Abstract
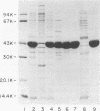
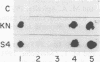
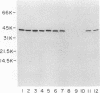
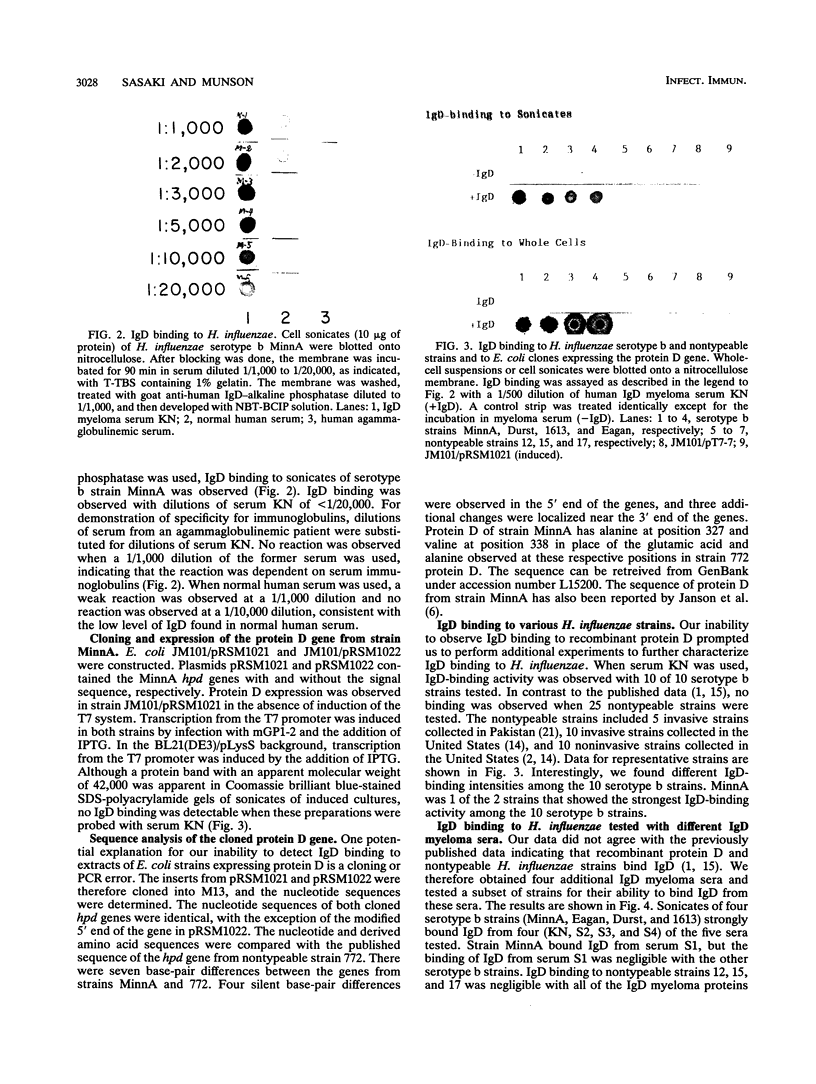
Haemophilus influenzae type b and nontypeable H. influenzae have been reported to bind human immunoglobulin D (IgD). IgD myeloma sera from five patients were tested for the ability of IgD to bind to H. influenzae. Serotype b strains bound human IgD in four of the five sera tested. IgD in the fifth serum bound strongly to type b strain MinnA but poorly to other type b strains. Additionally, IgD binding was not observed when nontypeable strains were tested. The gene for protein D, the putative IgD-binding protein, was cloned from the IgD-binding H. influenzae type b strain MinnA and expressed in Escherichia coli. IgD binding to E. coli expressing protein D was not demonstrable. Recombinant protein D was purified, and antisera were generated in rabbits. Using these rabbit sera, we detected protein D in nontypeable as well as serotype b strains by Western blotting (immunoblotting). In contrast, IgD myeloma protein 4490, which was previously reported to bind to protein D by Ruan and coworkers (M. Ruan, M. Akkoyunlu, A. Grubb, and A. Forsgren, J. Immunol. 145:3379-3384), bound strongly to both type b and nontypeable H. influenzae as well as to E. coli expressing protein D. Thus, IgD binding is a general property of H. influenzae type b strains but not a general property of nontypeable strains, although both type b and nontypeable strains produce protein D. With the exception of IgD myeloma protein 4490 binding, we have no evidence for a role of protein D in IgD binding to H. influenzae.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akkoyunlu M., Ruan M., Forsgren A. Distribution of protein D, an immunoglobulin D-binding protein, in Haemophilus strains. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1231–1238. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1231-1238.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Leininger E. Cloning, expression, and DNA sequence analysis of genes encoding nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae high-molecular-weight surface-exposed proteins related to filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1302–1313. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1302-1313.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Grubb A. O. Many bacterial species bind human IgD. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1468–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebink G. S. The microbiology of otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Jan;8(1 Suppl):S18–S20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson H., Hedén L. O., Grubb A., Ruan M. R., Forsgren A. Protein D, an immunoglobulin D-binding protein of Haemophilus influenzae: cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):119–125. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.119-125.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. S., Moxon E. R. Capsulation and gene copy number at the cap locus of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):859–864. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.859-864.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Kabeer M. H., Lenoir A. A., Granoff D. M. Epidemiology and prospects for prevention of disease due to Haemophilus influenzae in developing countries. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11 (Suppl 3):S588–S597. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_3.s588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Brodeur B., Chong P., Grass S., Martin D., Proulx C. Outer membrane proteins P1 and P2 of Haemophilus influenzae type b: structure and identification of surface-exposed epitopes. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165 (Suppl 1):S86–S89. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165-supplement_1-s86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Tolan R. W., Jr Molecular cloning, expression, and primary sequence of outer membrane protein P2 of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):88–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.88-94.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. V., White K. E., Pastor P., Gabriel L., Medley F., Granoff D. M., Osterholm M. T. Declining incidence of Haemophilus influenzae type b disease since introduction of vaccination. JAMA. 1993 Jan 13;269(2):246–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M., Selander R. K. Genetic relationships of serologically nontypable and serotype b strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):183–191. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.183-191.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruan M. R., Akkoyunlu M., Grubb A., Forsgren A. Protein D of Haemophilus influenzae. A novel bacterial surface protein with affinity for human IgD. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3379–3384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald E. R. Haemophilus influenzae as a cause of acute otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Jan;8(1 Suppl):S28–S30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg G. A., Ghafoor A., Ishaq Z., Nomani N. K., Kabeer M., Anwar F., Burney M. I., Qureshi A. W., Musser J. M., Selander R. K. Clonal analysis of Hemophilus influenzae isolated from children from Pakistan with lower respiratory tract infections. J Infect Dis. 1989 Oct;160(4):634–643. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.4.634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]