Abstract
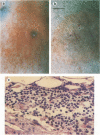
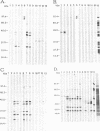
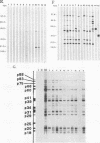
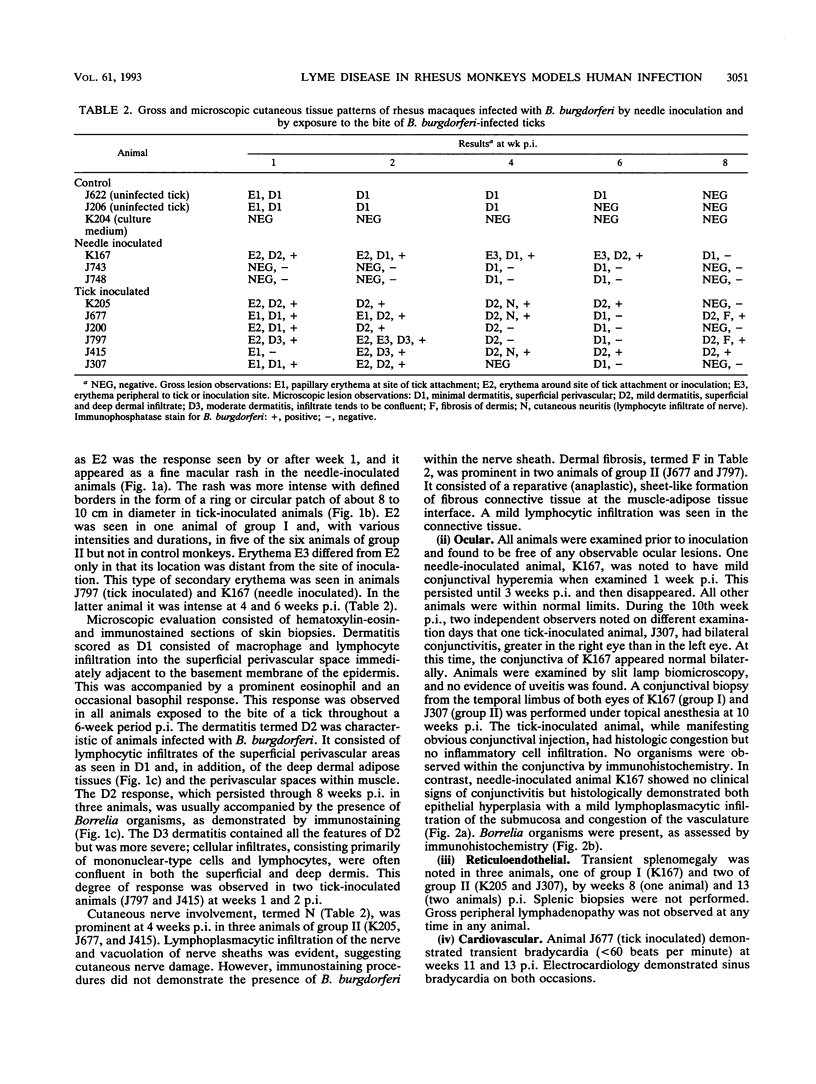
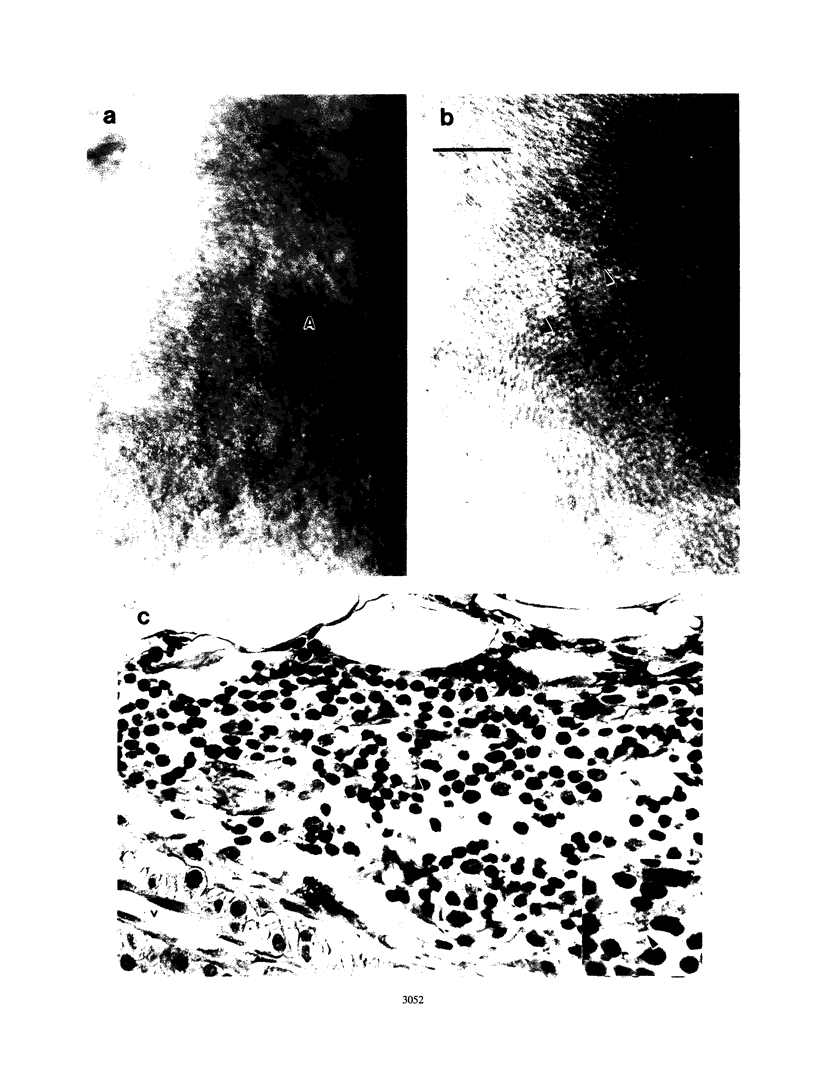
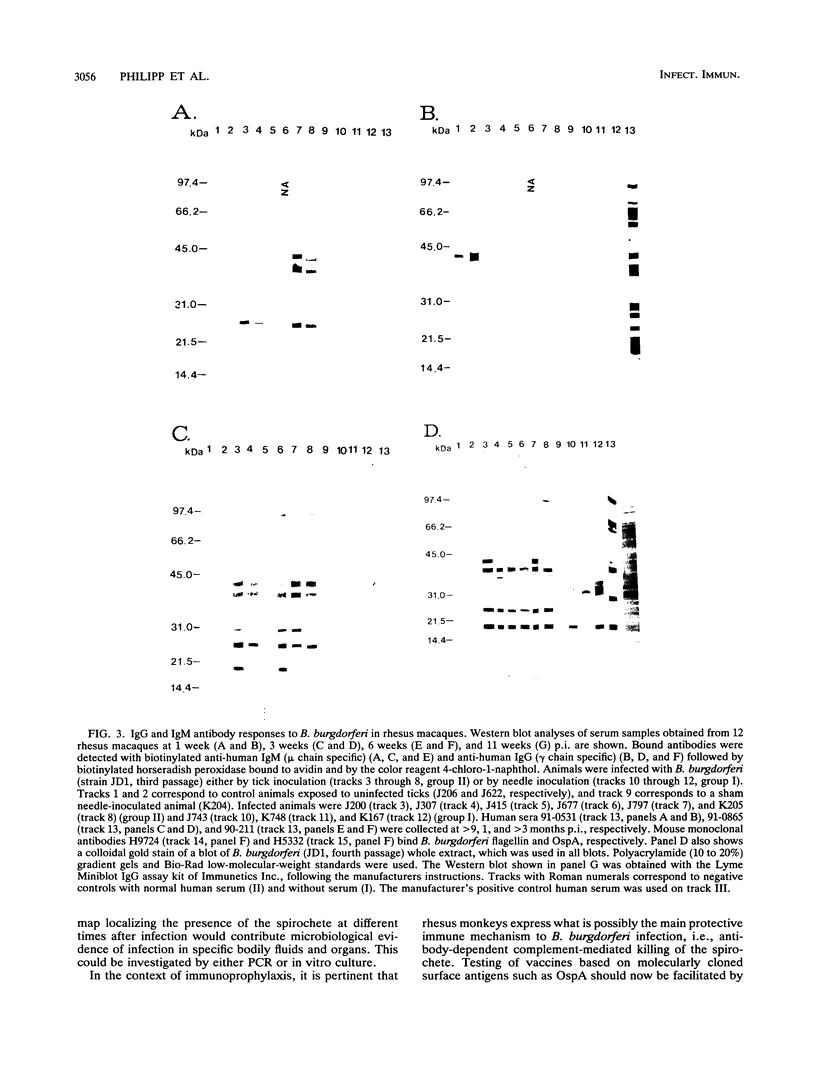
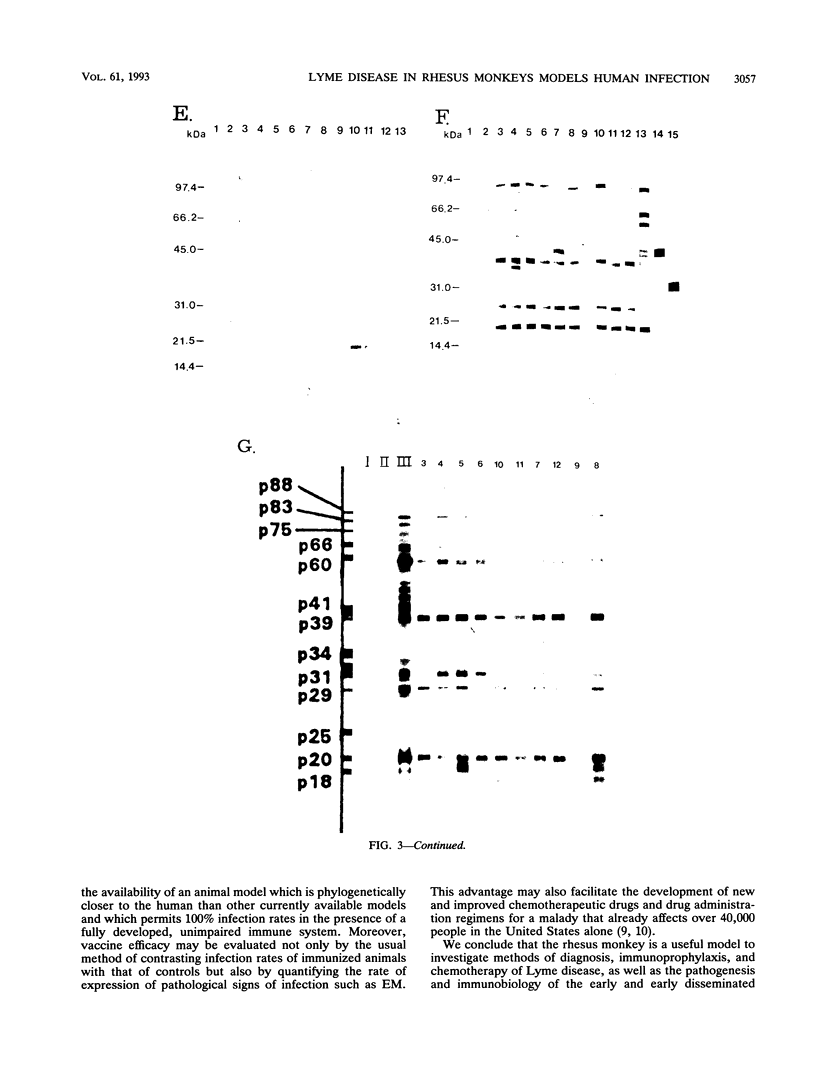
We demonstrate that Borrelia burgdorferi infection in the rhesus monkey mimics the early and early disseminated phases of human Lyme disease. Clinical, bacteriological, immunological, and pathological signs of infection were investigated during 13 weeks after inoculation of the spirochete. Three animals were given B. burgdorferi (strain JD1) by needle inoculations, six animals were exposed to the bite of B. burgdorferi-infected Ixodes dammini ticks, and three animals were uninfected controls. B. burgdorferi could be recovered from all animals that were given the spirochete. Bacteria were detectable until week 6 postinoculation (p.i.) in blood, until week 8 p.i. in skin biopsies, and at 10 weeks p.i. in the conjunctiva of one of two animals which developed conjunctivitis. Erythema migrans (EM) appeared in one of the three animals infected by needle inoculation and in five of the six animals infected by ticks. Deep dermal perivascular lymphocytic infiltrations (characteristic of human EM) were observed in all animals showing EM clinically. Both EM and conjunctivitis were documented concomitantly with the presence of the spirochete. Lethargy, splenomegaly, and cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis were also noted in some animals, but the direct connection of these signs with the infection was not shown. The appearance rate of immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G antibodies to B. burgdorferi, as well as the antigen spectra recognized, were remarkably similar to those seen in humans. Serum antibodies from infected animals were able to kill B. burgdorferi in vitro in the presence of rhesus complement. The rhesus monkey model appears to be useful for the investigation of the immunology and pathogenesis of Lyme disease and for the development of immunoprophylactic, diagnostic, and chemotherapeutic protocols.
Full text
PDF





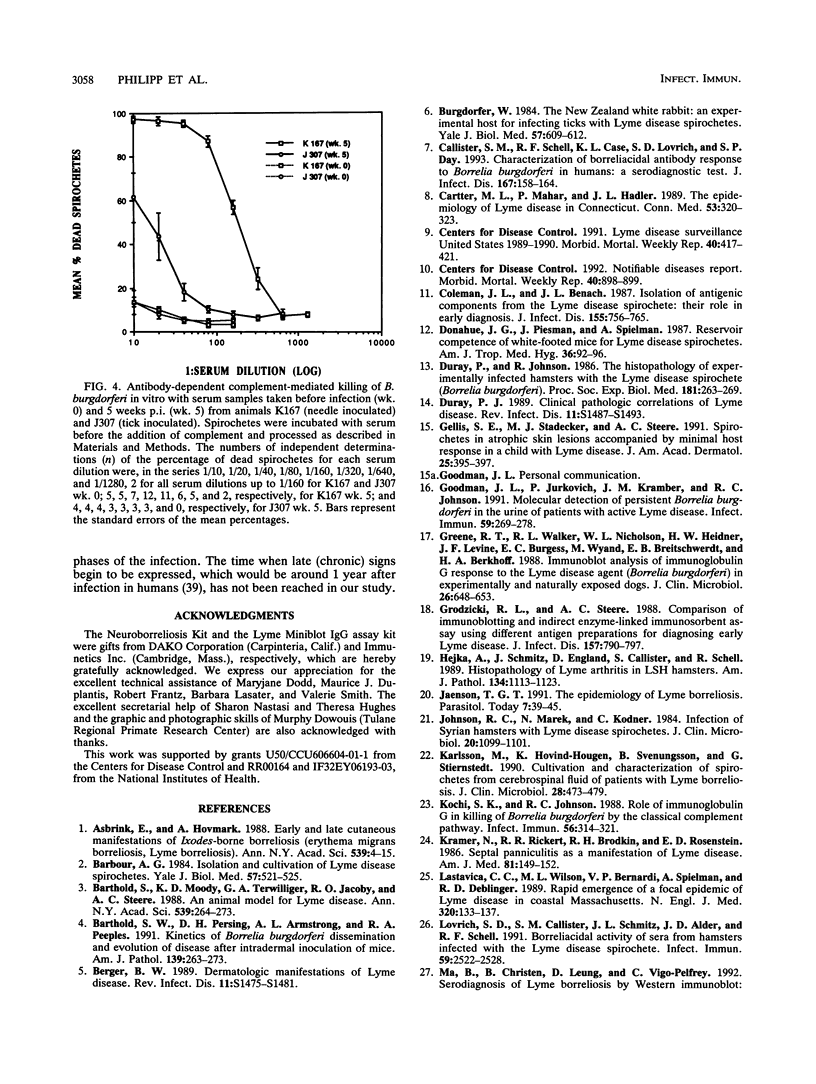

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A. Early and late cutaneous manifestations in Ixodes-borne borreliosis (erythema migrans borreliosis, Lyme borreliosis). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:4–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Moody K. D., Terwilliger G. A., Jacoby R. O., Steere A. C. An animal model for Lyme arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:264–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Persing D. H., Armstrong A. L., Peeples R. A. Kinetics of Borrelia burgdorferi dissemination and evolution of disease after intradermal inoculation of mice. Am J Pathol. 1991 Aug;139(2):263–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger B. W. Dermatologic manifestations of Lyme disease. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Sep-Oct;11 (Suppl 6):S1475–S1481. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_6.s1475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W. The New Zealand white rabbit: an experimental host for infecting ticks with Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):609–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callister S. M., Schell R. F., Case K. L., Lovrich S. D., Day S. P. Characterization of the borreliacidal antibody response to Borrelia burgdorferi in humans: a serodiagnostic test. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;167(1):158–164. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.1.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartter M. L., Mshar P., Hadler J. L. The epidemiology of Lyme disease in Connecticut. Conn Med. 1989 Jun;53(6):320–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Benach J. L. Isolation of antigenic components from the Lyme disease spirochete: their role in early diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):756–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue J. G., Piesman J., Spielman A. Reservoir competence of white-footed mice for Lyme disease spirochetes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Jan;36(1):92–96. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H. Clinical pathologic correlations of Lyme disease. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Sep-Oct;11 (Suppl 6):S1487–S1493. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_6.s1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H., Johnson R. C. The histopathology of experimentally infected hamsters with the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1986 Feb;181(2):263–269. doi: 10.3181/00379727-181-42251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellis S. E., Stadecker M. J., Steere A. C. Spirochetes in atrophic skin lesions accompanied by minimal host response in a child with Lyme disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991 Aug;25(2 Pt 2):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(91)70213-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. L., Jurkovich P., Kramber J. M., Johnson R. C. Molecular detection of persistent Borrelia burgdorferi in the urine of patients with active Lyme disease. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):269–278. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.269-278.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. T., Walker R. L., Nicholson W. L., Heidner H. W., Levine J. F., Burgess E. C., Wyand M., Breitschwerdt E. B., Berkhoff H. A. Immunoblot analysis of immunoglobulin G response to the Lyme disease agent (Borrelia burgdorferi) in experimentally and naturally exposed dogs. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):648–653. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.648-653.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Comparison of immunoblotting and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using different antigen preparations for diagnosing early Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):790–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hejka A., Schmitz J. L., England D. M., Callister S. M., Schell R. F. Histopathology of Lyme arthritis in LSH hamsters. Am J Pathol. 1989 May;134(5):1113–1123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenson T. G. The epidemiology of lyme borreliosis. Parasitol Today. 1991 Feb;7(2):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(91)90187-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson M., Hovind-Hougen K., Svenungsson B., Stiernstedt G. Cultivation and characterization of spirochetes from cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Lyme borreliosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):473–479. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.473-479.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochi S. K., Johnson R. C. Role of immunoglobulin G in killing of Borrelia burgdorferi by the classical complement pathway. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):314–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.314-321.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer N., Rickert R. R., Brodkin R. H., Rosenstein E. D. Septal panniculitis as a manifestation of Lyme disease. Am J Med. 1986 Jul;81(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastavica C. C., Wilson M. L., Berardi V. P., Spielman A., Deblinger R. D. Rapid emergence of a focal epidemic of Lyme disease in coastal Massachusetts. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 19;320(3):133–137. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901193200301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovrich S. D., Callister S. M., Schmitz J. L., Alder J. D., Schell R. F. Borreliacidal activity of sera from hamsters infected with the Lyme disease spirochete. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2522–2528. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2522-2528.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma B., Christen B., Leung D., Vigo-Pelfrey C. Serodiagnosis of Lyme borreliosis by western immunoblot: reactivity of various significant antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):370–376. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.370-376.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Schreier A. B., Ficke C. M. Clinical and serologic studies of canine borreliosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1987 Nov 1;191(9):1089–1094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millner M. M., Müllegger R. R., Spork K. D., Stanek G. Lyme borreliosis of central nervous system (CNS) in children: a diagnostic challenge. Infection. 1991 Jul-Aug;19(4):273–278. doi: 10.1007/BF01644966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadal D., Taverna C., Hitzig W. H. Immunoblot analysis of antibody binding to polypeptides of Borrelia burgdorferi in children with different clinical manifestations of Lyme disease. Pediatr Res. 1989 Oct;26(4):377–382. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198910000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J., Mather T. N., Sinsky R. J., Spielman A. Duration of tick attachment and Borrelia burgdorferi transmission. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):557–558. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.557-558.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J., Mather T. N., Telford S. R., 3rd, Spielman A. Concurrent Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti infection in nymphal Ixodes dammini. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):446–447. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.446-447.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehrig J. T., Piesman J., Hunt A. R., Keen M. G., Happ C. M., Johnson B. J. The hamster immune response to tick-transmitted Borrelia burgdorferi differs from the response to needle-inoculated, cultured organisms. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 1;149(11):3648–3653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Gay S., Museteanu C., Kramer M. D., Zimmer G., Eichmann K., Museteanu U., Simon M. M. Lyme borreliosis in the severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) mouse manifests predominantly in the joints, heart, and liver. Am J Pathol. 1990 Oct;137(4):811–820. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Lovrich S. D., Callister S. M., Schell R. F. Depletion of complement and effects on passive transfer of resistance to infection with Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3815–3818. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3815-3818.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Schell R. F., Hejka A., England D. M., Konick L. Induction of lyme arthritis in LSH hamsters. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2336–2342. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2336-2342.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek G. Laboratory diagnosis and seroepidemiology of Lyme borreliosis. Infection. 1991 Jul-Aug;19(4):263–267. doi: 10.1007/BF01644964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Bartenhagen N. H., Craft J. E., Hutchinson G. J., Newman J. H., Rahn D. W., Sigal L. H., Spieler P. N., Stenn K. S., Malawista S. E. The early clinical manifestations of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):76–82. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]