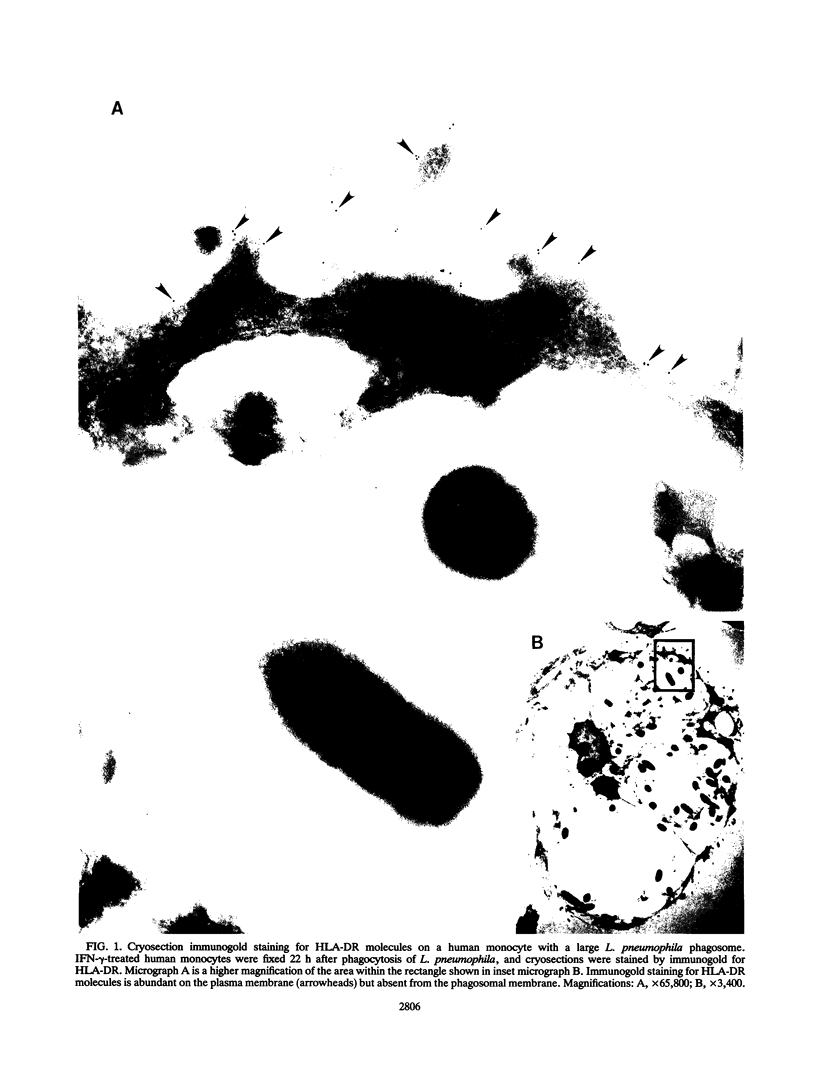
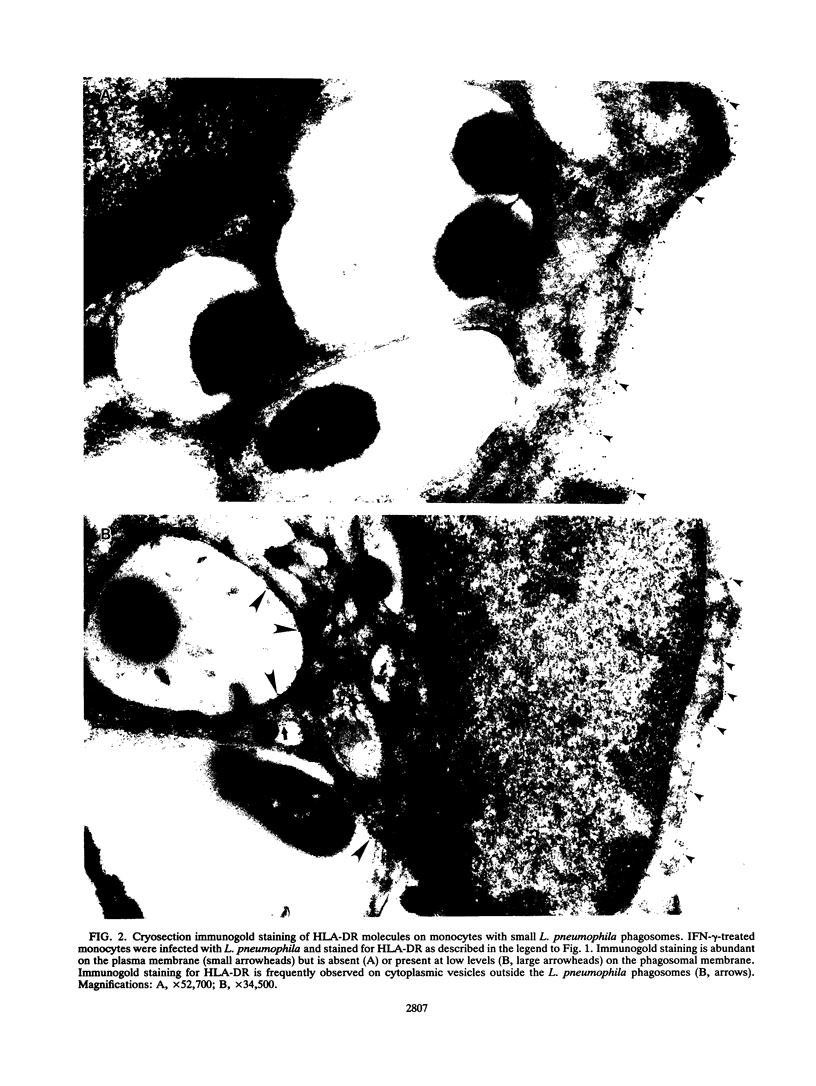
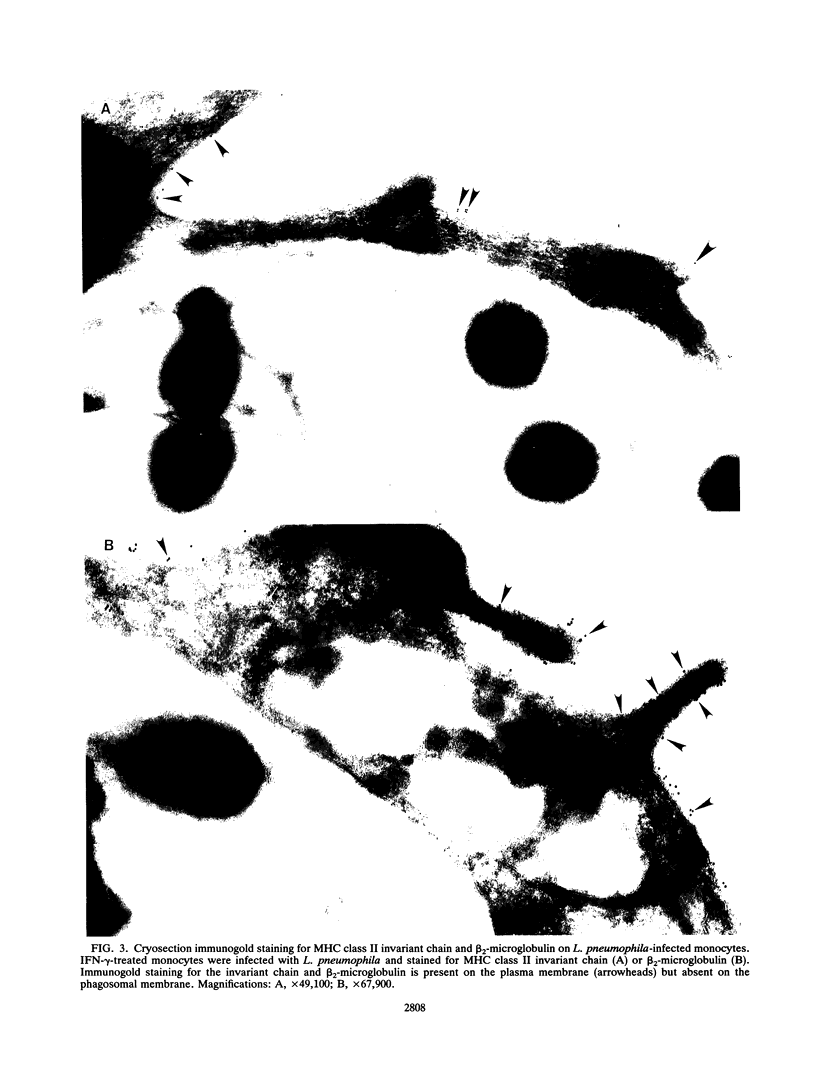
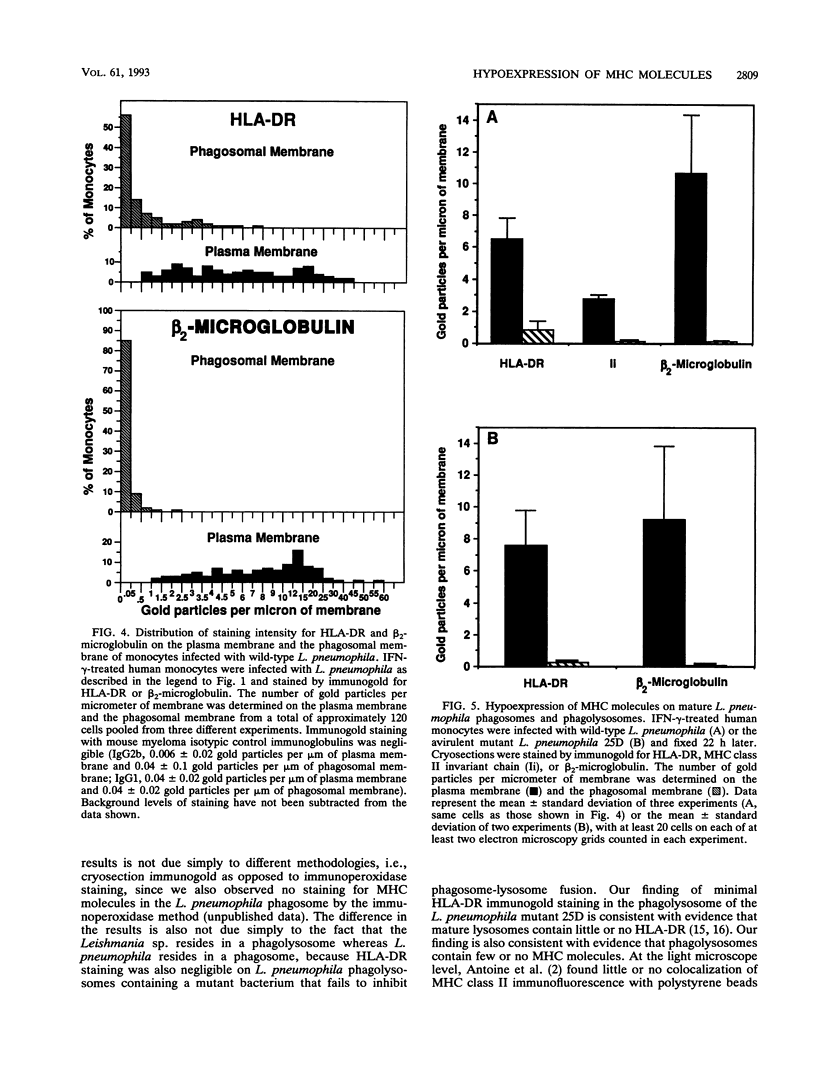
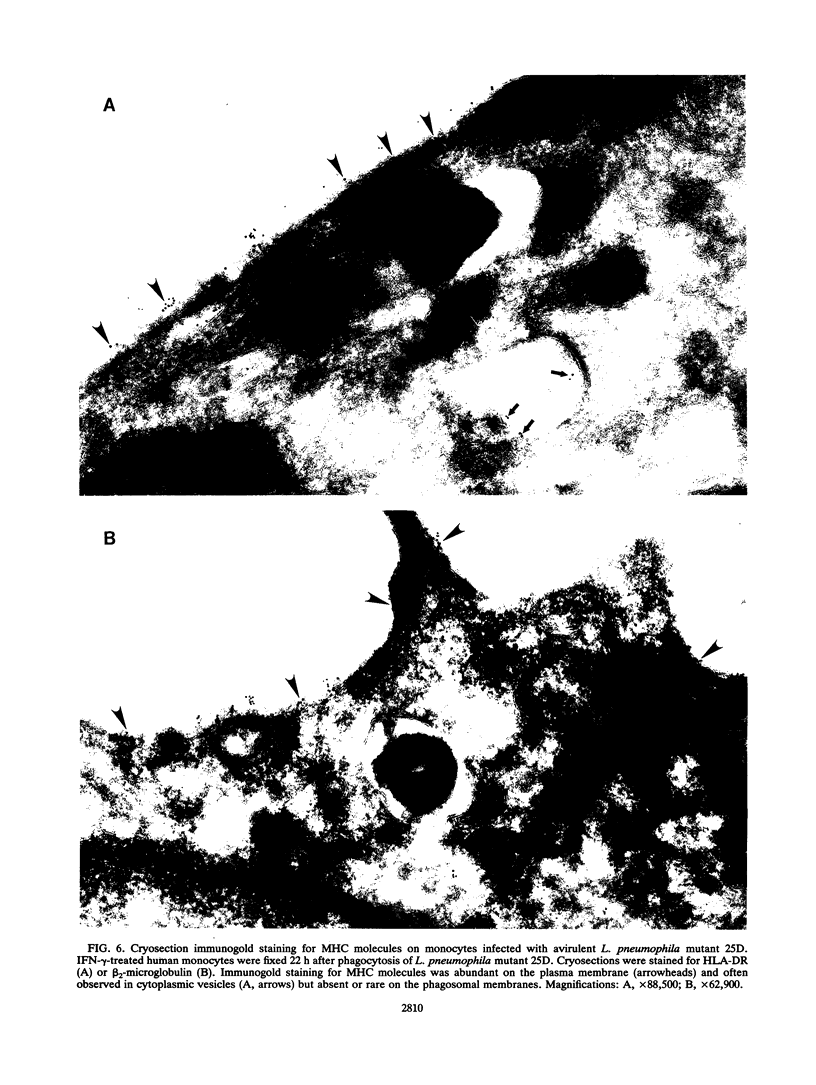
Legionella pneumophila is a facultative intracellular pathogen that parasitizes host mononuclear phagocytes. Cell-mediated immunity is pivotal to host defense against L. pneumophila, and the infected host cell may play a central role in processing and presenting parasite antigens to lymphocytes mediating cell-mediated immune response. However, in the case of L. pneumophila and intracellular parasites in general, little is known about the intracellular trafficking of parasite antigens, the influence of parasite infection on major histocompatibility complex (MHC) expression, or the relationship of MHC molecules to sites of parasite replication. To learn more about this, we have used flow cytometry to study the expression of HLA-DR by monocytes infected with L. pneumophila and cryosection immunogold electron microscopy to study the distribution of MHC class I and II molecules on L. pneumophila phagosomes. Flow cytometry analysis demonstrated that L. pneumophila infection has little effect on the overall expression of HLA-DR by monocytes. Cryosection immunogold studies revealed abundant staining for MHC class I and II molecules on the plasma membrane of infected monocytes but little or no staining on the membranes of mature L. pneumophila phagosomes. Cryosection immunogold studies of an avirulent mutant of L. pneumophila that, unlike the wild type, does not inhibit phagosome-lysosome fusion and subsequently survives but does not multiply in a phagolysosome yielded similar results. We have previously found that MHC class I and II molecules are excluded from nascent phagosomes during coiling and conventional phagocytosis. The present work demonstrates that MHC molecules do not accumulate appreciably in the L. pneumophila phagosome as it matures and at a point in the life cycle of the organism in which it is replicating and producing immunoprotective T-cell antigens. This suggests that L. pneumophila does not reside in a typical endosomal compartment in the host cell and that L. pneumophila antigens may encounter MHC molecules at extraphagosomal sites within the host cell.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoine J. C., Jouanne C., Lang T., Prina E., de Chastellier C., Frehel C. Localization of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules in phagolysosomes of murine macrophages infected with Leishmania amazonensis. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):764–775. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.764-775.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoine J. C., Prina E., Jouanne C., Bongrand P. Parasitophorous vacuoles of Leishmania amazonensis-infected macrophages maintain an acidic pH. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):779–787. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.779-787.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behbehani K., Pan S. C., Unanue E. R. Marked increase in Ia-bearing macrophages during Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 May;19(2):190–195. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Regulation of macrophage populations. I. Preferential induction of Ia-rich peritoneal exudates by immunologic stimuli. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1426–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj N., Nash T. W., Horwitz M. A. Interferon-gamma-activated human monocytes inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2662–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blander S. J., Breiman R. F., Horwitz M. A. A live avirulent mutant Legionella pneumophila vaccine induces protective immunity against lethal aerosol challenge. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):810–815. doi: 10.1172/JCI113962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blander S. J., Horwitz M. A. Vaccination with the major secretory protein of Legionella pneumophila induces cell-mediated and protective immunity in a guinea pig model of Legionnaires' disease. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):691–705. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breiman R. F., Horwitz M. A. Guinea pigs sublethally infected with aerosolized Legionella pneumophila develop humoral and cell-mediated immune responses and are protected against lethal aerosol challenge. A model for studying host defense against lung infections caused by intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):799–811. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of intracellular symbiosis in leishmaniasis. Int Rev Cytol Suppl. 1983;14:267–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens D. L., Horwitz M. A. Membrane sorting during phagocytosis: selective exclusion of major histocompatibility complex molecules but not complement receptor CR3 during conventional and coiling phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1317–1326. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein A. L., Marder R. J., Winter J. N., Fox R. I. Two new monoclonal antibodies (LN-1, LN-2) reactive in B5 formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues with follicular center and mantle zone human B lymphocytes and derived tumors. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):1028–1036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Austyn J., Stahl P. D., Gordon S. Surface properties of bacillus Calmette-Guérin-activated mouse macrophages. Reduced expression of mannose-specific endocytosis, Fc receptors, and antigen F4/80 accompanies induction of Ia. J Exp Med. 1981 Jul 1;154(1):60–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guagliardi L. E., Koppelman B., Blum J. S., Marks M. S., Cresswell P., Brodsky F. M. Co-localization of molecules involved in antigen processing and presentation in an early endocytic compartment. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):133–139. doi: 10.1038/343133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Unanue E. R. Antigen processing and intracellular Ia. Possible roles of endocytosis and protein synthesis in Ia function. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):12–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Unanue E. R., Slot J. W., Schwartz A. L., Geuze H. J. Functional and ultrastructural evidence for intracellular formation of major histocompatibility complex class II-peptide complexes during antigen processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5553–5557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Cell-mediated immunity in Legionnaires' disease. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1686–1697. doi: 10.1172/JCI110923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Characterization of avirulent mutant Legionella pneumophila that survive but do not multiply within human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1310–1328. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Formation of a novel phagosome by the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1319–1331. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Maxfield F. R. Legionella pneumophila inhibits acidification of its phagosome in human monocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):1936–1943. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) occurs by a novel mechanism: engulfment within a pseudopod coil. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Activated human monocytes inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionnaires' disease bacteria. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1618–1635. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Interaction of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) with human phagocytes. I. L. pneumophila resists killing by polymorphonuclear leukocytes, antibody, and complement. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):386–397. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Interaction of the legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) with human phagocytes. II. Antibody promotes binding of L. pneumophila to monocytes but does not inhibit intracellular multiplication. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):398–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) multiples intracellularly in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):441–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI109874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. The Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) inhibits phagosome-lysosome fusion in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2108–2126. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye P. M., Sims M., Feldmann M. Regulation of macrophage accessory cell activity by mycobacteria. II. In vitro inhibition of Ia expression by Mycobacterium microti. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Apr;64(1):28–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotteau V., Teyton L., Peleraux A., Nilsson T., Karlsson L., Schmid S. L., Quaranta V., Peterson P. A. Intracellular transport of class II MHC molecules directed by invariant chain. Nature. 1990 Dec 13;348(6302):600–605. doi: 10.1038/348600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. W., Libby D. M., Horwitz M. A. IFN-gamma-activated human alveolar macrophages inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3978–3981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. W., Libby D. M., Horwitz M. A. Interaction between the legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) and human alveolar macrophages. Influence of antibody, lymphokines, and hydrocortisone. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):771–782. doi: 10.1172/JCI111493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Ng W., McMaster W. R. Parasite-accessory cell interactions in murine leishmaniasis. II. Leishmania donovani suppresses macrophage expression of class I and class II major histocompatibility complex gene products. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1926–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerrett S. J., Martin T. R. Alveolar macrophage activation in experimental legionellosis. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):337–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztein M. B., Steeg P. S., Johnson H. M., Oppenheim J. J. Regulation of human peripheral blood monocyte DR antigen expression in vitro by lymphokines and recombinant interferons. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):556–565. doi: 10.1172/JCI111243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. Antigen-presenting function of the macrophage. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:395–428. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraight C. J., van Endert P., Möller P., Lipp J., Ling N. R., MacLennan I. C., Koch N., Moldenhauer G. Human major histocompatibility complex class II invariant chain is expressed on the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5787–5792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]