Abstract
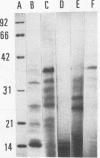
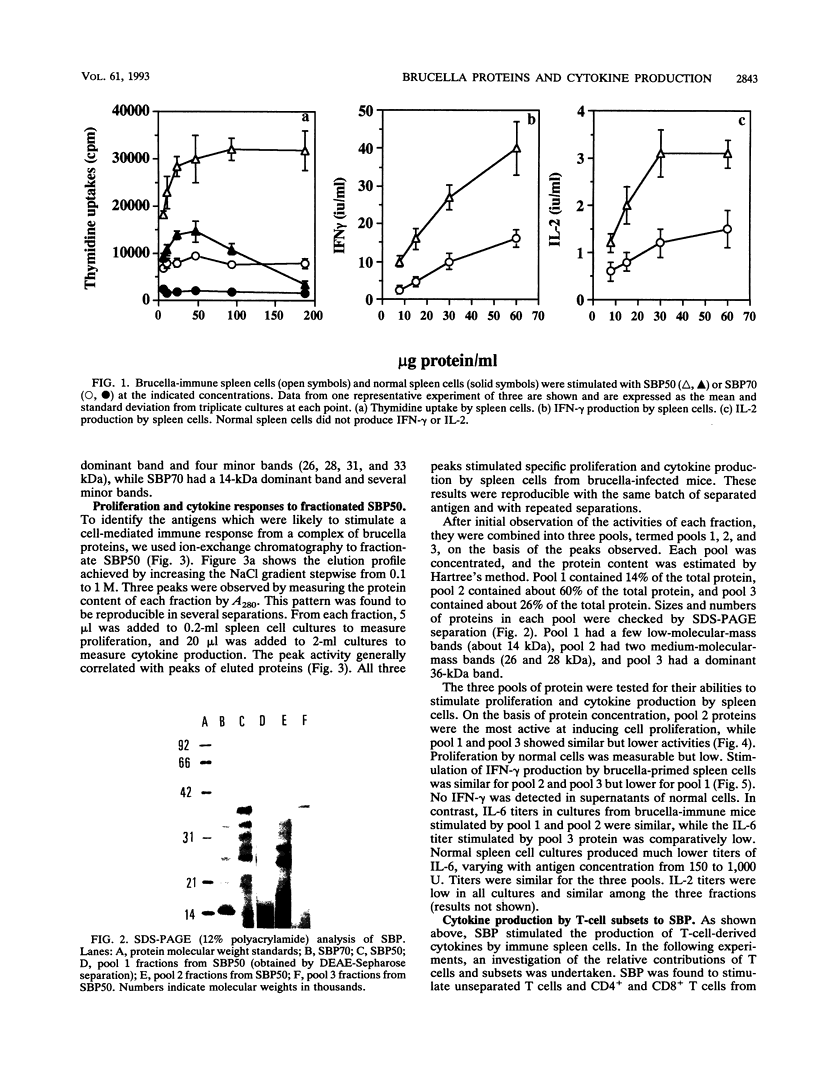
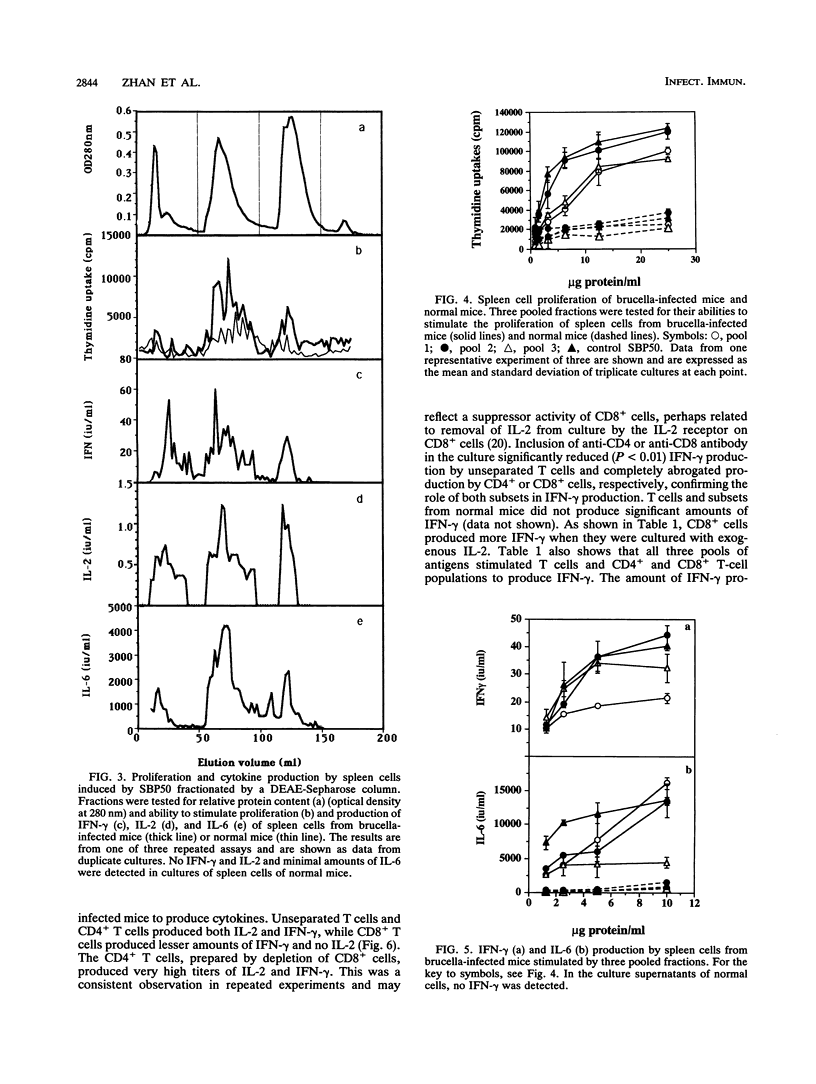
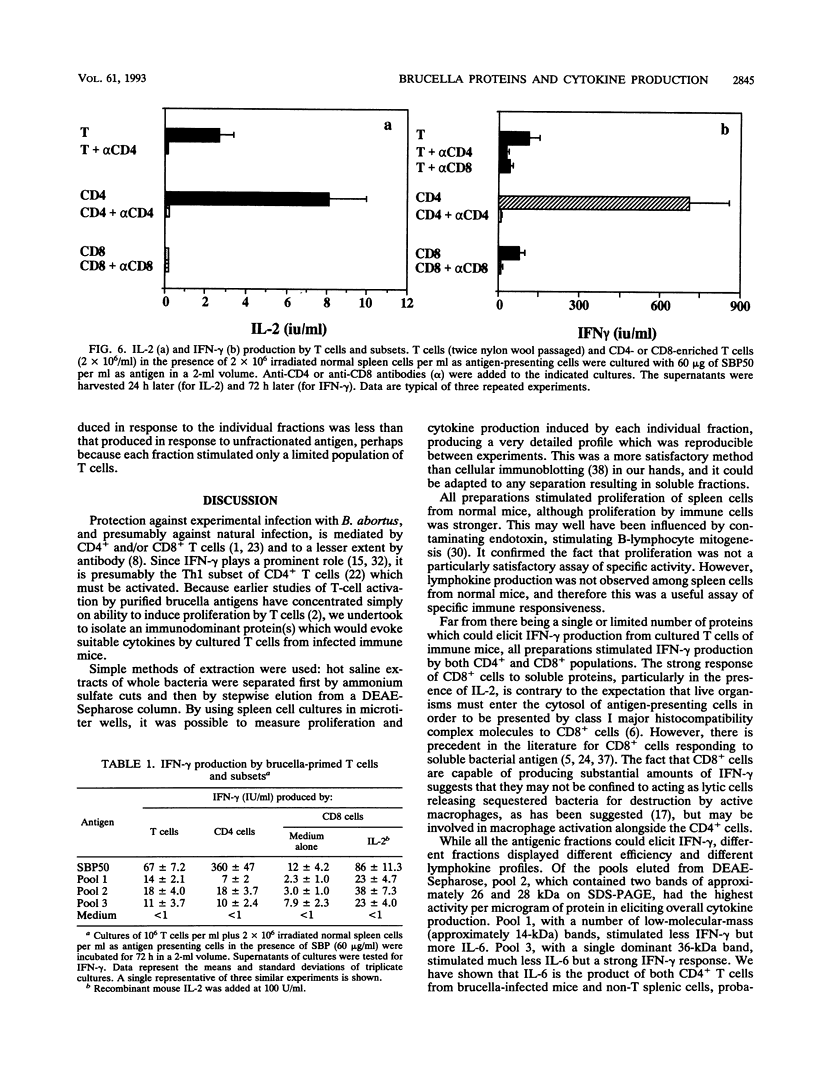
Hot saline extracts of Brucella abortus 19 were separated by successive differential precipitation with 50 and 70% ammonium sulfate, yielding fractions SBP50, with predominantly 36-kDa proteins and a number of medium-sized proteins (26 to 33 kDa), and SBP70, with 14-kDa and lower-molecular-mass proteins. Both fractions stimulated specifically proliferation and cytokine production by spleen cells from brucella-infected mice, although the activity of SBP50 was much higher than that of SBP70. Further separation of SBP50 by a DEAE-Sepharose column resulted in three distinct subfractions which were confirmed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The three subfractions were analyzed for their abilities to induce lymphocytes to proliferate and produce cytokines. The three subfractions were all active but with characteristic differences in magnitude. Subfraction 1 stimulated moderate proliferation, high interleukin 6 (IL-6) production, and relatively low production of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma). Subfraction 2 was the strongest stimulus for proliferation and production of IL-6 and IFN-gamma, while subfraction 3 stimulated moderate cell proliferation, a high level of IFN-gamma, and a low level of IL-6. IL-2 production stimulated by the three subfractions was similar. SBP50 and all three subfractions stimulated purified T cells of both CD4+ and CD8+ subsets to produce IFN-gamma. The production of IFN-gamma by CD8+ T cells to brucella antigens was enhanced with exogenous IL-2.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araya L. N., Elzer P. H., Rowe G. E., Enright F. M., Winter A. J. Temporal development of protective cell-mediated and humoral immunity in BALB/c mice infected with Brucella abortus. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3330–3337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. L., Verstreate D. R., Winter A. J. Immune response of cattle to Brucella abortus outer membrane proteins measured by lymphocyte blastogenesis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Aug;9(4):383–396. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(85)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berche P., Gaillard J. L., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes as a prerequisite for in vivo induction of T cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2266–2271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks-Alder B., Splitter G. A. Determination of bovine lymphocyte responses to extracted proteins of Brucella abortus by using protein immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2581–2586. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2581-2586.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. L., Fields P. E., Kurlander R. J. Metabolic requirements for macrophage presentation of Listeria monocytogenes to immune CD8 cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):555–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunt L. M., Portnoy D. A., Unanue E. R. Presentation of Listeria monocytogenes to CD8+ T cells requires secretion of hemolysin and intracellular bacterial growth. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3540–3546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Requirement of endogenous interferon-gamma production for resolution of Listeria monocytogenes infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7404–7408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannat A., Bousquet C., Serre A. Response of high and low antibody producer to Brucella. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1978 Jul-Sep;129 100(5):669–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corner L. A., Alton G. G. Persistence of Brucella abortus strain 19 infection in adult cattle vaccinated with reduced doses. Res Vet Sci. 1981 Nov;31(3):342–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzata G. K., Wyckoff J. H., 3rd, Confer A. W. Immunopotentiation of cattle vaccinated with a soluble Brucella abortus antigen with low LPS content: an analysis of cellular and humoral immune responses. Vet Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90107-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Attempts to characterize the mechanisms involved in mycobacterial growth inhibition by gamma-interferon-activated bone marrow macrophages. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1464–1469. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1464-1469.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. M., Winter A. J. Survival of virulent and attenuated strains of Brucella abortus in normal and gamma interferon-activated murine peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):3011–3014. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.3011-3014.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. CD8+ T lymphocytes in intracellular microbial infections. Immunol Today. 1988 Jun;9(6):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiderlen A. F., Kaufmann S. H., Lohmann-Matthes M. L. Protection of mice against the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes by recombinant immune interferon. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):964–967. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. S., Orme I. M. Patterns of IL-2 production and utilization in mice heavily infected with Mycobacterium bovis BCG reflect the phase of protective immunity being expressed. Immunology. 1989 Jun;67(2):221–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montaraz J. A., Winter A. J. Comparison of living and nonliving vaccines for Brucella abortus in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):245–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.245-251.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov H., Hogarth M., McKenzie I. F., Cheers C. In vivo and in vitro effects of monoclonal antibody to Ly antigens on immunity to infection. Cell Immunol. 1982 Jul 15;71(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90502-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees A., Scoging A., Mehlert A., Young D. B., Ivanyi J. Specificity of proliferative response of human CD8 clones to mycobacterial antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Dec;18(12):1881–1887. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. S., Boom W. H., Abbas A. K. Inhibition of B lymphocyte activation by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):767–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Steele J., Ainsworth M., Champion B. R. Activation of macrophages to inhibit proliferation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: comparison of the effects of recombinant gamma-interferon on human monocytes and murine peritoneal macrophages. Immunology. 1986 Nov;59(3):333–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. IgG or IgM monoclonal antibodies reactive with different determinants on the molecular complex bearing Lyt 2 antigen block T cell-mediated cytolysis in the absence of complement. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2665–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P., Pearce E., Natovitz P., Sher A. Vaccination against cutaneous leishmaniasis in a murine model. II. Immunologic properties of protective and nonprotective subfractions of soluble promastigote extract. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3118–3125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore B. J., Chiller J. M., Morrison D. C., Weigle W. O. Immunologic properties of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS): correlation between the mitogenic, adjuvant, and immunogenic activities. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):770–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., 3rd, Adams L. G., Sowa B. A., Ficht T. A. Induction of lymphocyte responsiveness by the outer membrane-peptidoglycan complex of rough strains of Brucella abortus. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Sep;26(1):31–48. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(90)90130-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens M. G., Pugh G. W., Jr, Tabatabai L. B. Effects of gamma interferon and indomethacin in preventing Brucella abortus infections in mice. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4407–4409. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4407-4409.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabatabai L. B., Deyoe B. L., Patterson J. M. Immunogenicity of Brucella abortus salt-extractable proteins. Vet Microbiol. 1989 May;20(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(89)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Lima G. C., Engers H. D., Louis J. A. Exacerbation of murine cutaneous leishmaniasis by adoptive transfer of parasite-specific helper T cell populations capable of mediating Leishmania major-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1594–1600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstreate D. R., Creasy M. T., Caveney N. T., Baldwin C. L., Blab M. W., Winter A. J. Outer membrane proteins of Brucella abortus: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):979–989. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.979-989.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink A., Coulie P. G., Wauters P., Nordan R. P., Van Snick J. B cell growth and differentiation activity of interleukin-HP1 and related murine plasmacytoma growth factors. Synergy with interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):607–612. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. R., Fellowes R., Hecht E. M., Lehner T. Characterization of streptococcal antigen-specific CD8+, MHC class I-restricted, T cell clones that down-regulate in vitro antibody synthesis. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 15;147(10):3370–3380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Lamb J. R. T lymphocytes respond to solid-phase antigen: a novel approach to the molecular analysis of cellular immunity. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):167–171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. J. Human brucellosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5(5):821–842. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.5.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]