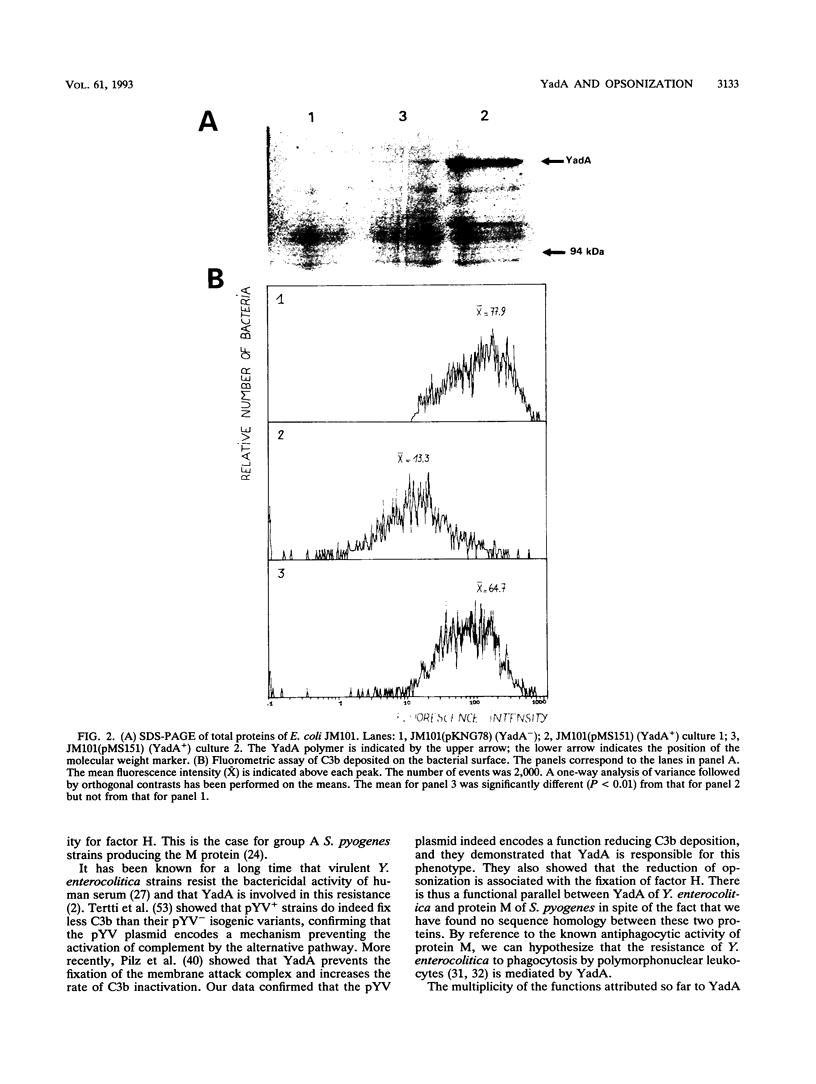
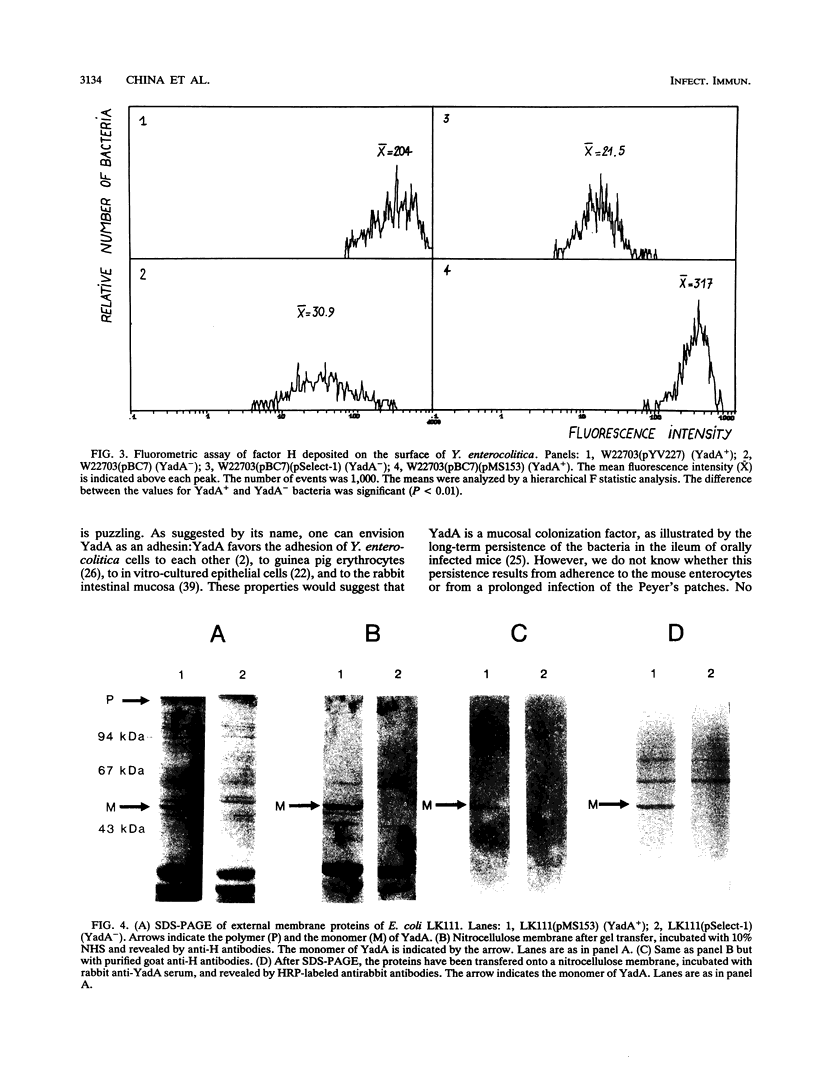
Abstract
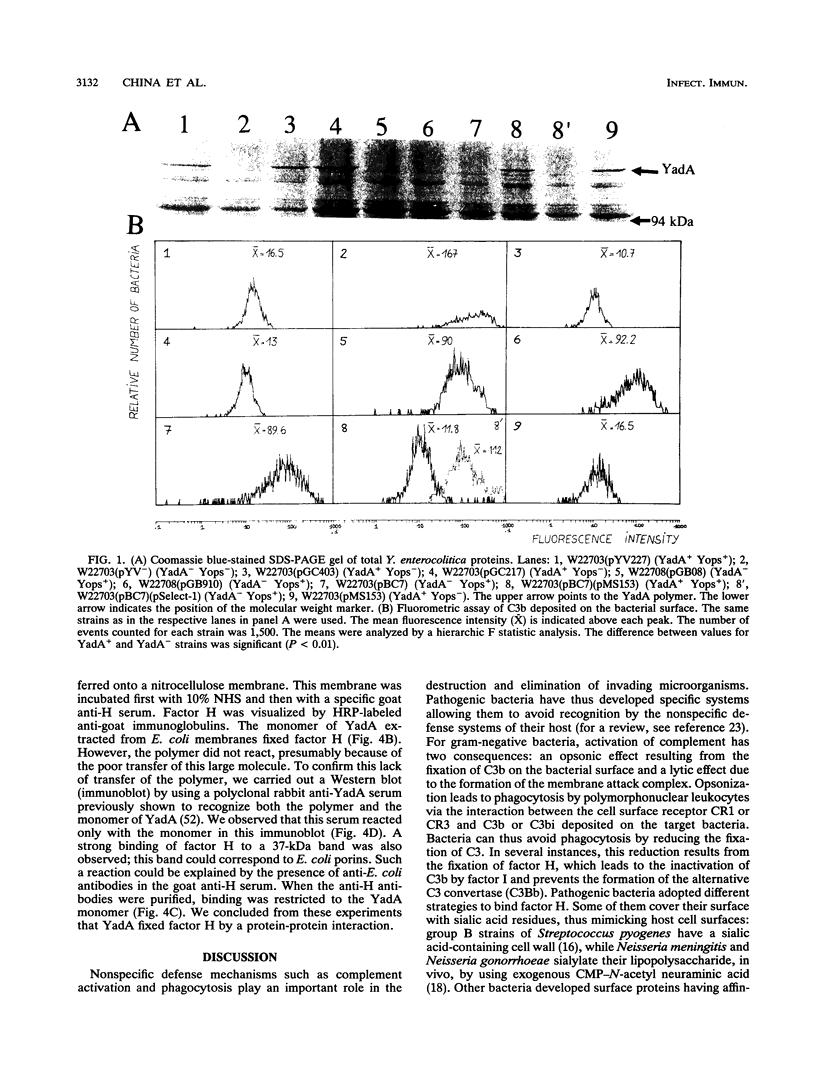
When mixed with normal human serum, wild-type pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica, previously incubated at 37 degrees C, fixed less C3b than its variant cured of the virulence plasmid pYV. Mutants unable to secrete the Yop proteins were still protected against C3b deposition. By contrast, mutants deficient in the production of outer membrane protein YadA fixed more C3b than their YadA+ parent. Gene yadA, cloned as a minimal polymerase chain reaction fragment and introduced in trans, complemented the mutations. Production of YadA by recombinant Escherichia coli LK111 also resulted in a reduction of the amount of C3b deposited on the bacterial surface. The reduction of C3b at the surface of Y. enterocolitica YadA+ compared with YadA- cells correlated with an increase of the amount of factor H fixed at the bacterial surface. The YadA monomer separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane was able to bind factor H. We conclude that factor H bound to YadA reduces the C3b deposition on the bacterial surface, probably by a rapid inactivation of C3b.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balligand G., Laroche Y., Cornelis G. Genetic analysis of virulence plasmid from a serogroup 9 Yersinia enterocolitica strain: role of outer membrane protein P1 in resistance to human serum and autoagglutination. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):782–786. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.782-786.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biot T., Cornelis G. R. The replication, partition and yop regulation of the pYV plasmids are highly conserved in Yersinia enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jun;134(6):1525–1534. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-6-1525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliska J. B., Clemens J. C., Dixon J. E., Falkow S. The Yersinia tyrosine phosphatase: specificity of a bacterial virulence determinant for phosphoproteins in the J774A.1 macrophage. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1625–1630. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliska J. B., Falkow S. Bacterial resistance to complement killing mediated by the Ail protein of Yersinia enterocolitica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3561–3565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukholm G., Kapperud G., Skurnik M. Genetic evidence that the yopA gene-encoded Yersinia outer membrane protein Yop1 mediates inhibition of the anti-invasive effect of interferon. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2245–2251. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2245-2251.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAUGH D. C., RANDALL R. The role of multiplication of Pasteurella pestis in mononuclear phagocytes in the pathogenesis of flea-borne plague. J Immunol. 1959 Oct;83:348–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- China B., Michiels T., Cornelis G. R. The pYV plasmid of Yersinia encodes a lipoprotein, YlpA, related to TraT. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1585–1593. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G. R., Sluiters C., Delor I., Geib D., Kaniga K., Lambert de Rouvroit C., Sory M. P., Vanooteghem J. C., Michiels T. ymoA, a Yersinia enterocolitica chromosomal gene modulating the expression of virulence functions. Mol Microbiol. 1991 May;5(5):1023–1034. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Colson C. Restriction of DNA in Yersinia enterocolitica detected by recipient ability for a derepressed R factor from Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):285–291. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Laroche Y., Balligand G., Sory M. P., Wauters G. Yersinia enterocolitica, a primary model for bacterial invasiveness. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):64–87. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Sluiters C., de Rouvroit C. L., Michiels T. Homology between virF, the transcriptional activator of the Yersinia virulence regulon, and AraC, the Escherichia coli arabinose operon regulator. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):254–262. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.254-262.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Sory M. P., Laroche Y., Derclaye I. Genetic analysis of the plasmid region controlling virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica 0:9 by Mini-Mu insertions and lac gene fusions. Microb Pathog. 1986 Aug;1(4):349–359. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Vanootegem J. C., Sluiters C. Transcription of the yop regulon from Y. enterocolitica requires trans acting pYV and chromosomal genes. Microb Pathog. 1987 May;2(5):367–379. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. S., Kasper D. L., Jennings H. J., Baker C. J., Nicholson-Weller A. Capsular sialic acid prevents activation of the alternative complement pathway by type III, group B streptococci. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1278–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emödy L., Heesemann J., Wolf-Watz H., Skurnik M., Kapperud G., O'Toole P., Wadström T. Binding to collagen by Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis: evidence for yopA-mediated and chromosomally encoded mechanisms. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6674–6679. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6674-6679.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. J., Curry A., Jones D. M., Demarco de Hormaeche R., Parsons N. J., Cole J. A., Smith H. The surface structure seen on gonococci after treatment with CMP-NANA is due to sialylation of surface lipopolysaccharide previously described as a 'capsule'. Microb Pathog. 1991 Sep;11(3):199–210. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90050-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galyov E. E., Håkansson S., Forsberg A., Wolf-Watz H. A secreted protein kinase of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is an indispensable virulence determinant. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):730–732. doi: 10.1038/361730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity of an essential virulence determinant in Yersinia. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2166336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstmann R. D., Sievertsen H. J., Knobloch J., Fischetti V. A. Antiphagocytic activity of streptococcal M protein: selective binding of complement control protein factor H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1657–1661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstmann R. D. Target recognition failure by the nonspecific defense system: surface constituents of pathogens interfere with the alternative pathway of complement activation. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):721–727. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.721-727.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Namork E., Skurnik M., Nesbakken T. Plasmid-mediated surface fibrillae of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica: relationship to the outer membrane protein YOP1 and possible importance for pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2247–2254. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2247-2254.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Skarpeid H. J., Solberg R., Bergan T. Outer membrane proteins and plasmids in different Yersinia enterocolitica serogroups isolated from man and animals. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Feb;93(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert de Rouvroit C., Sluiters C., Cornelis G. R. Role of the transcriptional activator, VirF, and temperature in the expression of the pYV plasmid genes of Yersinia enterocolitica. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(3):395–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K. Y., Reisner B. S., Straley S. C. YopM inhibits platelet aggregation and is necessary for virulence of Yersinia pestis in mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3262–3271. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3262-3271.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K. Y., Straley S. C. The yopM gene of Yersinia pestis encodes a released protein having homology with the human platelet surface protein GPIb alpha. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4623–4632. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4623-4632.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian C. J., Hwang W. S., Pai C. H. Plasmid-mediated resistance to phagocytosis in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1176–1183. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1176-1183.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian C. J., Pai C. H. Inhibition of human neutrophil chemiluminescence by plasmid-mediated outer membrane proteins of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):145–151. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.145-151.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J. Thermoregulation-dependent expression of Yersinia enterocolitica protein 1 imparts serum resistance to Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3732–3739. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3732-3739.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels T., Vanooteghem J. C., Lambert de Rouvroit C., China B., Gustin A., Boudry P., Cornelis G. R. Analysis of virC, an operon involved in the secretion of Yop proteins by Yersinia enterocolitica. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):4994–5009. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.4994-5009.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular organization and function of the complement system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:321–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paerregaard A., Espersen F., Jensen O. M., Skurnik M. Interactions between Yersinia enterocolitica and rabbit ileal mucus: growth, adhesion, penetration, and subsequent changes in surface hydrophobicity and ability to adhere to ileal brush border membrane vesicles. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):253–260. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.253-260.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilz D., Vocke T., Heesemann J., Brade V. Mechanism of YadA-mediated serum resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O3. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):189–195. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.189-195.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice M. Transfusing Yersinia enterocolitica. BMJ. 1992 Sep 19;305(6855):663–664. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6855.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner B. S., Straley S. C. Yersinia pestis YopM: thrombin binding and overexpression. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5242–5252. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5242-5252.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Bölin I., Wolf-Watz H. Inhibition of phagocytosis in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis: a virulence plasmid-encoded ability involving the Yop2b protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2139–2143. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2139-2143.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Forsberg A., Rimpiläinen M., Bergman T., Wolf-Watz H. The cytotoxic protein YopE of Yersinia obstructs the primary host defence. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):657–667. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Skurnik M., Wolf-Watz H. Increased virulence of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis by two independent mutations. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):522–524. doi: 10.1038/334522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhauser T. J., Helinski D. R. Regions of broad-host-range plasmid RK2 involved in replication and stable maintenance in nine species of gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):446–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.446-455.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Koops H., Burkhardt H., Heesemann J., von der Mark K., Emmrich F. Plasmid-encoded outer membrane protein YadA mediates specific binding of enteropathogenic yersiniae to various types of collagen. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2153–2159. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2153-2159.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M., Bölin I., Heikkinen H., Piha S., Wolf-Watz H. Virulence plasmid-associated autoagglutination in Yersinia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1033–1036. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1033-1036.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M., Wolf-Watz H. Analysis of the yopA gene encoding the Yop1 virulence determinants of Yersinia spp. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):517–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Identification, developmental regulation, and response to heat shock of two antigenically related forms of a major nuclear envelope protein in Drosophila embryos: application of an improved method for affinity purification of antibodies using polypeptides immobilized on nitrocellulose blots. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):20–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sory M. P., Cornelis G. Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 as a potential live oral carrier for protective antigens. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jun;4(6):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sory M. P., Tollenaere J., Laszlo C., Biot T., Cornelis G. R., Wauters G. Detection of pYV+ Yersinia enterocolitica isolates by P1 slide agglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2403–2408. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2403-2408.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tertti R., Eerola E., Lehtonen O. P., Ståhlberg T. H., Viander M., Toivanen A. Virulence-plasmid is associated with the inhibition of opsonization in Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 May;68(2):266–274. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tertti R., Skurnik M., Vartio T., Kuusela P. Adhesion protein YadA of Yersinia species mediates binding of bacteria to fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):3021–3024. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.3021-3024.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachter E., Brade V. Influence of surface modulations by enzymes and monoclonal antibodies on alternative complement pathway activation by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1984–1989. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1984-1989.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaleska M., Lounatmaa K., Nurminen M., Wahlström E., Mäkelä P. H. A novel virulence-associated cell surface structure composed of 47-kd protein subunits in Yersinia enterocolitica. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1013–1018. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03732.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D. L., Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Vanderzant C., Vickery J. C., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. Plasmid-mediated tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):224–226. doi: 10.1038/283224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]