Abstract
The interaction of the macrophage cell line P388D1 with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the absence of stimulators or opsonins led to substantial association of bacteria, as judged by visual counting and FACScan assays. This association was observable within 5 min of addition of bacteria, could not be disturbed by exhaustive washing, and occurred with pilus- or flagellum-deficient mutants but not with rpoN mutants, which have been proposed to lack a secondary adhesin. In contrast, specific antibody was capable of causing similar enhancement of bacterial uptake regardless of the rpoN phenotype. Fibronectin stimulated uptake of bacteria with the pilus as an adhesin, and stimulation was observable within 5 min. Both fibronectin-enhanced and antibody-opsonized uptake were susceptible to inhibition by pertussis toxin but not by cholera toxin. The influence of fibronectin on P388D1 cells was distinguishable from that of lipopolysaccharide, which caused substantial morphological changes in cells. Although lipopolysaccharide stimulated bacterial uptake, it actually suppressed fibronectin-mediated enhancement of uptake at high concentrations.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjerknes R. Flow cytometric assay for combined measurement of phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Candida albicans. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Aug 3;72(1):229–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Sklar L. A., Smolen J. E. Guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins as transducers of receptor-stimulated neutrophil activation. Int J Tissue React. 1987;9(4):285–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Newell A. M., Gresham H. D. Molecular regulation of phagocyte function. Evidence for involvement of a guanosine triphosphate-binding protein in opsonin-mediated phagocytosis by monocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3777–3782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi E., Mehl T., Nunn D., Lory S. Interaction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with A549 pneumocyte cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):822–828. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.822-828.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. B., Barsoum I. S., Ramwell P. W., Yeager H., Jr Human alveolar macrophages: effects of endotoxin in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):753–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.753-758.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn D. L., Barke R. A., Knight N. B., Humphrey E. W., Simmons R. L. Role of resident macrophages, peripheral neutrophils, and translymphatic absorption in bacterial clearance from the peritoneal cavity. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):257–264. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.257-264.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Raffle V. J., Nicas T. I. Involvement of the outer membrane in gentamicin and streptomycin uptake and killing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):777–785. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Wieczorek A. A., Mutharia L. M., Poole K. Monoclonal antibodies against Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane antigens: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):166–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.166-171.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara-Kuge S., Amano F., Nishijima M., Akamatsu Y. Isolation of a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-resistant mutant, with defective LPS binding, of cultured macrophage-like cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6606–6610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett M. M., Klaus G. G. G protein regulation of receptor signalling. Immunol Today. 1988 Oct;9(10):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensler T., Raulf M., Megret F., Alouf J. E., König W. Modulation of leukotriene generation by pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3165–3171. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3165-3171.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K., Lory S. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants with altered piliation. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5663–5667. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5663-5667.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly N. M., Kluftinger J. L., Pasloske B. L., Paranchych W., Hancock R. E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa pili as ligands for nonopsonic phagocytosis by fibronectin-stimulated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3841–3845. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3841-3845.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluftinger J. L., Kelly N. M., Hancock R. E. Stimulation by fibronectin of macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):817–822. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.817-822.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluftinger J. L., Kelly N. M., Jost B. H., Hancock R. E. Fibronectin as an enhancer of nonopsonic phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by macrophages. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2782–2785. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2782-2785.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Handwerger B. S., Wunderlich J. R. Identification of macrophage-like characteristics in a cultured murine tumor line. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):894–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara M., Kang M. S., Yamada K. M. Site-directed mutagenesis of the cell-binding domain of human fibronectin: separable, synergistic sites mediate adhesive function. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obi C. L., Coker A. O. The role of macrophages in experimental Campylobacter-infections of mice in Lagos, Nigeria. Trop Geogr Med. 1989 Apr;41(2):154–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Textor J. A., Vann J. M., Mosher D. F. Role of fibronectin in human monocyte and macrophage bactericidal activity. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):629–637. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.629-637.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
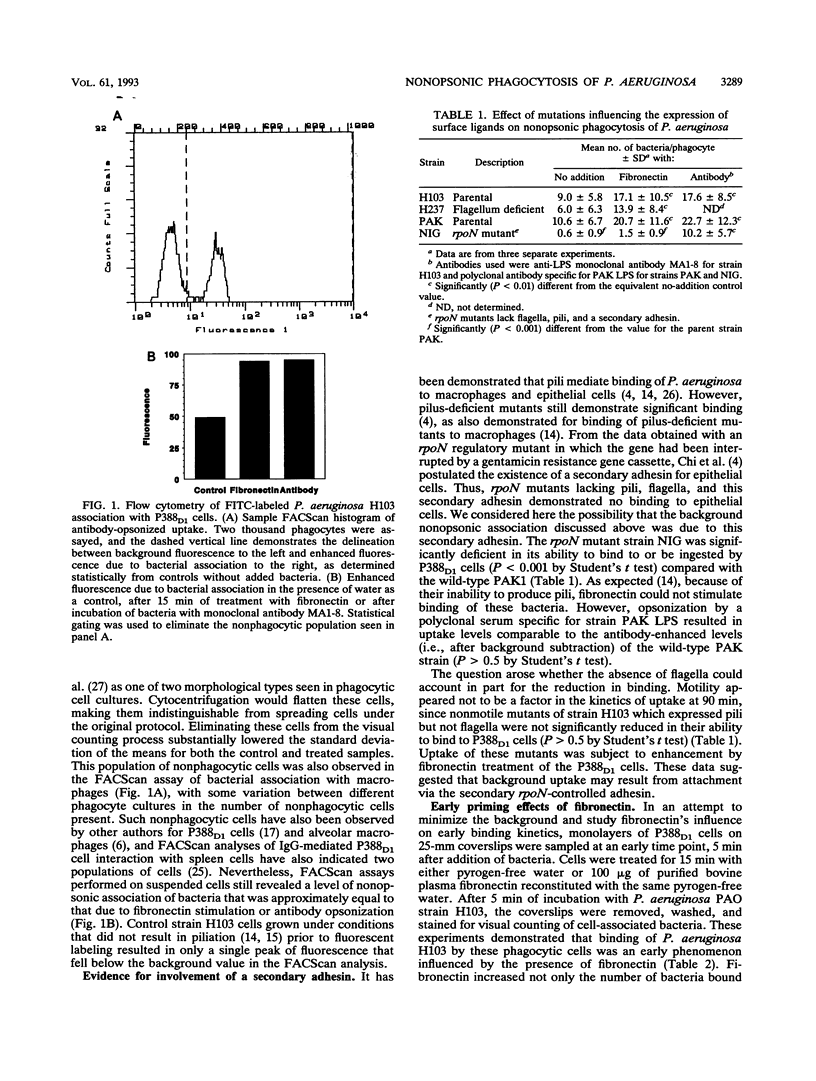
- Ramphal R., Koo L., Ishimoto K. S., Totten P. A., Lara J. C., Lory S. Adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pilin-deficient mutants to mucin. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1307–1311. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1307-1311.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose R. M. Pulmonary macrophages in nosocomial pneumonia: defense function and dysfunction, and prospects for activation. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Jan;8(1):25–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01964116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner T., Keller H. U., Hess M. W., Cottier H. Macrophage functions in antimicrobial defense. Klin Wochenschr. 1982 Jul 15;60(14):720–726. doi: 10.1007/BF01716563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Stephany D. A. The mechanism of intercellular aggregation. I. The kinetics of the Fc gamma receptor-mediated aggregation of P388D1 cells with antibody-coated lymphocytes at 4 degrees C. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1924–1930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speert D. P., Eftekhar F., Puterman M. L. Nonopsonic phagocytosis of strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1006–1011. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1006-1011.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Licht M. R., Craigmyle L. S., Silverstein S. C. Communication between receptors for different ligands on a single cell: ligation of fibronectin receptors induces a reversible alteration in the function of complement receptors on cultured human monocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):336–339. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Meyer B. C. Fibronectin receptor of human macrophages recognizes the sequence Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):762–767. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Reber A. M., Dahinden C. A. The role of formylpeptide receptors, C5a receptors, and cytosolic-free calcium in neutrophil priming. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):242–249. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]