Abstract
The importance of fatty acids to the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, and differences due to a type I fatty acid synthesis (FAS) pathway in the parasite, make it an attractive drug target. In the present study, we developed and a utilized a pharmacophore to select compounds for testing against PfKASIII, the initiating enzyme of FAS. This effort identified several PfKASIII inhibitors that grouped into various chemical classes of sulfides, sulfonamides, and sulfonyls. Approximately 60% of the submicromolar inhibitors of PfKASIII inhibited in vitro growth of the malaria parasite. These compounds inhibited both drug sensitive and resistant parasites and testing against a mammalian cell line revealed an encouraging in vitro therapeutic index for the most active compounds. Docking studies into the active site of PfKASIII suggest a potential binding mode that exploits amino acid residues at the mouth of the substrate tunnel.
Introduction
Plasmodium falciparum, the deadliest species of malaria worldwide, is responsible for the deaths of 2.7 million people and the infection of 400–900 million annually.1 Resistance to known antimalarials and the lack of an effective vaccine has created an urgent need to discover new biologically active compounds. Many apicomplexan parasites, including Plasmodium falciparum, harbor a four-membrane plastid organelle (called the apicoplast) that is believed to have arisen through endosymbiosis of an algal cell that had previously incorporated a cyanobacterium.2–4 Because of its prokaryotic origin, the apicoplast contains metabolic pathways that differ significantly from those found in the human host and are potential targets for new therapeutics.5,6
Perhaps the best studied apicoplast metabolic pathway is fatty acid biosynthesis. Most eukaryotes rely on type I fatty acid synthase (FASa) enzymes, which are large multifunctional enzymes composed of one or two polypeptides. Malaria parasites of the genus Plasmodium do not contain a type I FAS, and rely instead on a type II FAS for the de novo production of fatty acids. The type II FAS of P. falciparum is composed of six discrete enzymes and the acyl carrier protein (PfACP), which serves to shuttle the nascent fatty acid between the enzymes of the pathway.5 All six enzymes and PfACP have been produced as pure recombinant proteins and characterized in a variety of assays.7–12 Compound screening efforts have yielded micro-molar inhibitors for several of the P. falciparum enzymes and three of these have been structurally characterized to aid in drug discovery efforts.13–16
Erythrocytic stage malaria parasites scavenge the majority of their fatty acids from the host.17 Thus, the type II FAS is not responsible for bulk membrane biogenesis but is probably necessary for the production of certain fatty acids and related compounds. One possible function of FAS is for the production of lipoate. Lipoic acid is a cofactor that is indispensable for the function of key enzyme complexes involved in oxidative metabolism such as pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH). In P. falciparum, all four subunits of PDH have been exclusively localized to the apicoplast18 and the E2 subunit has been shown to be covalently modified with lipoate.19 Although lipoate can be scavenged from the host, scavenged lipoate is not trafficked to the apicoplast and attached to PDH.19 Thus, apicoplast lipoate is derived from some other source, and although alternative pathways have been suggested, all of them rely on fatty acids produced by the type II FAS.20
The initiating steps of P. falciparum type II FAS rely on PfACP and two enzymes. Malonyl-coenzyme A:ACP transacylase (PfMCAT) catalyzes the formation of malonyl-ACP from malonyl-coenzyme A (malonyl-CoA).8 β-Ketoacyl–ACP synthase III (PfKASIII) catalyzes the condensation of malonyl-ACP and acetyl-CoA, forming a β-ketoacetyl–ACP product (Figure 1).7,8 This reaction is identical to that catalyzed by FabH (the PfKASIII orthologue in E. coli), an enzyme that is being actively pursued as an antimicrobial drug target.21 The FabH crystal structure has been determined,22 and there is a growing collection of FabH inhibitors, most notably those based on the natural product thiolactomycin.23 Thiolactomycin, and its analogues, were first studied as inhibitors of the type II FAS systems of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Pastuerella multocida.24,25 With little or no toxicity in mammals24 and antimicrobial activity, thiolactomycin and analogues were an excellent starting point for drugs against malaria. Thiolactomycin was also known to selectively target type II but not type I FAS in vitro and in vivo.26,27 Although there was some antimalarial activity reported for thiolactomycin against P. falciparum (IC50 = 50 μM),8,28 there was no activity observed against the PfKASIII enzyme (IC50 > 330 μM). The antimalarial activity of thiolactomycin is probably due to its inhibition of a paralogue of PfKASIII called PfKASI/II.10 However, Prigge et al. did test several 1,2-dithiole-3-one derivatives of thiolactomycin and found three compounds (HR12, HR19, HR45) that inhibit PfKASIII activity (IC50 values between 0.5 and 10 μM) and inhibit the growth of P. falciparum parasites (IC50 values between 8 and 45 μM in both the W2 and D6 strains).8
Figure 1.

Fatty acid initiation in P. falciparum. Malonyl-coenzyme A:ACP transacylase (MCAT) catalyzes the formation of malonyl-ACP from malonyl-coenzyme A. β-Ketoacyl–ACP synthase III (KASIII) catalyzes the condensation of malonyl-ACP and acetyl-CoA. The product of KASIII (β-ketoacetyl–ACP) is then elongated by the sequential action of four other FAS enzymes.
The characterization of PfKASIII and the wealth of information from studies focused on bacterial FabH enzymes made an excellent beginning for an investigation of PfKASIII as an antimalarial drug target. Our laboratory optimized a 96-well plate PfKASIII inhibitory screen and determined the inhibitory activity of compounds from the Walter Reed Chemical Library as well as several commercial libraries. In this study, we report the identification 13 compounds with IC50 values below 1.0 μM, eight of which inhibit the growth of P. falciparum parasites at concentrations below 10 μM. These PfKASIII inhibitors fall into three new chemotypes (sulfides, sulfonamides, sulfonyls) and were identified based on a guided selection process rather than by brute force screening. In this report, we describe how our rational structure-based drug design program combined powerful virtual screening tools, such as an iteratively refined 3D-pharmacophore and quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR), to greatly increase our ability to select and identify PfKASIII inhibitors.
Results and Discussion
Development of a PfKASIII Pharmacophore
Thiolactomycin (TLM) is a known inhibitor of bacterial KAS enzymes with the reported in vivo IC50 of 75 μM.26 In the initial stages of this work, we focused on TLM and related compounds8,29 with the rationale that similar compounds could be specific PfKASIII inhibitors. We used TLM to compute our preliminary pharmacophore for searching for lead compounds in our in-house chemicals database (Chemical Information Systems, CIS) as follows. The global energy minimum conformation of TLM was calculated by computing a conformational model for TLM using the systematic search algorithm and also the Monte Carlo simulated annealing algorithm. Because only the surface accessible chemical functions can interact with the target protein or receptor, we used the molecular electrostatic surface potential map based on solvent accessible Connolly surface.30 The electrostatic surface map showed four accessible chemical functions as two hydrogen bond acceptors sites, one each for the carbonyl oxygen and sulfur atoms, and two hydrophobic sites for the ethylene moiety and the methyl group alpha to the carbonyl carbon. Thus, the preliminary pharmacophore with two hydrogen bond acceptors and two hydrophobic functions was computed using the geometry optimized global minimum conformer of TLM. The overlay of TLM on the preliminary pharmacophore is shown in Figure 2A. Virtual screening of CIS using the preliminary pharmacophore gave several lead compounds. We iteratively refined our pharmacophore with the IC50 data of these lead compounds to furnish an intermediate pharmacophore. The intermediate pharmacophore comprised of two hydrogen bond acceptors and one hydrophobic function. The overlay of TLM on the intermediate pharmacophore is shown in Figure 2B.
Figure 2.

Refinement of the PfKASIII pharmacophore. (A) Initial pharmacophore mapped onto thiolactomycin. (B) Refined pharmacophore no longer maps to thiolactomycin.
Further virtual screening of CIS using the intermediate pharmacophore furnished compounds belonging to four chemical classes (sulfides, sulfonamides, sulfonyls, and other miscellaneous). After measuring the experimental PfKASIII inhibition IC50 values, as described later in this article, we refined and validated the final pharmacophore as follows. A data set, shown in Table 1, of 28 compounds from all the chemical classes were selected for 3D-QSAR computation, such that they not only provide a diverse selection of compounds with broad range of activity but also a bias for the more active compounds. The compounds were categorized into three activity classes with 1 order of magnitude for each class and based on the observed bioactivity data distribution with 0.1–15 μM as very active represented by symbol +++, 15–150 μM as moderately active represented by symbol ++, and >150 μM as less active represented by symbol +. There were 15 very active, nine moderately active, and four less active compounds selected. The data set had a range of activity of at least 3 orders of magnitude with the most active compound showing 0.1 μM and the least active compound showing 195 μM activity, as prescribed in Catalyst.31 We divided the data set of 28 compounds into a training set and test set of 16 and 12 compounds (~40% in test set) using a random selection approach. All the training and test set compounds were subjected to the best quality conformational search, using a constraint of 20 kcal mol−1 energy threshold above the global energy minimum and the default Charmm force field parameters.32 To ensure maximum coverage of the conformational space, a maximum of 250 conformers were generated. The common functions found in all compounds were hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA) and ring aromatic (RA), while the differing functions found among data set compounds were hydrogen bond donor (HBD), hydrophobic aromatic type (HYD-Aro), and hydrophobic aliphatic type (HYD-Ali). For the pharmacophore development, we selected the common functions hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, hydrophobic (which includes both the HYD-Aro and HYD-Ali), and ring aromatic with the minimum and maximum count to 0 and 5 respectively for all the functions. Catalyst produced 10 hypotheses and Hypo1A was found to be the best and statistically most significant with the following metrics. Hypo1A showed a correlation coefficient of 0.79 with the total cost of 531.26, when the null cost was 4914.9 and the fixed cost was 31.36, at the uncertainty value of 1.1. The regression plot of observed vs predicted bioactivities of Hypo1A is presented in Figure 3. The predicted activities, error values, and the observed and predicted activity class values for the training and test set compounds are shown in Table 1. Hypo1A is shown in Figure 4A. The overlay of the most active representative compounds 3a and 4a on Hypo1A display an excellent mapping as shown in parts B and C of Figure 4, whereas the overlay of least active representative compounds 2b and 3l on Hypo1A result in the poor mapping as shown in parts D and E of Figure 4.
Table 1.
Training and test set values for Hypo1A
| Training Set Observed and Predicted Values for Hypo1A | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| compd | observed KASIII IC50 (μM) | predicted KASIII IC50 (μM) | error | observed activity class | predicted activity class |
| 2d | 2.2 | 1.6 | −1.4 | +++ | +++ |
| 3a | 0.38 | 0.64 | 1.7 | +++ | +++ |
| 3b | 0.44 | 0.64 | 1.5 | +++ | +++ |
| 3d | 157.5 | 160 | 1 | + | + |
| 3e | 63.8 | 86 | 1.3 | ++ | ++ |
| 3f | 192.6 | 94 | −2.1 | + | ++ |
| 3g | 22.5 | 59 | 2.6 | ++ | ++ |
| 3h | 114.6 | 85 | −1.3 | ++ | ++ |
| 3i | 27.2 | 110 | 3.9 | ++ | ++ |
| 3l | 53.7 | 57 | 1.1 | ++ | ++ |
| 3m | 18.3 | 7.8 | −2.4 | ++ | +++ |
| 3n | 0.52 | 1.1 | 2.2 | +++ | +++ |
| 3p | 164.6 | 110 | −1.5 | + | ++ |
| 3q | 62.9 | 62 | −1 | ++ | ++ |
| 3s | 38.2 | 6.1 | −6.2 | ++ | +++ |
| 4a | 1.5 | 1.3 | −1.2 | +++ | +++ |
| Test Set Observed and Predicted Values for Hypo1 | |||||
| 1e | 1.9 | 4.2 | 2.3 | +++ | +++ |
| 1f | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.32 | +++ | +++ |
| 1h | 0.13 | 0.12 | −0.01 | +++ | +++ |
| 1i | 1.4 | 3.7 | 2.3 | +++ | +++ |
| 1k | 0.53 | 0.21 | −0.32 | +++ | +++ |
| 2a | 5.0 | 27 | 5.4 | +++ | ++ |
| 2b | 195.2 | 58 | −3.4 | + | ++ |
| 2f | 5.2 | 0.76 | −6.8 | +++ | +++ |
| 3c | 0.13 | 130 | 1018 | +++ | + |
| 3k | 48.1 | 10 | −4.8 | ++ | +++ |
| 3r | 0.32 | 0.44 | 1.4 | +++ | +++ |
| 4b | 3.2 | 0.1 | −3.1 | +++ | +++ |
| activity class | IC50 range (μM) | symbol | |||
| veryactive | 0.001–15 | +++ | |||
| modactive | 15–150 | ++ | |||
| less active | >150 | + | |||
Figure 3.
Regression plot of observed vs predicted bioactivity of pharmacophore hypothesis Hypo1A.
Figure 4.
Specificity of the refined PfKASIII pharmacophore. (A) Pharmacophore hypothesis Hypo1A (green, hydrogen bond acceptor; orange, ring aromatic; cyan, hydrophobic). (B) Compound 3a mapped onto Hypo1A showing the para methyl phenyl ring acting as the ring aromatic moiety, the hydroxyl group ortho to the sulfonyl group acting as the hydrogen bond acceptor while the naphthyl ring contributes as the hydrophobic moiety. (C) Compound 4a mapped onto Hypo1A showing the para methoxy phenyl ring acting as the ring aromatic moiety, the sulfur group acting as the hydrogen bond acceptor while the phenyl ring of the benzene sulfonic acid portion contributes as the hydrophobic moiety. (D) Compound 2b mapped onto Hypo1A showing the phenyl ring of the benzene sulfonic acid part acting as the ring aromatic moiety, no mapping on the hydrogen bond acceptor, and a poor mapping of the chlorine as the hydrophobic moiety. (E) Compound 3l mapped onto Hypo1A showing the naphthyl ring acting as the ring aromatic moiety, no mapping on the hydrogen bond acceptor, and a moderate mapping of the para methyl group of the toulamide portion as the hydrophobic moiety.
Identification of Distinct Chemical Classes as PfKASIII Inhibitors
Using the PfKASIII specific pharmacophore and analogue search criteria, the Walter Reed Chemical Information System (WR-CIS) database was searched for potential inhibitors. This effort resulted in the identification of numerous PfKASIII inhibitors that could be grouped into four distinct chemical classes. These classes include the sulfides, sulfonamides, sulfonyls, and a miscellaneous group containing a mixture of structurally unrelated compounds. A detailed SAR analysis, however, could not be provided because these compounds were identified through pharmacophore fitness and not through derivatization of a lead compound. In addition to testing the identified compounds against PfKASIII, all compounds were evaluated for antimalarial activity using an in vitro growth inhibition assay. The drug sensitive D6 and drug resistant W2 strains of P. falciparum were used to assess differences in inhibitor sensitivities. In some cases, the multidrug resistant strain, TM91C235, was included to establish a broader anti-malarial profile.
a. Sulfides
A group of eleven phenylsulfanyl-phenol compounds were identified that contained potent activity against PfKASIII with an IC50 value range of 11.0–0.1 μM (Table 2). Within this class, the disulfides were the most potent at submicromolar concentrations. The trisulfide substituents were equally active against PfKASIII (compare 1f and 1k). The presence of chlorine or hydroxyl groups within the phenol rings of the disulfide compounds had little effect on PfKASIII activity (compare compounds against 1d). Disulfides have been previously reported as potent PfKASIII inhibitors. The compounds HR12, HR19, and HR45 were potent in the low to submicromolar range.8 Those particular compounds, however, are simple disulfides that also inhibit bacterial FabH.33 Most recently, several alkyl-CoA disulfides were shown to be effective inhibitors through a sulfhydryl–disulfide exchange with the catalytic cysteine buried within the bacterial FabH active site.34 Significant identity between bacterial FabH and PfKASIII active sites suggests that the sulfide compounds reported in this study may also inhibit PfKASIII through a similar mechanism. Interestingly, compounds 1b and 1c are extremely similar to recently published inhibitors of β-ketoacyl–ACP reductase (PfKAR).14 PfKAR uses the product of the PfKASIII reaction and catalyzes the first step in the elongation cycle of fatty acids. The similarity between PfKASIII inhibitors and inhibitors of other FAS enzymes is not as surprising as it may seem. The active sites of FAS enzymes must share certain features which enable them to accommodate the binding of acyl-CoA and/or acyl–ACP substrates.
Table 2.
Sulfides
| Sulfides | Biological Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Structure | KASIII IC50 (μM) | P.f. W2 IC50 (μM) | P.f. D6 IC50 (μM) |
| 1a | 2.8 | 4.7 | 5.2 | |
| 1b |  |
3.1 | 21.5 | 20.5 |
| 1c |  |
10.8 | >49.9 | >49.9 |
| 1d |  |
0.65 | 6.7 | 5.0 |
| 1e |  |
1.9 | 15.0 | 14.9 |
| 1f |  |
0.14 | 12.0 | 12.4 |
| 1g | 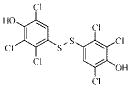 |
0.24 | 5.5 | 3.9 |
| 1h |  |
0.13 | 6.6 | 7.2 |
| 1i | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.5 | |
| 1j | 0.63 | 2.1 | 2.5 | |
| 1k |  |
0.53 | 1.4 | 2.3 |
The entire class of sulfide compounds showed moderate activity against the malaria parasite. Approximately 70% of the compounds exhibited less than a 10 μM IC50 value (Table 2). No significant difference was observed between drug sensitive and resistant parasites.
b. Sulfonamides
Seven sulfonamides were identified for testing. These compounds were not as potent as the phenylsulfonyl–phenol compounds (Table 2), but they did offer structural variation with a range of IC50 values from 0.3 μM to >1.0 mM (Table 3). The most active compounds from this group were the thiophene sulfonic phenylamides (2d and 2g). Two compounds from this group failed to inhibit PfKASIII at the highest concentration tested (2c and 2e), suggesting that modifications of the phenol–sulfonamide core can dramatically alter PfKASIII inhibition. From this data set, we conclude that the thiophene sulfonamide derivatives are better PfKASIII inhibitors than the phenyl–sulfonamides.
Table 3.
Sulfonamides
| Sulfonamides | Biological Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Structure | KASIII IC50 (μM) | P.f. W2 IC50 (μM) | P.f. D6 IC50 (μM) |
| 2a | 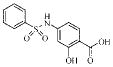 |
50 | >12.7 | >12.7 |
| 2b |  |
195.2 | >49.9 | >49.9 |
| 2c |  |
>1mM | 6.1 | 0.04 |
| 2d |  |
2.2 | >49.9 | >49.9 |
| 2e | >1mM | >49.9 | >49.9 | |
| 2f |  |
5.2 | 11.4 | 10.3 |
| 2g |  |
0.28 | 16.4 | 15.4 |
The majority of the sulfonamide compounds displayed poor antimalarial activity (Table 3). The most potent PfKASIII inhibitor, 2g, demonstrated modest activity against both drug resistant and sensitive parasites. Compound 2c failed to inhibit PfKASIII with concentrations as high as 1.0 mM; however, this compound demonstrated robust antimalarial activity, suggesting a mechanism of action other than PfKASIII inhibition. This compound was approximately 100-fold more active against D6 than W2 parasites, possibly reflecting differences of inhibitor efflux or genetic differences in the targeted mechanism of action. While compound 2c can not be developed as a PfKASIII-specific inhibitor, it may be a useful tool for future studies to understand drug resistance mechanisms between parasites with diverse drug sensitivities.
c. Sulfonyls
Numerous sulfonyl compounds were identified as inhibitors of PfKASIII. Five of the 19 compounds tested were potent at submicromolar concentrations (Table 4). Four of these compounds were relatively equivalent in their capacity to inhibit PfKASIII and parasite growth and could be further grouped into two distinct classes, benzenesulfonyl–naphthalenes and benzene-sulfonyl–benzenes. A benzenesulfonyl-naphthalene-1,4-diol displayed the greatest activity, suggesting that the addition of hydroxyl groups on the naphthalene ring may increase activity of the PfKASIII inhibitor (compare 3a and 3l). Benzenesulfonyl–benzene compounds containing the same reactive hydroxyl groups were not as active (compare 3a and 3f), suggesting that integrity of the naphthalene ring system is important to maintain potency against PfKASIII. One exception to this observation is with compound 3c in which the benzene rings populated with amines and halogens result in the most potent compound within the class of sulfonyls. Benzenesulfonyl-quinazoline-2,4-diamine compounds failed to inhibit PfKASIII, suggesting that substitution of a more reactive ring system does not result in better inhibitory properties.
Table 4.
Sulfonyls
| Sulfonyls | Biological Data | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Structure | KASIII IC50 (μM) | P.f. W2 IC50 (μM) | P.f. D6 IC50 (μM) | P.f. TM91C235 IC50 (μM) |
| 3a |  |
0.38 | 3.2 | 3.6 | ND |
| 3b |  |
0.44 | 20.4 | 3.9 | ND |
| 3c | 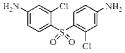 |
0.13 | 5.5 | 0.01 | ND |
| 3d | 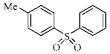 |
157.5 | 68.9 | 35.7 | 111.9 |
| 3e | 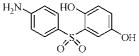 |
63.8 | 3.6 | 0.79 | 5.3 |
| 3f |  |
192.6 | 64.3 | 37.8 | 60.5 |
| 3g | 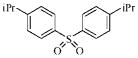 |
22.5 | 23.5 | 18.5 | 32.7 |
| 3h | 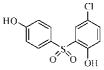 |
114.6 | 45.7 | 38.6 | 80.8 |
| 3i | 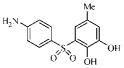 |
27.2 | 23.6 | 19.7 | 3.4 |
| 3j |  |
22.0 | >55.3 | 0.30 | >55.3 |
| 3k |  |
48.1 | 20.7 | 29.2 | 31.7 |
| 3l | 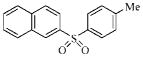 |
53.7 | >230.2 | >230.2 | >230.2 |
| 3m |  |
18.3 | 1.2 | 0.43 | 1.4 |
| 3n | 0.52 | 5.8 | 3.0 | ND | |
| 3o |  |
447.7 | >50.1 | >50.1 | ND |
| 3p | 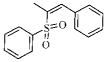 |
164.6 | >50.1 | 28.0 | ND |
| 3q |  |
62.9 | 84.1 | 45.3 | >203.7 |
| 3r | 0.32 | >41.2 | >41.2 | ND | |
| 3s | 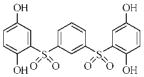 |
38.2 | 7.1 | 26.0 | 4.5 |
The sulfonyl compounds showed a broad range of activity against malaria parasites in culture. In general, the most potent PfKASIII inhibitors displayed the best activity against the parasites (Table 4). Several of the sulfonyls displayed better activity against the drug sensitive D6 parasites, for example, compounds 3c, 3e, and 3j. This phenomenon was not dependent on the potency of the compounds for PfKASIII and was not a characteristic of the entire class of compounds. To further characterize the drug sensitivity differences, several compounds were tested against the multidrug resistant strain TM91C235. The inhibitory profile mirrored that of the drug resistant W2 strain, suggesting that a general drug resistant mechanism such as efflux or transport may confer resistance to these inhibitors rather than differences in a molecular target.
d. Miscellaneous Compounds
The use of a pharmacophore to select compounds for testing rather than obtaining derivatives of a single chemical class, resulted in the identification of structurally unrelated compounds. These compounds therefore were grouped independently (Table 5). Four compounds provide unique chemotypes that lack sulfur atoms and were moderately active against both PfKASIII and parasites in culture. No significant difference in antimalarial activity was observed between drug sensitive and resistant parasites. Sulfur containing compounds comprise the majority of known FabH (KASIII) inhibitors, and the new chemotypes identified here represent a departure from this trend. Compounds such as 4d may serve as leads for further derivatization, leading to potent inhibitors that do not contain sulfur.
Table 5.
Miscellaneous Compounds
| Miscellaneous | Biological Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Structure | KASIII IC50 (μM) | P.f. W2 IC50 (μM) | P.f. D6 IC50 (μM) |
| 4a |  |
1.5 | 22.5 | 22.5 |
| 4b | 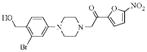 |
3.2 | 8.9 | 8.9 |
| 4c |  |
4.9 | >49.9 | >49.9 |
| 4d |  |
0.24 | 14.6 | 24.7 |
| 4e |  |
25.8 | >49.9 | 20.4 |
Correlation between Antimalarial Activity and PfKASIII Inhibition
All compounds from this study were tested for antimalarial activity using an in vitro malaria assay with both drug sensitive and resistant strains of P. falciparum. Most of the compounds tested demonstrated significant anti-malarial activity. Establishing a true correlation between PfKASIII inhibition and antimalarial activity is difficult to achieve in the absence of a genetic model. A pharmacological correlation could however be established; approximately 60% of the compounds with submicomolar PfKASIII IC50 values also inhibit parasite growth at concentrations less than 10 μM (Table 6). This study did not address the issue of target validation; therefore, we cannot conclude that antimalarial activity was solely due to inhibition of PfKASIII. Previous work has demonstrated that inhibitors of additional FAS enzymes results in parasite death, suggesting that a correlation may exist.5 A few compounds, for example 3r, are potent inhibitors of PfKASIII but fail to inhibit parasite growth. One explanation for this discrepancy could possibly be due to poor permeability of the compounds. Fatty acid biosynthesis occurs in the four membraned organelle known as the apicoplast, and therefore compounds with poor lipid solubility may fail to enter the apicoplast and inhibit PfKASIII.
Table 6.
Correlation between PfKASIII Inhibition and Antimalarial Activity
| compound classa | no. compounds <1.0 μM PfKASIII IC50 valueb | no. compoundsc <10.0 μM Pf W2 IC50 valued |
|---|---|---|
| sulfides (11) | 6 (0.13–11) | 5 (1 to >50) |
| sulfonamides (7) | 1 (0.28 to >1000) | 0 (11 to >50) |
| sulfonyls (19) | 5 (0.13–448) | 3 (1 to >230) |
| miscellaneous compounds (5) | 1 (0.24–26) | 0 (9 to >50) |
The total number of compounds tested from each class in shown in parenthesis.
The values in parenthesis represent the range of PfKASII IC50 values (μM) for the entire compound class.
Only compounds with PfKASIII IC50 values less than 1.0 μM were considered.
The values in parenthesis represent the range of W2 IC50 values (μM) for the entire compound class
FAS is poorly understood in the malaria parasite, therefore it is difficult to predict what effect inhibition of FAS has on malaria growth. For example, it is unknown if partial inhibition of a FAS enzyme will effect parasite growth. The extent of any tolerance for FAS inhibition will have a direct consequence on establishing a correlation between PfKASIII inhibition and parasite death. PfKASIII initiates the FAS cycle, and therefore inhibition of PfKASIII may effect the parasite differently than inhibition of a FAS enzyme involved in the elongation cycle. FAS has not been compared between drug sensitive and drug resistant parasites, and therefore possible differences may exist in both the regulation of FAS and the requirement for fatty acids. Several FAS inhibitors have been tested against drug resistant and sensitive strains of P. falciparum. PfENR inhibitors were found to possess different antimalarial activities between strains with diverse drug susceptibilities,35,36 while PfKAS inhibitors showed equal potency against both drug sensitive and resistant parasites.8,28 It is unclear if this disparity in FAS inhibitor sensitivities between the various strains is due to influx or efflux specific to these compounds or whether differences in the regulation of FAS exist. We find that most of the PfKASIII inhibitors reported in this study do not differ in their ability to inhibit drug resistant and drug sensitive parasites (Tables 2–5). A recent report suggest that FAS may be important for liver stage development of the malaria parasite, accordingly, future studies should test the PfKASIII inhibitors reported here for liver stage activity.37
Structural Studies
To explore potential binding modes of the more potent compounds, we used systematic docking and optimization. The majority of the compounds were in poses similar to that of 3a shown in Figure 5, an aromatic system positioned near the active site residues at the bottom of the substrate tunnel with the remainder of the molecule extending up the substrate tunnel seeking out interaction commensurate with the remaining functional groups in the specific compound. The highest scoring poses for the closely related compound 3b had the fused ring system in the same position as 3a. The requirements for low- and medium-affinity binding to the distal portion of the active site tunnel are minimal, as indicated in our initial pharmacophore model, and have led to our identification of numerous medium-affinity hits. More challenging, however, is teasing out higher affinity binding and optimizing the interactions for a single lead compound class.
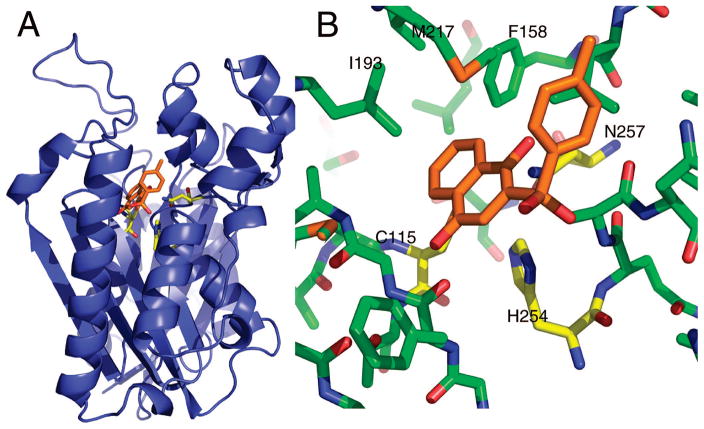
Figure 5.
PfKASIII molecular model. (A) A ribbon representation of the PfKASIII homology model. The active site residues, cysteine 115, histidine 254, and asparagine 257, are shown in yellow sticks. The enzyme active site is buried near the core of the protein with a long substrate tunnel extending to the surface. This tunnel, largely, but not completely, lined with hydrophobic residues, binds coenzyme A, the acyl group donor for the reaction.60 The docked pose of compound 3a is shown in the active site. (B) The predicted interactions between 3a and PfKASIII. The position of the two ring systems in this pose is similar to the predicted poses for the majority of sulfones and sulfonamides: one ring system making van der Waals contacts with the active site triad and the other aligned up the active site tunnel rotated to make optimal contacts based on the particular composition of the second ring.
The clearest docking results were obtained with the sulfonyl compounds containing rings on both sides of the sulfonyl group. This collection of compounds ranged over 3 orders of magnitude in potency despite fairly subtle differences in structure. In particular, ring substituents such as the hydroxyls on compound 3a (IC50 0.38 μM), can have a big impact on potency (compare with compound 3l, IC50 53.7 μM). The general conformation of compound 3a in Figure 5 suggests that the sulfonyl group may interact with the active site histidine (H254) while ring substituents can be poised to interact with the third member of the active site triad (N257). Indeed, compounds without appropriately positioned ring substituents (3d, 3g, 3j, 3k, 3l, 3m, 3o, 3p) tend to be less potent. There are a few exceptions to this trend, most notably compound 3f. It is difficult to explain why substitution of the naphthalene-1,4-diol in 3a with the benzene-1,4-diol in 3f leads to a dramatic loss in potency. One difficulty in modeling KAS enzymes is the possibility that compounds may bind to other structural states. Recent biochemical studies with M. tuberculosis KASIII indicates that KAS enzymes have an open state that has not yet been structurally characterized.38,39 Similarly, work with bacterial KASII shows that the inhibitor platensimycin binds preferentially to the enzyme after acylation of the active site cysteine.40
As mentioned above, a promising approach to increase inhibitor specificity for the PfKASIII enzyme may be exploiting key differences on the surface of the enzyme at the mouth of the substrate tunnel. This approach has already been used successfully by Daines et al., who used structure based design to understand not only shape complementarity within the active site tunnel but also key interactions with surface arginines that are critical for specific, high-affinity binding to the S. pneumoniae FabH enzyme.41 Similar logic may be quite beneficial to our own structure based design efforts for PfKASIII. A sequence alignment of PfKASIII with its counterpart from E. coli reveals five residues that are different between the two substrate tunnels, four of which are surface exposed at the mouth of the tunnel. The Ile155 (Ec) to Leu 201 (Pf) substitution may impart some shape variation within the hydrophobic substrate tunnel, but the substitutions at the mouth of the tunnel provide a much more substantial difference between the two proteins that may be more straightforward to exploit. The substitutions at the surface are as follows, with the E. coli residue listed first in each pair: Gly 152 to Asn 197, Ala 208 to Asn 262, Asn 210 to Lys 264, and Ala 216 to Thr 270. These four amino acid differences result in a more constricted environment at the mouth of the tunnel, with relatively small side chains being replaced by much bulkier ones. Additionally, the polarity of the surface is also quite different. In particular, the lysine at position 264 in PfKASIII may be exploited as the target of an ionic interaction analogous to that incorporated by Daines et al. As those authors also point out, a charged group on the inhibitor could also help with aqueous solubility of the compound.
Therapeutic index
An in vitro therapeutic index was calculated using a J774 murine monocyte-like macrophage clone. The index was calculated as the IC50 of the macrophage cells divided by the IC50 of the P. falciparum W2 strain. The W2 strain was chosen over D6 to factor in possible drug resistance into the index. For many of the compounds, however, either D6 or W2 parasites could have been chosen because no significant growth inhibition differences were observed between these two strains. Many of the sulfonyl compounds were selected for testing because emphasis was placed on these compounds for further development. As expected, we observed variation in the index (Table 7). Compounds 2b, 3g, 3n, and 3r displayed significant toxicity against the mammalian cell line. However, only 3n was potent against both PfKASIII and the parasites. Therefore, down selecting compounds based on a poor toxicity profile does not discard the most efficacious compounds found in this study. In fact, the most efficacious compound against both PfKASIII and the parasites displayed little toxicity (see compounds 1d, 3a, and 3b). In this study, the sulfonyl compounds were by far the most potent compounds and further development may focus on this class. In this regard, we tested most of the sulfonyls in the toxicity assay and found that most of these compounds displayed encouraging therapeutic indexes. In vivo studies are currently planned for several of these compounds to gain a better picture for both toxicity and efficacy.
Table 7.
Selected Compounds Were Tested for Toxicity in Vitro against a Subclone (G8) of the Murine Monocyte-like Macrophage line J774
| compda | mammalian cell in vitro toxicity (IC50, μM) | in vitro therapeutic indexb |
|---|---|---|
| 1d | 123.8 | 12.4 |
| 1h | >1428.0 | >204.0 |
| 2a | >2544.0 | 195.6 |
| 2b | 31.3 | <0.62 |
| 2c | >1612.0 | >268.7 |
| 3a | >3184.0 | >1061.3 |
| 3b | 104.8 | 5.3 |
| 3d | 134.0 | 1.9 |
| 3e | >1886.0 | >471.5 |
| 3f | >1893.0 | >29.6 |
| 3g | 7.3 | 0.30 |
| 3h | 107.0 | 2.3 |
| 3i | 27.6 | 1.2 |
| 3k | >1618.0 | >77.0 |
| 3l | >1773.0 | 7.7 |
| 3m | >2849.0 | >2849.0 |
| 3n | 0.85 | 0.15 |
| 3o | 705.8 | <14.0 |
| 3p | 205.0 | <4.1 |
| 3q | >1618.0 | >19.3 |
| 3r | 33.6 | <0.83 |
| 3s | >1184.0 | >169.1 |
Conclusion
We report for the first time the identification of a diverse set of PfKASIII inhibitors with submicromolar IC50 values. Future efforts with these compounds should strive to develop a structure–activity relationship because derivatives may yield better activity. As a drug discovery project, we were interested in first identifying novel chemotypes and then selecting those for derivatization and further development. With the rapid nature of drug resistance in the malaria parasite, new chemotypes must be introduced into the drug discovery pipeline. The compounds identified in this study may lead to novel antimalarial compounds. Studies are now planned to move a few of these compounds into animal malaria models to determine in vivo efficacy, toxicity, and pharmacological parameters.
Bacterial FabH has been pursued as an antibacterial drug target resulting in the identification of several classes of inhibitors.21,33,41–49 Published reports demonstrate inhibitor sensitivity differences between bacterial FabH and PfKASIII.8,49 A comparison of these enzymes highlights structural features that may account for inhibitor specificities between bacterial FabH and PfKASIII.49 Because of structural and inhibitory sensitivity differences, we chose to identify unique inhibitors of PfKASIII rather than derivatize bacterial FabH inhibitors. Studies are ongoing to address the specificity of these compounds. The compounds identified in this study may also inhibit a second β-ketoacyl–ACP synthase (PfKASI/II) involved in malaria FAS. Studies have demonstrated that PfKASI/II is more sensitive to thiolactomycin than PfKASIII.10 Recently, compounds isolated from natural products displayed potent inhibition profiles for both FabH and FabF.42,44,45 It is exciting to speculate that compounds identified in this study may inhibit two separate enzymes of the malaria FAS pathway. Current antimalarial therapies employ the strategy of combining two or more inhibitors to slow the development of malaria drug resistance. A compound that inhibits both malaria KAS enzymes could behave similarly. To date, no studies have reported combination testing of multiple FAS inhibitors against malaria.
We have developed a PfKASIII pharmacophore with an excellent correlation coefficient of 0.8. The pharmacophore, comprising a hydrogen bond acceptor, ring aromatic, and hydrophobic feature, maps extremely well onto our identified PfKASIII inhibitors. The use of the pharmacophore identified several novel PfKASIII inhibitors that have moderate antimalarial activity. These inhibitors provide a solid foundation for continued medicinal chemistry efforts. Such compound diversity with moderate activity against both the enzyme and parasite provide flexibility to improve pharmacological properties while preserving the inhibitor properties of the compounds. Future efforts will focus on derivatization of these compounds to establish a complete SAR specific for each inhibitor class and to improve potency against PfKASIII and the parasite.
Experimental Section
Protein Expression and Purification of PfKASIII and PfACP
Both PfKASIII and PfACP were expressed and purified from Escherichia coli as a 6xHIS tagged protein. The expression and purification of PfKASIII was previously reported.8 Briefly, 6xHIS-pfKASIII in E. coli was grown in LB broth at 37 °C and induced with 0.4 mM (final concentration) IPTG for 12 h at 20 °C. The culture is then harvested by centrifugation at 6000g and 4 °C for 15 min. The cell pellets are resuspended in cell lysis buffer (20 mM Na/K phosphate, pH7.5, 1 mg/mL lysozyme (Sigma), 2.5 μg/mL DNaseI (Sigma), 200 mM NaCl) and incubated on ice for 10 min followed by sonication and centrifugation. The cell lysate is then applied to a 5 mL HiTrap chelating HP column (Amersham Biosciences/GE Healthcare) and eluted with imidazole. The 6xHIS-PfKASIII fractions are pooled and applied to a HIPrep 26/10 desalting and 5 mL HiTrap SP FF columns (Amersham Biosciences/GE Healthcare). Pure 6xHIS-PfKASIII is eluted from the cation exchange column with NaCl and stored at −80 C.
The 6xHIS-PfACP in E. coli was grown in LB broth at 37 °C and induced with 0.4 mM (final concentration) IPTG for 4 h at 37 °C. The culture is then harvested by centrifugation at 6000 rpm and 4 °C for 15 min. The cell pellets are resuspended in cell lysis buffer (20 mM Na/K phosphate, pH7.5, 1 mg/mL lysozyme (Sigma), 2.5 μg/mL DNaseI (Sigma), 200 mM NaCl) and incubated on ice for 10 min followed by sonication (for 1 min) and centrifugation 16000 rpm for 20 min). The cell lysate is then run over a 5 mL HiTrap FF crude column (Amersham Biosciences/GE Healthcare) and eluted with imidazole. The 6xHIS-PfACP fractions are dialyzed into 4 L of dialysis buffer (20 mM Na/K, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, pH6.5, 4 °C) for 1 h using 10000 MWCO dialysis cassettes (Pierce Scientific). After 1 h, the dialysis cassettes are transferred into a fresh 4 L of buffer for one more hour before aliquoting and freezing.
PfKASIII Inhibitor Screen
We developed a 96-well microplate assay that measures the inhibition of the PfKASIII enzyme by detecting the transfer of [1-14C]-acetyl-CoA to ACP, forming [1-14C]-acetyl–ACP as previously described.5 In the presence of an effective PfKASIII inhibitor, the radiolabel will not be incorporated, resulting in a corresponding decrease in counts per minute. The assay was performed in an untreated clear flat-bottom 96-well plate (Nunc). Each plate includes background, activity, control, and compound reactions. Compounds are first tested in a prescreen at three concentrations (50, 10, and 1 μM); those that show inhibition ≥60% are subsequently tested at concentrations from 50 μM to 24 nM across 12 wells to determine IC50 values. For the dilution plate, compounds were first serially diluted in a separate plate, then 1 μL of each was added to the reaction. Reactions were incubated at 37 °C for 25 min, then quenched with 10% TCA. In both the prescreen and dilution plates, the reactions are transferred to a Whatman Unifilter P81 cellulose filter plate on a vacuum manifold and washed six times with 10% TCA. After drying, the plate bottom was sealed and 30 μL of scintillation fluid (Microscint-O, PerkinElmer) was added to each well. The plate was then sealed and counted in a TopCount scintillation counter (Packard/PerkinElmer). The PfKASI-II assay has a variability of approximately ±0.91 μM, with compounds displaying IC50 values less than 10 μM. Dose–response curves were considered valid if the respective R2 values were greater than 0.80. Compound HR45, a potent inhibitor of PfKASIII,8 was consistently assayed with each batch of investigative compounds and served as an internal control for PfKASIII inhibition. IC50 calculations were determined by nonlinear regression with variable slope using the GraphPad Prism software program.
In Vitro Parasite Assay
The chloroquine-sensitive D6 clone of Sierra Leone I and chloroquine-resistant W2 clone of Indochina I were grown in a continuous culture supplemented with mixed gas (90% nitrogen, 5% oxygen, 5% carbon dioxide), 10% human serum, and 6% hematocrit of A+ red blood cells. Once cultures reached a parasitemia of 3% with at least a 70% ring developmental stage present, parasites were transferred to a 96-well microtiter plate predosed with specific concentrations of known antimalarials drugs and test compounds. Plates were incubated in a mixed gas incubator for 24 h. Following the specified incubation time, [3H]-hypoxanthine was added and parasites were allowed to grow for an additional 18 h. Cells were harvested by a plate harvester (TomTec) onto 96-well filter plates and washed to eliminate unincorporated isotope. Parasite growth was measured as a function of hypoxanthine incorporation in a microtiter plate scintillation counter (Packard). Data from the counter was analyzed by DataAspects Plate Manager software program (DataAspects, Inc., Glencoe, CA) and IC50 values determined from a four parameter nonlinear regression analysis.
Toxicity Assay
Selected compounds were tested for toxicity in vitro against a subclone (G8) of the murine monocyte-like macrophage line J774. The cell line was obtained from Dr. Jose Alunda, Departmento de Sanidad Animal, Facultad de Veterinaria, Universidad Complutense, Madrid, Spain. Murine cells were maintained in 75-cm2 tissue culture flasks in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (GIBCO) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum, 2 mM L-glutamine, 50 μg/mL gentamicin under humidified 5% CO2/95% air at 37 °C. Toxicity tests were performed in 96-well tissue culture plates using an aqueous tetrazolium/formazan system as described.50 Cells were plated at a density of 1 × 104 cells/well in 100 μL of culture medium. After 24 h under culture conditions, 10 μL of test compound or vehicle control were diluted to appropriate concentrations in culture medium and added to each well. After incubating for 72 h, 20 μL of a solution containing [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, inner salt; MTS] (Technical Bulletin: CellTiter 96 AQeousOne Solution Cell Proliferation Assay Technical Bulletin no. TB245, Promega Corporation) and the plates cultured for 1–2 h at 37 °C. A Spectra MAX Plus microtiter plate reader (Molecular Devices) was used to measure the optical density (OD) at a wavelength of 490 nm. Vehicle control values were subtracted from test compound values.
Pharmacophore Development
To develop a pharmacophore model for inhibition of PfKASIII, we have carried out both semiempirical (AM1) and ab initio HF self-consistent field (Hartree–Fock SCF) quantum mechanics (QM) calculations on thiolactomycin, a known inhibitor for FabH and FabF. Catalyst version 4.10,51 Spartan version 5.0,52 and Guassian9853 running on a Silicon Graphics Octane workstation under a IRIX 6.5 operating system were used for all of the modeling work presented here. Unless otherwise noted, all default settings were used for all computations. The conformational model of thiolactomycin was built using the systematic search algorithm and Monte Carlo simulated annealing algorithm with MM2 force field parameters. All of the conformational search parameters in Spartan such as Rings, Duplicate-check, Min-Population, Energy-upper-limit, etc, were set to their default values. The parameter CisTrans, which permits cis/trans flip, was set to false. The geometry optimized global minimum energy conformation was computed using HF/6-31G** basis sets as implemented in Guassian98 with all default parameters.54
The statistical significance and validation tests of the refined pharmacophore were performed as follows. Catalyst uses bits as a metric for measuring the statistical significance of the pharmacophore hypothesis.32 The fixed cost (FC) represents the perfect model with correlation coefficient of 1.0, while the null cost (NC) represents the worst model that predicts the activity of all compounds as the average activity with correlation coefficient of 0.0. Thus a meaningful model having total cost (TC) would have the largest difference between the values (TC–FC) and (NC–FC). The ratio of (TC–FC) to (NC–FC) is often used to compare two different hypotheses and thus lower the ratio the more statistically significant is the pharmacophore hypothesis model. Among the best ratios reported is the one in the tutorial manual of 0.095,32 while ratios of good predictive models reported in the literature are 0.2989 by Chopra et al.31 and 0.363 by Du et al.55 The (TC–FC) to (NC–FC) ratio for Hypo1A is an excellent 0.102. The configuration cost of Hypo1A is 14.62, which is well within the prescribed configuration cost of 17.0.56 The Fischer randomization test as implemented in the CatScramble module of Catalyst was used to rule out the possibility of chance correlation model. The validation test done at 99% confidence level showed that none of the random hypothesis cost values and correlation coefficients were any where close to Hypo1A. On an external test set of 16 compounds, Hypo1A predicted the activity of 15 within the widely accepted prediction accuracy of one log unit of the observed activity, which is an excellent 94% prediction accuracy.
Homology Modeling and Ligand Docking
A collection of comparative homology models of PfKASIII were built using SWISS-MODEL51 and MODELER.52,53 The models were evaluated for overall geometric quality using PROCHECK and compared using PROCOMP.57 One model was selected and used for all ligand docking and analysis presented in this paper. Docking was used to explore potential inhibitor binding modes. Ligand docking was performed using the FastDock module of BioMedCAChe (Fujitsu). FastDock, a proprietary Fujitsu algorithm, is a Lamarckian genetic algorithm-based ligand docking scheme very similar to AutoDock.58 For the calculations discussed here, FastDock was used in the flexible active site, flexible ligand mode. The PfKASIII active site and substrate-binding tunnel were explicitly defined and those sidechains were flexible during docking. 25000 generations and three independent runs were performed. PyMol59 was used to interactively analyze models and produce Figure 5.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the authors, and are not to be construed as official, or as reflecting true views of the Department of the Army or the Department of Defense. This research was performed while one of the authors (J.B.B.) held a National Research Council Research Associateship Award at Walter Reed Army Institute of Research. J.B.B. also gratefully acknowledges the logistic support from Astha Consultancy, Inc.
Footnotes
Abbreviations: ACP, acyl carrier protein; PfKASIII, β-ketoacyl–ACP synthase III; FAS, fatty acid synthesis.
Supporting Information Available: Cross reference identification of compound numbers with WRAIR chemical database accession numbers. Elemental analysis of key compounds used to develop the PfKASIII pharmacophore. Overlay of compounds onto the Hypo1A pharmacophore. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.Breman JG. The ears of the hippopotamus: manifestations, determinants, and estimates of the malaria burden. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;64:1–11. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2001.64.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fast NM, Kissinger JC, Roos DS, Keeling PJ. Nuclear-encoded, plastid-targeted genes suggest a single common origin for apicomplexan and dinoflagellate plastids. Mol Biol Evol. 2001;18:418–426. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Williamson DH, Gardner MJ, Preiser P, Moore DJ, Rangachari K, et al. The evolutionary origin of the 35 kb circular DNA of Plasmodium falciparum: new evidence supports a possible rhodophyte ancestry. Mol Genet Genomics. 1994;243:249–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00280323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wilson RJ. Progress with parasite plastids. J Mol Biol. 2002;319:257–274. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lu JZ, Lee PJ, Waters NC, Prigge ST. Fatty acid synthesis as a target for antimalarial drug discovery. Comb Chem High Throughput Screening. 2005;8:15–26. doi: 10.2174/1386207053328192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Seeber F. Biosynthetic pathways of plastid-derived organelles as potential drug targets against parasitic apicomplexa. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metab Disord. 2003;3:99–109. doi: 10.2174/1568008033340261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Waters NC, Kopydlowski KM, Guszczynski T, Wei L, Sellers P, et al. Functional characterization of the acyl carrier protein (PfACP) and beta-ketoacyl–ACP synthase III (PfKASIII) from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2002;123:85–94. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(02)00140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Prigge ST, He X, Gerena L, Waters NC, Reynolds KA. The initiating steps of a type II fatty acid synthase in Plasmodium falciparum are catalyzed by pfACP, pfMCAT, and pfKASIII. Biochemistry. 2003;42:1160–1169. doi: 10.1021/bi026847k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pillai S, Rajagopal C, Kapoor M, Kumar G, Gupta A, et al. Functional characterization of beta-ketoacyl–ACP reductase (FabG) from Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;303:387–392. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)00321-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lack G, Homberger-Zizzari E, Folkers G, Scapozza L, Perozzo R. Recombinant expression and biochemical characterization of the unique elongating beta-ketoacyl–acyl carrier protein synthase involved in fatty acid biosynthesis of Plasmodium falciparum using natural and artificial substrates. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:9538–9546. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509119200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kapoor M, Dar MJ, Surolia A, Surolia N. Kinetic determinants of the interaction of enoyl-ACP reductase from Plasmodium falciparum with its substrates and inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;289:832–837. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.6061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sharma SK, Kapoor M, Ramya TN, Kumar S, Kumar G, et al. Identification, characterization, and inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum beta-hydroxyacyl–acyl carrier protein dehydratase (FabZ) J Biol Chem. 2003;278:45661–45671. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304283200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Goodman CD, McFadden GI. Fatty acid biosynthesis as a drug target in apicomplexan parasites. Curr Drug Targets. 2007;8:15–30. doi: 10.2174/138945007779315579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wickramasinghe SR, Inglis KA, Urch JE, Muller S, van Aalten DM, et al. Kinetic, inhibition and structural studies on 3-oxoacyl–ACP reductase from Plasmodium falciparum, a key enzyme in fatty acid biosynthesis. Biochem J. 2006;393:447–457. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Freundlich JS, Wang F, Tsai HC, Kuo M, Shieh HM, et al. X-ray structural analysis of Plasmodium falciparum enoyl–acyl carrier protein reductase as a pathway toward the optimization of triclosan antimalarial efficacy. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:25436–25444. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701813200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Swarnamukhi PL, Sharma SK, Bajaj P, Surolia N, Surolia A, et al. Crystal structure of dimeric FabZ of Plasmodium falciparum reveals conformational switching to active hexamers by peptide flips. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:2653–2660. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.04.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Vial HJ, Ancelin ML. Malaria: parasite biology, pathogenesis, and protection. ASM Press: Washington, DC; 1998. Malarial lipids; pp. 159–175. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Foth BJ, Stimmler LM, Handman E, Crabb BS, Hodder AN, et al. The malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum has only one pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which is located in the apicoplast. Mol Microbiol. 2005;55:39–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Allary M, Lu JZ, Zhu L, Prigge ST. Scavenging of the cofactor lipoate is essential for the survival of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Microbiol. 2007;63:1331–1344. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gunther S, Wallace L, Patzewitz EM, McMillan PJ, Storm J, et al. Apicoplast Lipoic Acid Protein Ligase B Is Not Essential for Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS Pathog. 2007;3:e189. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Heath RJ, White SW, Rock CO. Inhibitors of fatty acid synthesis as antimicrobial chemotherapeutics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002;58:695–703. doi: 10.1007/s00253-001-0918-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Davies C, Heath RJ, White SW, Rock CO. The 1.8 A crystal structure and active-site architecture of beta-ketoacyl–acyl carrier protein synthase III (FabH) from Escherichia coli. Struct Fold Des. 2000;8:185–195. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00094-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Price AC, Choi KH, Heath RJ, Li Z, White SW, et al. Inhibition of beta-ketoacyl–acyl carrier protein synthases by thiolactomycin and cerulenin. Structure and mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:6551–6559. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007101200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Oishi H, Noto T, Sasaki H, Suzuki K, Hayashi T, et al. Thiolactomycin, a new antibiotic. I. Taxonomy of the producing organism, fermentation and biological properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982;35:391–395. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sakya SM, Suarez-Contreras M, Dirlam JP, O’Connell TN, Hayashi SF, et al. Synthesis and structure–activity relationships of thiotetronic acid analogues of thiolactomycin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001;11:2751–2754. doi: 10.1016/s0960-894x(01)00567-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jackowski S, Murphy CM, Cronan JE, Jr, Rock CO. Acetoacetyl–acyl carrier protein synthase. A target for the antibiotic thiolactomycin. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:7624–7629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Miyakawa S, Suzuki K, Noto T, Harada Y, Okazaki H. Thiolactomycin, a new antibiotic. IV. Biological properties and chemotherapeutic activity in mice. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982;35:411–419. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Waller RF, Keeling PJ, Donald RG, Striepen B, Handman E, et al. Nuclear-encoded proteins target to the plastid in Toxoplasma gondii and Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:12352–12357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jones SM, Urch JE, Kaiser M, Brun R, Harwood JL, et al. Analogues of thiolactomycin as potential antimalarial agents. J Med Chem. 2005;48:5932–5941. doi: 10.1021/jm049067d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Connolly ML. Solvent-accessible surfaces of proteins and nucleic acids. Science. 1983;221:709–713. doi: 10.1126/science.6879170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chopra M, Mishra AK. Ligand-based molecular modeling study on a chemically diverse series of cholecystokinin-B/gastrin receptor antagonists: generation of predictive model. J Chem Inf Model. 2005;45:1934–1942. doi: 10.1021/ci050257m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Brooks BR, Bruccoleri RE, Olafson BD, States DJ, Swaminathan S, et al. CHARMM: A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J Comput Chem. 1983;4:187–217. [Google Scholar]
- 33.He X, Reynolds KA. Purification, characterization, and identification of novel inhibitors of the beta-ketoacyl–acyl carrier protein synthase III (FabH) from Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:1310–1318. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.5.1310-1318.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Alhamadsheh MM, Musayev F, Komissarov AA, Sachdeva S, Wright HT, et al. Alkyl-CoA disulfides as inhibitors and mechanistic probes for FabH enzymes. Chem Biol. 2007;14:513–524. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2007.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.McLeod R, Muench SP, Rafferty JB, Kyle DE, Mui EJ, et al. Triclosan inhibits the growth of Plasmodium falciparum and Toxoplasma gondii by inhibition of apicomplexan Fab I. Int J Parasitol. 2001;31:109–113. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(01)00111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Freundlich JS, Yu M, Lucumi E, Kuo M, Tsai HC, et al. Synthesis and biological activity of diaryl ether inhibitors of malarial enoyl–acyl carrier protein reductase. Part 2: 2′-substituted triclosan derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006;16:2163–2169. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tarun AS, Peng X, Dumpit RF, Ogata Y, Silva-Rivera H, et al. A combined transcriptome and proteome survey of malaria parasite liver stages. Proc Natl Acad Sci US A. 2008;105:305–310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710780104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sachdeva S, Musayev FN, Alhamadsheh MM, Scarsdale JN, Wright HT, et al. Separate entrance and exit portals for ligand traffic in Mycobacterium tuberculosis FabH. Chem Biol. 2008;15:402–412. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lu JZ, Prigge ST. The tail of mycolic acids. Chem Biol. 2008;15:309–310. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wang J, Soisson SM, Young K, Shoop W, Kodali S, et al. Platensimycin is a selective FabF inhibitor with potent antibiotic properties. Nature. 2006;441:358–361. doi: 10.1038/nature04784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Daines RA, Pendrak I, Sham K, Van Aller GS, Konstantinidis AK, et al. First X-ray cocrystal structure of a bacterial FabH condensing enzyme and a small molecule inhibitor achieved using rational design and homology modeling. J Med Chem. 2003;46:5–8. doi: 10.1021/jm025571b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ondeyka JG, Zink DL, Young K, Painter R, Kodali S, et al. Discovery of bacterial fatty acid synthase inhibitors from a Phoma species as antimicrobial agents using a new antisense-based strategy. J Nat Prod. 2006;69:377–380. doi: 10.1021/np050416w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Singh S, Soni LK, Gupta MK, Prabhakar YS., III Eur J Med Chem. 2008;43:1071–1080. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2007.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wang J, Kodali S, Lee SH, Galgoci A, Painter R, et al. Discovery of platencin, a dual FabF and FabH inhibitor with in vivo antibiotic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci US A. 2007;104:7612–7616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700746104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Young K, Jayasuriya H, Ondeyka JG, Herath K, Zhang C, et al. Discovery of FabH/FabF inhibitors from natural products. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:519–526. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.2.519-526.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ashek A, Cho SJ. A combined approach of docking and 3D QSAR study of beta-ketoacyl–acyl carrier protein synthase III (FabH) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006;14:1474–1482. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2005.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.He X, Reeve AM, Desai UR, Kellogg GE, Reynolds KA. 1,2-Dithiole-3-ones as potent inhibitors of the bacterial 3-ketoacyl–acyl carrier protein synthase III (FabH) Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:3093–3102. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.8.3093-3102.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Nie Z, Perretta C, Lu J, Su Y, Margosiak S, et al. Structure-based design, synthesis, and study of potent inhibitors of beta-ketoacyl–acyl carrier protein synthase III as potential antimicrobial agents. J Med Chem. 2005;48:1596–1609. doi: 10.1021/jm049141s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Alhamadsheh MM, Waters NC, Huddler DP, Kreishman-Deitrick M, Florova G, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of thiazolidine-2-one 1,1-dioxide as inhibitors of Escherichia coli beta-ketoacyl–ACP-synthase III (FabH) Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007;17:879–883. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.11.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cory AH, Owen TC, Barltrop JA, Cory JG. Use of an aqueous soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth assays in culture. Cancer Commun. 1991;3:207–212. doi: 10.3727/095535491820873191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Schwede T, Kopp J, Guex N, Peitsch MC. SWISS-MODEL: An automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3381–3385. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Marti-Renom MA, Stuart AC, Fiser A, Sanchez R, Melo F, et al. Comparative protein structure modeling of genes and genomes. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2000;29:291–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.29.1.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sali A, Blundell TL. Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol Biol. 1993;234:779–815. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Bartlett RJ, Stanton JF. Applications of Post-Hartree–Fock Methods: A Tutorial. VCH Publishers; New York: 1994. pp. 65–169. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Du LP, Tsai KC, Li MY, You QD, Xia L. The pharmacophore hypotheses of IKr potassium channel blockers: novel class III antiarrhythmic agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004;14:4771–4777. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.06.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Catalyst. 4.10. Accelrys Software Inc; San Diego, CA: [Google Scholar]
- 57.Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM. PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Crystallogr. 1993;26:283–291. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, et al. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem. 1998;19:1639–1662. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Delano WL. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System. DeLano Scientific; Palo Alto, CA: 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Musayev F, Sachdeva S, Scarsdale JN, Reynolds KA., III J Mol Biol. 2005;346:1313–1321. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.12.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.