Abstract
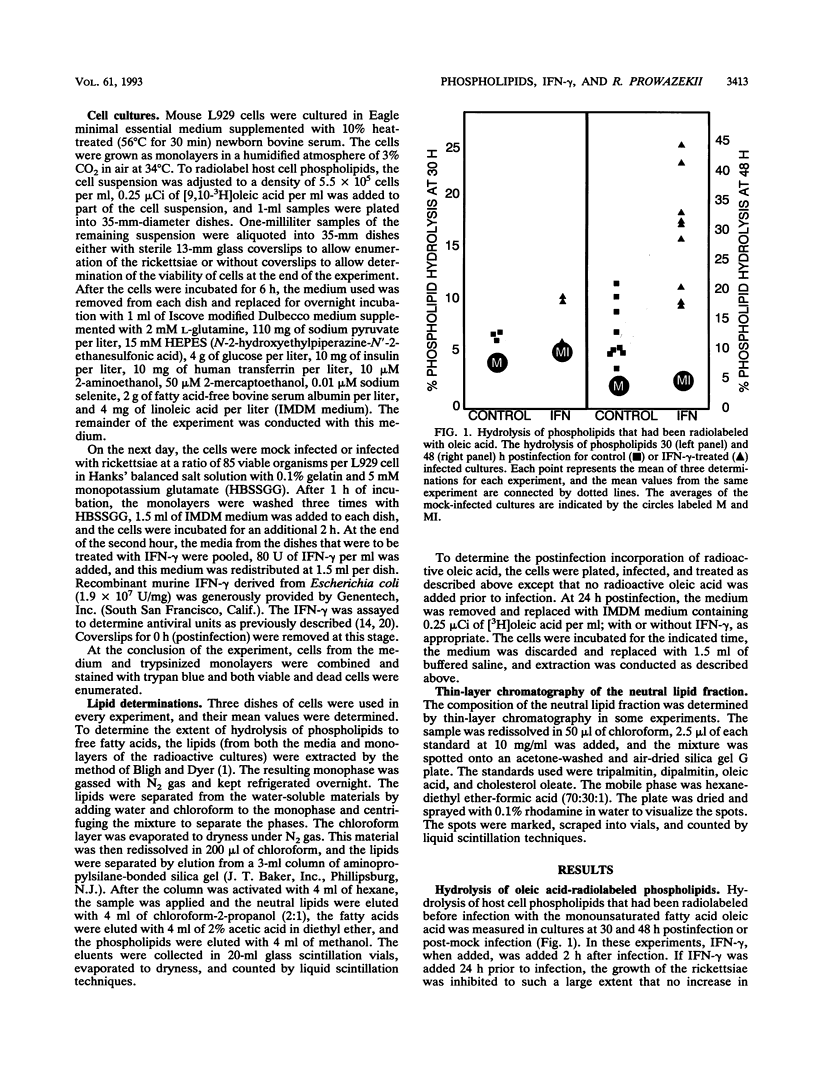
Treatment of Rickettsia prowazekii-infected L929 cells with gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) immediately after infection altered the lipid metabolism of the host cells as determined by measurement of phospholipid hydrolysis and oleic acid incorporation into phospholipids and neutral lipids. At 48 h postinfection, there was increased phospholipid hydrolysis in infected cultures relative to mock-infected cultures and a further increase in radiolabeled phospholipid hydrolysis in IFN-gamma-treated infected cultures. Oleic acid, the radiolabeled product of hydrolysis, was found in both the free fatty acid and neutral lipid fractions. None of the mock-infected cultures demonstrated increased hydrolysis of their radiolabeled phospholipids in response to treatment with IFN-gamma. Most of the radiolabeled oleic acid incorporated into cultures in the interval between 24 and 48 h after infection and IFN-gamma treatment was present in the phospholipid fraction. However, the neutral lipid fraction from the infected cultures that had been IFN-gamma treated was labeled to a greater extent than that from the untreated cultures. Thin-layer chromatographic analysis of the neutral lipid fractions from both the hydrolysis and incorporation experiments demonstrated that most of the radiolabel was in triglycerides. The infected cultures at 30 h were intact as assessed by the exclusion of trypan blue, but at 48 h postinfection in the IFN-gamma-treated infected cultures more than half of the cells were unable to exclude trypan blue. In no case did the mock-infected cells show substantial damage as a result of IFN-gamma treatment.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomalaski J. S., Freundlich B., Steiner S., Clark M. A. The role of fatty acid metabolites in the differentiation of the human monocyte-like cell line U937. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Jul;44(1):51–57. doi: 10.1002/jlb.44.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boraschi D., Censini S., Bartalini M., Scapigliati G., Barbarulli G., Vicenzi E., Donati M. B., Tagliabue A. Interferon inhibits prostaglandin biosynthesis in macrophages: effects on arachidonic acid metabolism. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1987–1992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boraschi D., Censini S., Bartalini M., Tagliabue A. Regulation of arachidonic acid metabolism in macrophages by immune and nonimmune interferons. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):502–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dore-Duffy P., Perry W., Kuo H. H. Interferon-mediated inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis in human mononuclear leukocytes. Cell Immunol. 1983 Jul 15;79(2):232–239. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldor A., Vlodavsky I., Hy-Am E., Atzmon R., Weksler B. B., Raz A., Fuks Z. Cultured endothelial cells increase their capacity to synthesize prostacyclin following the formation of a contact inhibited cell monolayer. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Feb;114(2):179–183. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041140206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong S. T., Mednis A., Remold H. G. Interferon-gamma stimulates lipid metabolism in human monocytes. Cell Immunol. 1992 Aug;143(1):108–117. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90009-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuse A., Mahmud I., Kuwata T. Mechanism of stimulation by human interferon of prostaglandin synthesis in human cell lines. Cancer Res. 1982 Aug;42(8):3209–3214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIMENEZ D. F. STAINING RICKETTSIAE IN YOLK-SAC CULTURES. Stain Technol. 1964 May;39:135–140. doi: 10.3109/10520296409061219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike K., Hirota K., Ohmichi M., Kadowaki K., Ikegami H., Yamaguchi M., Miyake A., Tanizawa O. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases release of arachidonate and prolactin from rat anterior pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1991 Jun;128(6):2791–2798. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-6-2791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzoni M., Montaldo P. G., Cornaglia-Ferraris P. Stimulation of receptor-coupled phospholipase A2 by interferon-gamma. FEBS Lett. 1992 Sep 21;310(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81136-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premecz G., Markovits A., Bagi G., Farkas T., Földes I. Phospholipase C and phospholipase A2 are involved in the antiviral activity of human interferon-alpha. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Keysary A., Winkler H. H. Interferon-gamma- and rickettsia-induced killing of macrophage-like cells is inhibited by anti-rickettsial antibodies and does not require the respiratory burst. J Interferon Res. 1989 Oct;9(5):615–629. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Cloned mouse interferon-gamma inhibits the growth of Rickettsia prowazekii in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2159–2164. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Comparison of the properties of antirickettsial activity and interferon in mouse lymphokines. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.27-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Effect of mouse lymphokines and cloned mouse interferon-gamma on the interaction of Rickettsia prowazekii with mouse macrophage-like RAW264.7 cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):303–308. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.303-308.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Gamma-interferon-induced inhibition of the growth of Rickettsia prowazekii in fibroblasts cannot be explained by the degradation of tryptophan or other amino acids. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):38–46. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.38-46.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Inhibition of the growth of Rickettsia prowazekii in cultured fibroblasts by lymphokines. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):974–986. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Selection of alpha/beta interferon- and gamma interferon-resistant rickettsiae by passage of Rickettsia prowazekii in L929 cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3279–3285. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3279-3285.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl L. M., Corcoran M. E., Mergenhagen S. E., Finbloom D. S. Inhibition of phospholipase activity in human monocytes by IFN-gamma blocks endogenous prostaglandin E2-dependent collagenase production. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3518–3522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Rickettsial hemolysis: rapid method for enumeration of metabolically active typhus rickettsiae. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):645–647. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.645-647.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Daugherty R. M. Phospholipase A activity associated with the growth of Rickettsia prowazekii in L929 cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):36–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.36-40.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Early events in the interaction of the obligate intracytoplasmic parasite, Rickettsia prowazekii, with eucaryotic cells: entry and lysis. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 May-Jun;137A(3):333–336. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Miller E. T. Phospholipase A activity in the hemolysis of sheep and human erythrocytes by Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):316–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.316-321.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Miller E. T. Phospholipase A and the interaction of Rickettsia prowazekii and mouse fibroblasts (L-929 cells). Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):109–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.109-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. Interferonlike factors from antigen- and mitogen-stimulated human leukocytes with antirickettsial and cytolytic actions on Rickettsia prowazekii. Infected human endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1780–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaron M., Yaron I., Gurari-Rotman D., Revel M., Lindner H. R., Zor U. Stimulation of prostaglandin E production in cultured human fibroblasts by poly(I)-poly(C) and human interferon. Nature. 1977 Jun 2;267(5610):457–459. doi: 10.1038/267457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



