Abstract
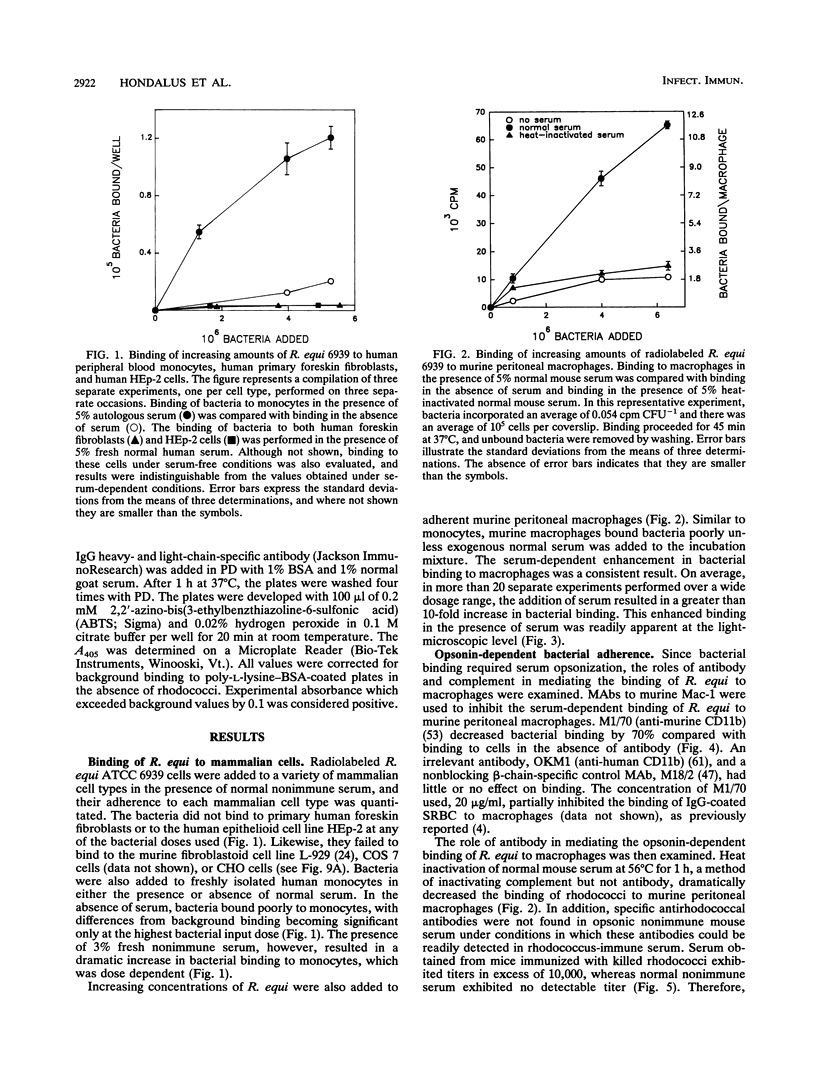
Rhodococcus equi is a facultative intracellular bacterium of macrophages that causes disease in immunocompromised individuals, particularly those with AIDS. In this report, we demonstrate that R. equi binding to mammalian cells requires complement and is mediated primarily by the leukocyte complement receptor, Mac-1. Bacteria bind to macrophages poorly unless exogenous complement is added to the incubation medium. The addition of fresh nonimmune serum, which contains no detectable antibodies to R. equi, greatly enhances bacterial binding to macrophages, whereas heat inactivation of this serum or immunological depletion of C3 from the serum reduces binding to levels only slightly higher than those of binding under serum-free conditions. Human serum depleted of C2 or C4 is fully opsonic, indicating that complement activation and fixation occur by the alternative pathway. The serum-dependent binding of rhodococci to macrophages is mediated primarily by the macrophage complement receptor type 3, Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18). Bacteria do not bind to fibroblastoid or epithelial cells that lack this receptor. Most of the bacterial binding to macrophages is inhibited by a monoclonal antibody to Mac-1 but is unaffected by a monoclonal antibody to complement receptor type 1. Furthermore, opsonized, but not unopsonized, bacteria bind to purified Mac-1 immobilized on plastic. In addition, in the presence of opsonic complement, rhodococci bind efficiently to fibroblastoid cells transfected with cloned Mac-1 but relatively poorly to cells transfected with the complement receptor type 1. Hence, R. equi fixes complement by activating the alternative complement pathway, and this fixation is a requirement for bacterial adhesion and invasion. Furthermore, complement fixation defines rhodococcal host cell tropism, since R. equi binds specifically and exclusively to cells expressing Mac-1.
Full text
PDF


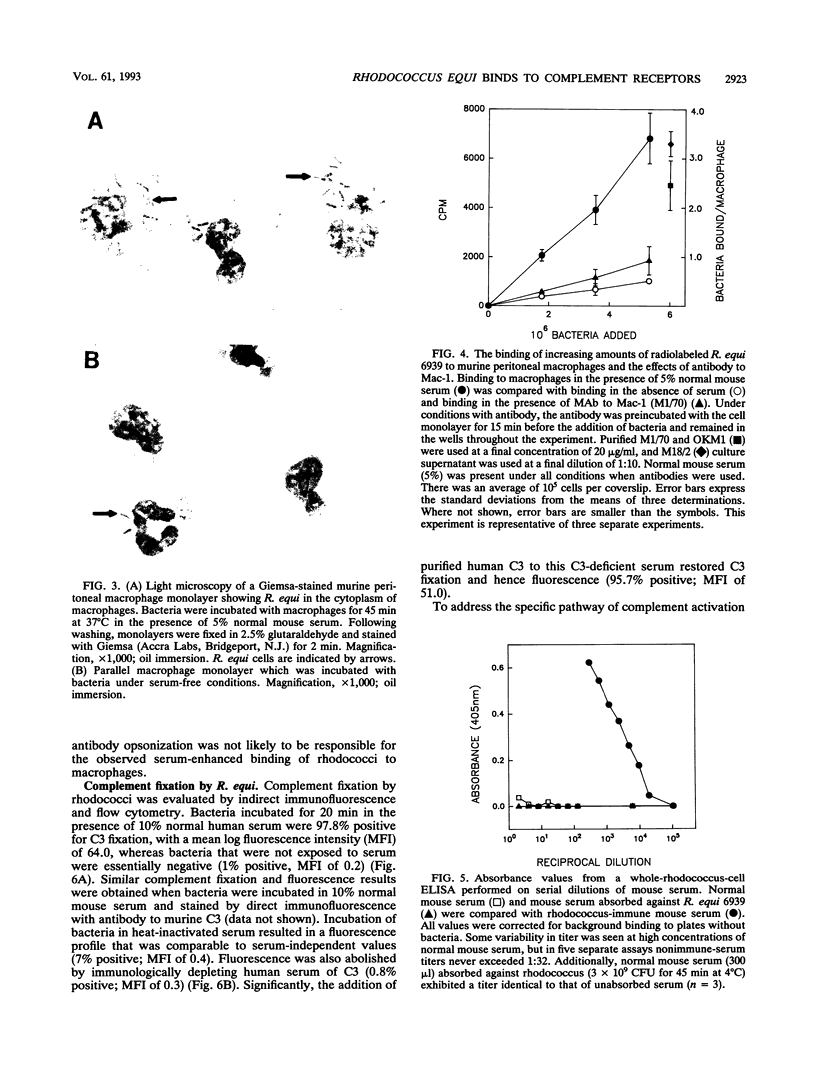
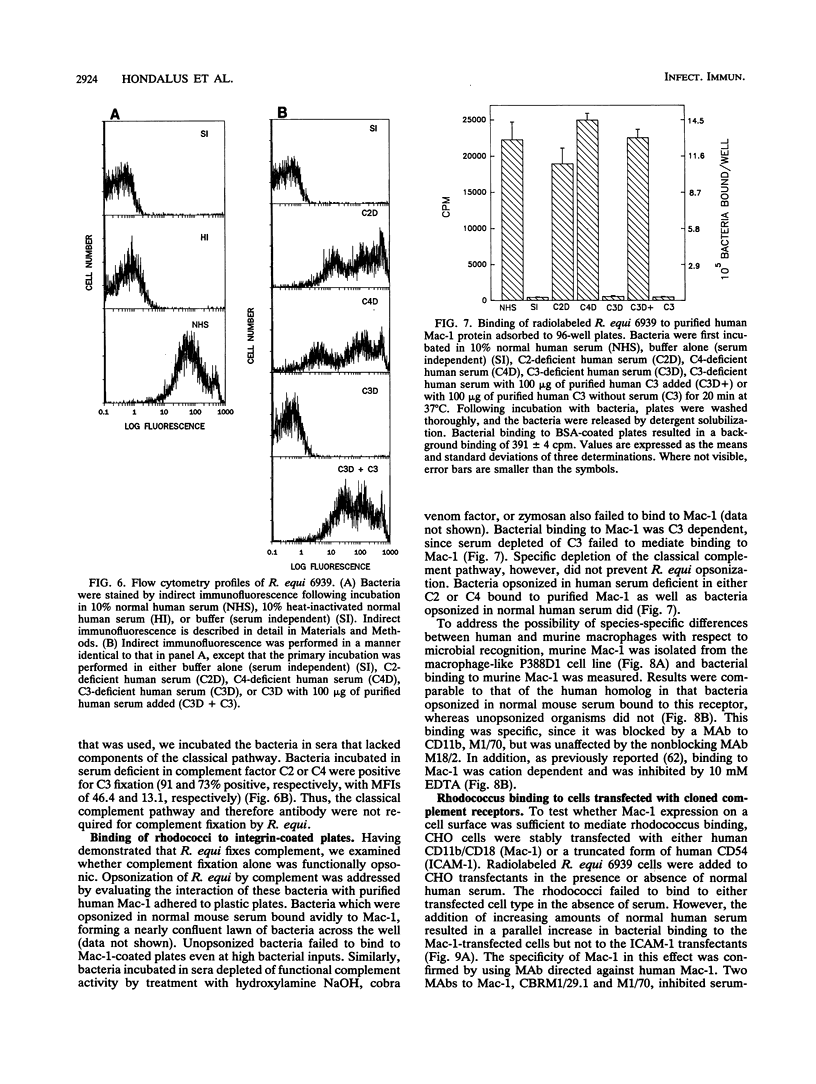
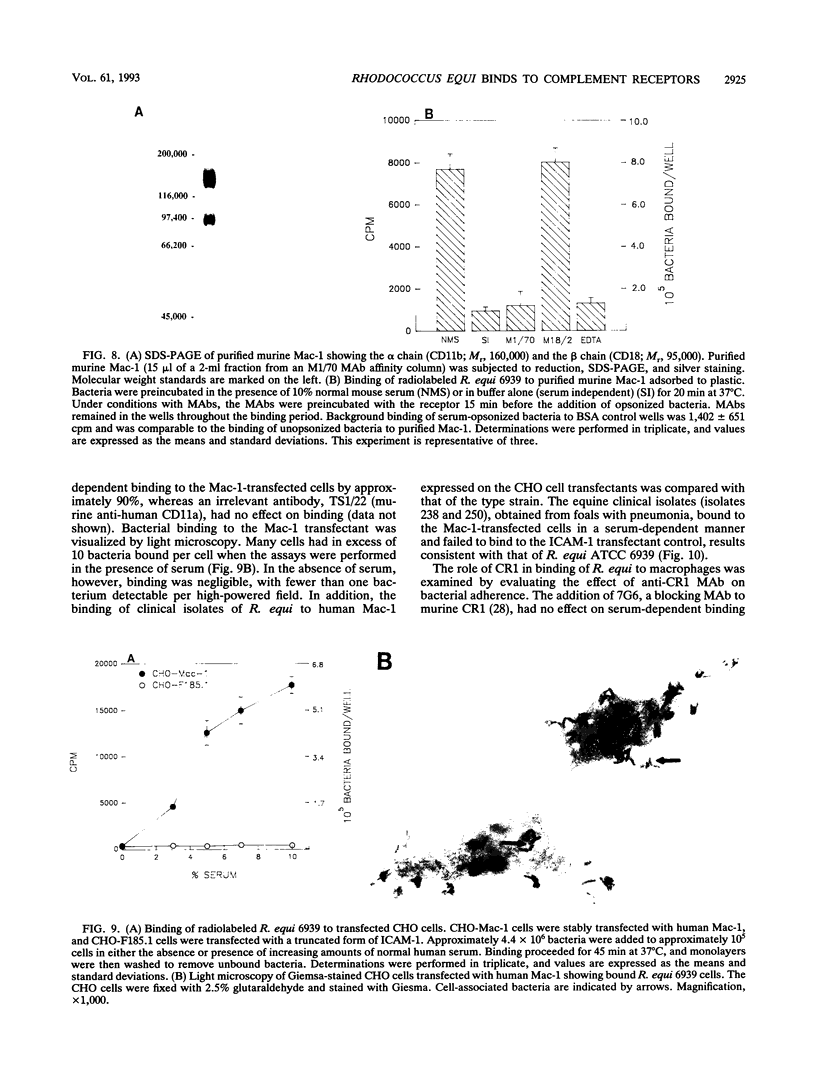
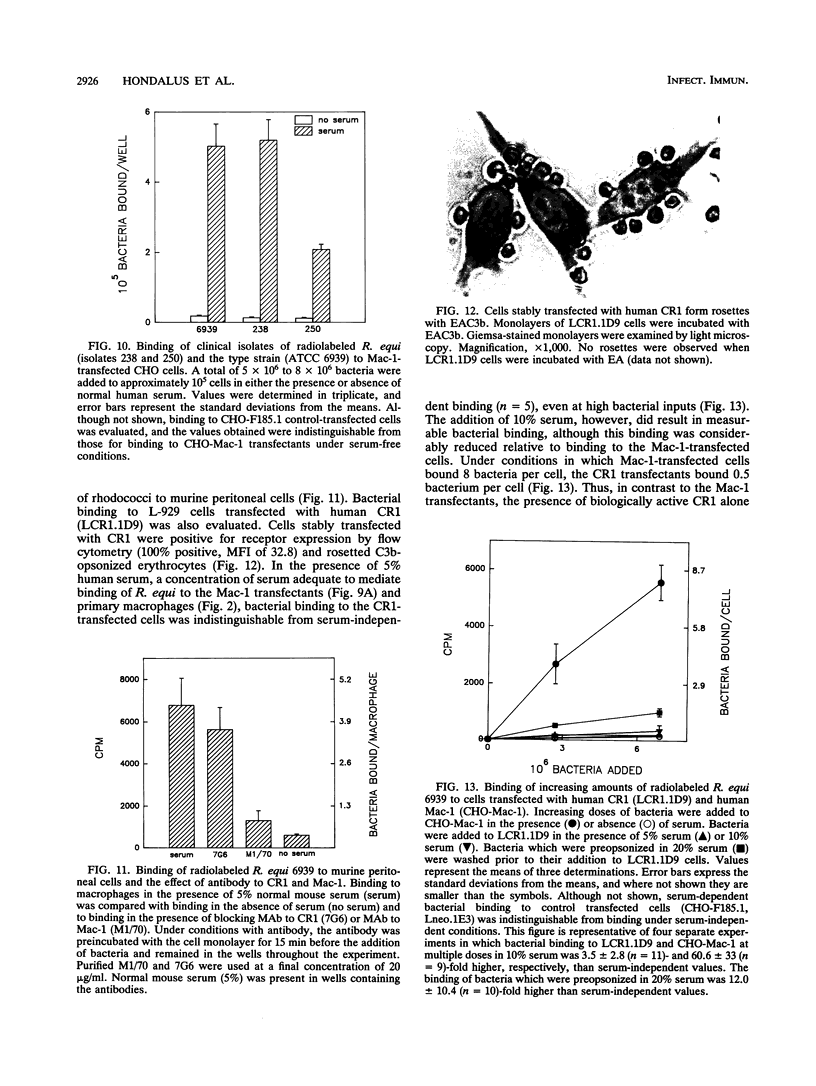



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beller D. I., Springer T. A., Schreiber R. D. Anti-Mac-1 selectively inhibits the mouse and human type three complement receptor. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1000–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornson A. B., Bjornson H. S. Activation of complement by opportunist pathogens and chemotypes of Salmonella minnesota. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):748–753. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.748-753.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Bohnsack J. F., Gresham H. D. Mechanism of inhibition of immunoglobulin G-mediated phagocytosis by monoclonal antibodies that recognize the Mac-1 antigen. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):365–375. doi: 10.1172/JCI113328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Hosea S. W., Hammer C. H., Burch C. G., Frank M. M. A quantitative analysis of the interactions of antipneumococcal antibody and complement in experimental pneumococcal bacteremia. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):85–98. doi: 10.1172/JCI110444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E., Hendler E. Rhodococcus peritonitis in a patient treated with peritoneal dialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1989 Nov;14(5):417–418. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(89)80177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Wright S. D. Role of the adherence-promoting receptors, CR3, LFA-1, and p150,95, in binding of Histoplasma capsulatum by human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):195–210. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. S., Garcia-Aguilar J., Bickford J. K., Corbi A. L., Springer T. A. The I domain is a major recognition site on the leukocyte integrin Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) for four distinct adhesion ligands. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(4):1031–1043. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.4.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. S., Staunton D. E., de Fougerolles A. R., Stacker S. A., Garcia-Aguilar J., Hibbs M. L., Springer T. A. ICAM-1 (CD54): a counter-receptor for Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18). J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3129–3139. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig C., Gill M. J., Church D. L. Rhodococcus equi--an easily missed opportunistic pathogen. Scand J Infect Dis. 1991;23(1):1–6. doi: 10.3109/00365549109023367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drevets D. A., Campbell P. A. Roles of complement and complement receptor type 3 in phagocytosis of Listeria monocytogenes by inflammatory mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2645–2652. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2645-2652.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. T-cell receptor cross-linking transiently stimulates adhesiveness through LFA-1. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):619–624. doi: 10.1038/341619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons W., Reichwein B., Winslow D. L. Rhodococcus equi infection in the patient with AIDS: literature review and report of an unusual case. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jan-Feb;13(1):91–96. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filley E. A., Rook G. A. Effect of mycobacteria on sensitivity to the cytotoxic effects of tumor necrosis factor. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2567–2572. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2567-2572.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., May J., Gaither T., Ellman L. In vitro studies of complement function in sera of C4-deficient guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):176–187. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewurz H., Shin H. S., Mergenhagen S. E. Interactions of the complement system with endotoxic lipopolysaccharide: consumption of each of the six terminal complement components. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):1049–1057. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. L., Sunstrum J. C. Rhodococcus equi infection in patients with and without human immunodeficiency virus infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jan-Feb;13(1):139–145. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan N. F., Cutilli J. R., Douglas S. D. Isolation of highly purified human blood monocytes for in vitro HIV-1 infection studies of monocyte/macrophages. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Jul 3;130(2):283–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hietala S. K., Ardans A. A. Interaction of Rhodococcus equi with phagocytic cells from R. equi-exposed and non-exposed foals. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Aug;14(3):307–320. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillerdal G., Riesenfeldt-Orn I., Pedersen A., Ivanicova E. Infection with Rhodococcus equi in a patient with sarcoidosis treated with corticosteroids. Scand J Infect Dis. 1988;20(6):673–677. doi: 10.3109/00365548809035669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hondalus M. K., Sweeney C. R., Mosser D. M. An assay to quantitate the binding of Rhodococcus equi to macrophages. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 May;32(3-4):339–350. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(92)90055-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Prescott J. F., Markham R. J. The pathology of experimental Corynebacterium equi infection in foals following intrabronchial challenge. Vet Pathol. 1983 Jul;20(4):440–449. doi: 10.1177/030098588302000407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalli K. R., Ahearn J. M., Fearon D. T. Interaction of iC3b with recombinant isotypic and chimeric forms of CR2. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):590–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann Y., Tseng E., Springer T. A. Cloning of the murine lymphocyte function-associated molecule-1 alpha-subunit and its expression in COS cells. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):369–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Takeda J., Hong K., Kozono H., Sakai H., Inoue K. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse complement receptor type 1 (CR1). Their use in a distribution study showing that mouse erythrocytes and platelets are CR1-negative. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3066–3072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., Larson R. S., Corbi A. L., Dustin M. L., Staunton D. E., Springer T. A. The leukocyte integrins. Adv Immunol. 1989;46:149–182. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klickstein L. B., Bartow T. J., Miletic V., Rabson L. D., Smith J. A., Fearon D. T. Identification of distinct C3b and C4b recognition sites in the human C3b/C4b receptor (CR1, CD35) by deletion mutagenesis. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1699–1717. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Goebel W. Identification of an extracellular protein of Listeria monocytogenes possibly involved in intracellular uptake by mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.55-61.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky J. A., Pulkingham N., Powers M. A., Durack D. T. Rhodococcus equi causing human pulmonary infection: review of 29 cases. South Med J. 1991 Oct;84(10):1217–1220. doi: 10.1097/00007611-199110000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., Tabuni A. Binding of Cryptococcus neoformans by human cultured macrophages. Requirements for multiple complement receptors and actin. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):528–535. doi: 10.1172/JCI115027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE A. E., SABACHEWSKY L., TOOLAN H. W. Culture characteristics of four permanent lines of human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1955 Oct;15(9):598–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan K. L., Mangano M. F. Infections with Rhodococcus equi in children. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Jul-Aug;14(4):347–352. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(91)90026-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micklem K. J., Sim R. B. Isolation of complement-fragment-iC3b-binding proteins by affinity chromatography. The identification of p150,95 as an iC3b-binding protein. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 1;231(1):233–236. doi: 10.1042/bj2310233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. M., Burke S. K., Coutavas E. E., Wedgwood J. F., Edelson P. J. Leishmania species: mechanisms of complement activation by five strains of promastigotes. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Dec;62(3):394–404. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. M., Edelson P. J. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by Leishmania promastigotes: parasite lysis and attachment to macrophages. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1501–1505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. M., Edelson P. J. The mouse macrophage receptor for C3bi (CR3) is a major mechanism in the phagocytosis of Leishmania promastigotes. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2785–2789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. M., Edelson P. J. The third component of complement (C3) is responsible for the intracellular survival of Leishmania major. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):329–331. doi: 10.1038/327329b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. M., Springer T. A., Diamond M. S. Leishmania promastigotes require opsonic complement to bind to the human leukocyte integrin Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18). J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):511–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myones B. L., Dalzell J. G., Hogg N., Ross G. D. Neutrophil and monocyte cell surface p150,95 has iC3b-receptor (CR4) activity resembling CR3. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):640–651. doi: 10.1172/JCI113643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldham L. J., Rodgers F. G. Adhesion, penetration and intracellular replication of Legionella pneumophila: an in vitro model of pathogenesis. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Apr;131(4):697–706. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-4-697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Legionella pneumophila is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1377–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F. Rhodococcus equi: an animal and human pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):20–34. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Madrid F., Krensky A. M., Ware C. F., Robbins E., Strominger J. L., Burakoff S. J., Springer T. A. Three distinct antigens associated with human T-lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis: LFA-1, LFA-2, and LFA-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7489–7493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Madrid F., Simon P., Thompson S., Springer T. A. Mapping of antigenic and functional epitopes on the alpha- and beta-subunits of two related mouse glycoproteins involved in cell interactions, LFA-1 and Mac-1. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):586–602. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger L. S., Bellinger-Kawahara C. G., Payne N. R., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors and complement component C3. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2771–2780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger L. S., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of leprosy bacilli is mediated by complement receptors CR1 and CR3 on human monocytes and complement component C3 in serum. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1304–1314. doi: 10.1172/JCI114568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. M., Romney B. M., Weiden M. D., White C. S., O'Toole K. M. Rhodococcus equi endobronchial mass with lung abscess in a patient with AIDS. Thorax. 1992 Jan;47(1):62–63. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirera G., Romeu J., Clotet B., Velasco P., Arnal J., Rius F., Foz M. Relapsing systemic infection due to Rhodococcus equi in a drug abuser seropositive for human immunodeficiency virus. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 May-Jun;13(3):509–510. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.3.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfré G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Mac-1: a macrophage differentiation antigen identified by monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Apr;9(4):301–306. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacker S. A., Springer T. A. Leukocyte integrin P150,95 (CD11c/CD18) functions as an adhesion molecule binding to a counter-receptor on stimulated endothelium. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):648–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talamás-Rohana P., Wright S. D., Lennartz M. R., Russell D. G. Lipophosphoglycan from Leishmania mexicana promastigotes binds to members of the CR3, p150,95 and LFA-1 family of leukocyte integrins. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4817–4824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peterson P. K., Nguyen B. Y., Sisson S. P., Kim Y. Opsonization of encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus: the role of specific antibody and complement. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1681–1687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Sisson S. P., Kim Y., Peterson P. K. Localization of the third component of complement on the cell wall of encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M: implications for the mechanism of resistance to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1159–1163. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1159-1163.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelstein J. A., Tomasz A. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by pneumococcal cell wall teichoic acid. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):174–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. C., Ewing E. P., Jr, Callaway C. S., Peacock W. L., Jr Intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila in cultured human embryonic lung fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1014–1018. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1014-1018.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong W. W., Klickstein L. B., Smith J. A., Weis J. H., Fearon D. T. Identification of a partial cDNA clone for the human receptor for complement fragments C3b/C4b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7711–7715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Rao P. E., Van Voorhis W. C., Craigmyle L. S., Iida K., Talle M. A., Westberg E. F., Goldstein G., Silverstein S. C. Identification of the C3bi receptor of human monocytes and macrophages by using monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5699–5703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Silverstein S. C. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters stimulate C3b and C3b' receptor-mediated phagocytosis in cultured human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1149–1164. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yager J. A. The pathogenesis of Rhodococcus equi pneumonia in foals. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Aug;14(3):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink M. C., Yager J. A., Prescott J. F., Fernando M. A. Electron microscopic investigation of intracellular events after ingestion of Rhodococcus equi by foal alveolar macrophages. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Aug;14(3):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink M. C., Yager J. A., Smart N. L. Corynebacterium equi Infections in Horses, 1958-1984: A Review of 131 Cases. Can Vet J. 1986 May;27(5):213–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]