Abstract
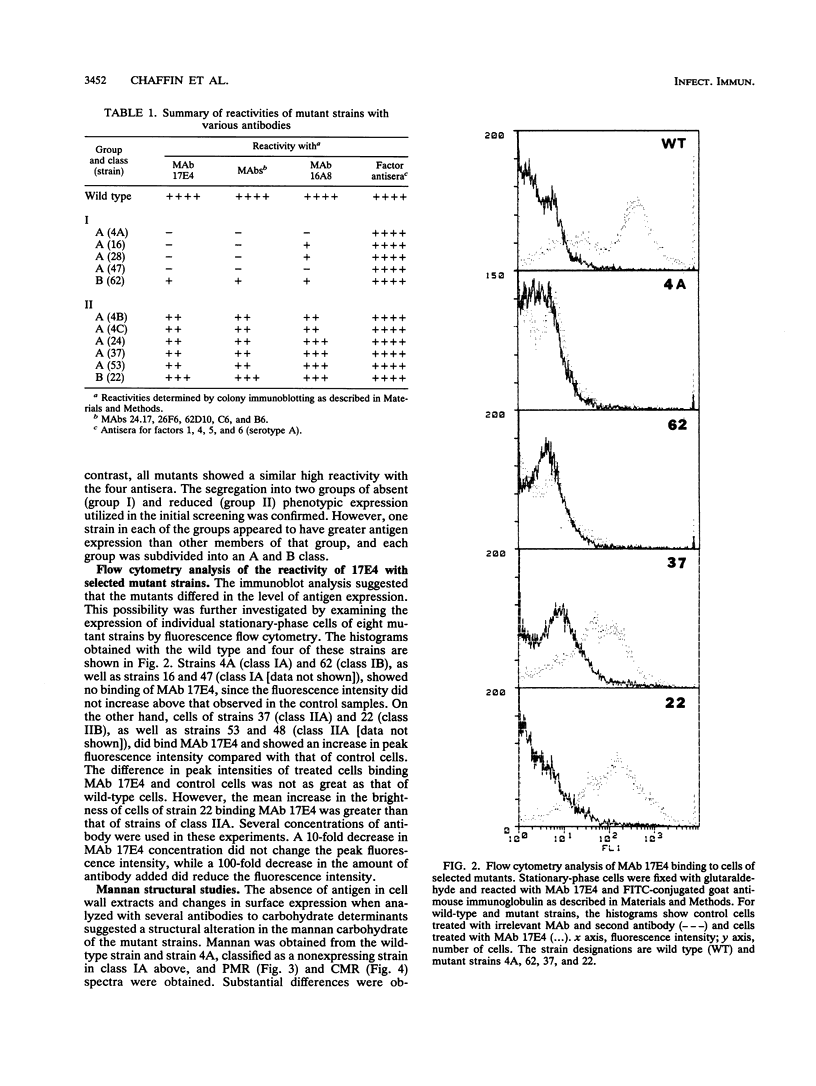
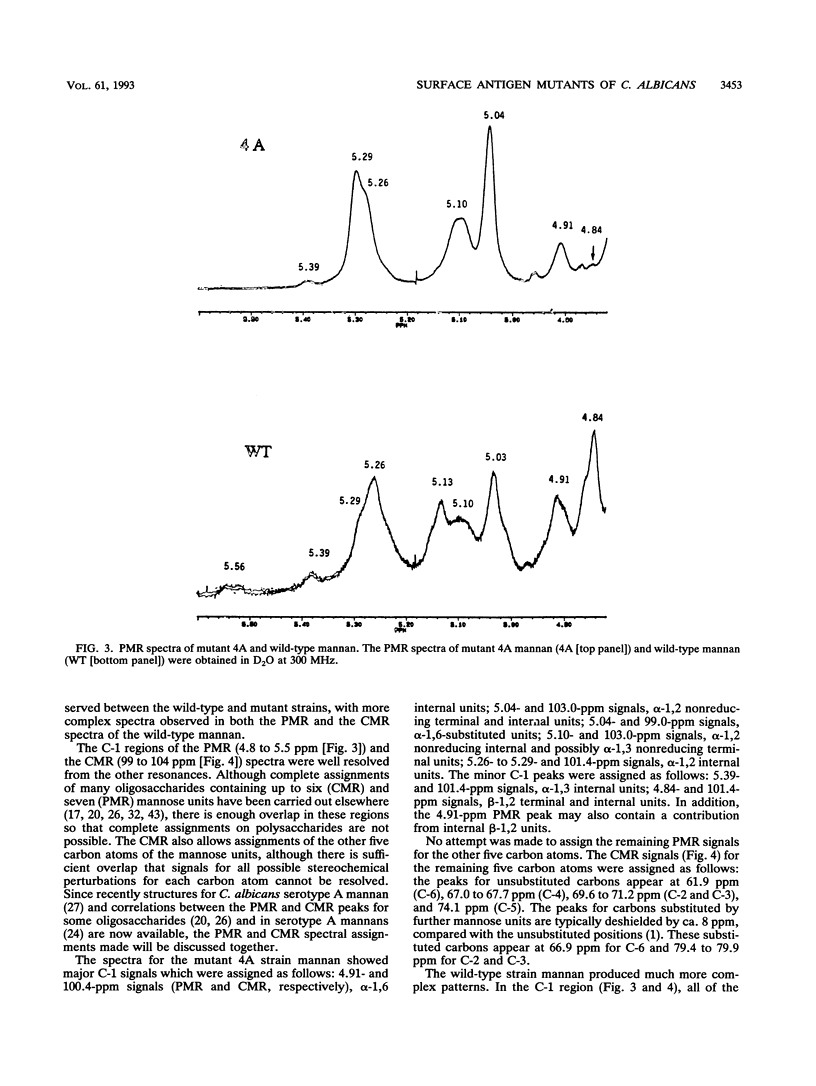
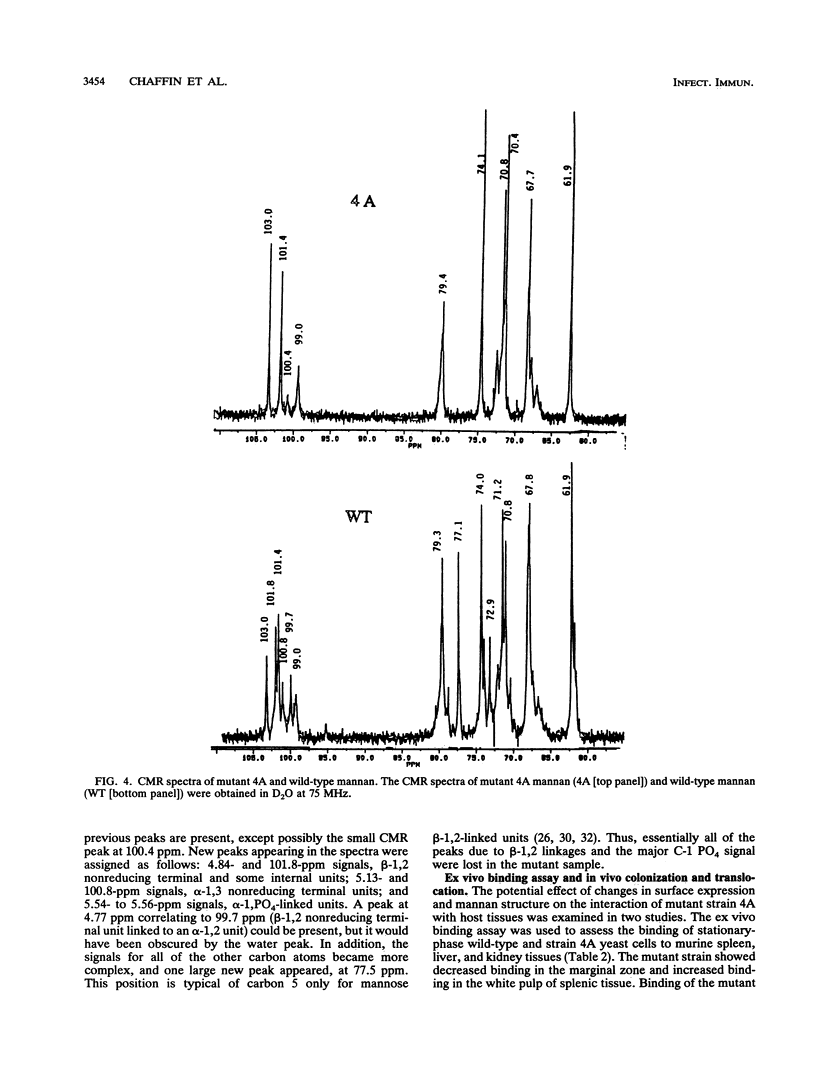
Monoclonal antibody (MAb) 17E4 reacts with a surface carbohydrate determinant and agglutinates cells of Candida albicans. Using this MAb, we have isolated N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced nonagglutinating mutants. Eleven of these were characterized for the presence and expression of the surface antigen recognized by MAb 17E4 by immunoblot analysis of whole cells and by fluorescence flow cytometry. Soluble cell wall extracts from five mutant strains were negative by immunoblot analysis. The reactivities of the strains with several other MAbs and commercial antisera (Candida Check; Iatron Laboratories, Tokyo, Japan) which also recognize carbohydrate determinants were examined by immunoblot analysis of whole cells. Mutant strains showed no or reduced expression of the MAb 17E4 antigen and could be placed into at least two distinct phenotypic classes. Recognition by the other MAbs tested showed a similar pattern, while recognition by the commercial antisera was unchanged in the mutant strains. 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectral analysis of mannan prepared from the wild type and nonexpressing mutant-strain 4A showed that the spectra from the mutant strain were simpler than those of the wild type. Most of the beta-1,2 linkages and all of the C-1 phosphate linkages were absent in the 4A mannan spectra, which suggested that the mutant mannan lacked the phosphate-bound beta-1,2-linked mannooligosaccharides. The effect of the surface defect on the ability of mutant strain 4A to adhere and to invade host tissue was examined in two murine models. In ex vivo binding assays, strain 4A showed reduced binding to the marginal zone and increased binding to the white pulp of splenic tissue, decreased binding to kidney tissue, and no change in binding to liver tissue compared with the wild type. In vivo, no difference was observed in translocation of the wild type or strain 4A to liver following immuno-compromising treatment of infant mice which had been challenged with either strain by the oral-intragastric route.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakerspigel A. The keratinophilic fungi of Ontario, Canada. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1974 Aug 30;53(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF02127194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou C. E. Isolation, characterization, and properties of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mnn mutants with nonconditional protein glycosylation defects. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:440–470. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85038-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou C. E., Raschke W. C. Polymorphism of the somatic antigen of yeast. Science. 1974 Apr 12;184(4133):127–134. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4133.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E. Ultrastructural and biochemical studies of two dynamically expressed cell surface determinants on Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):327–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.327-336.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E. Variability in expression of a cell surface determinant on Candida albicans as evidenced by an agglutinating monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):966–972. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.966-972.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E. Variability in expression of cell surface antigens of Candida albicans during morphogenesis. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):337–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.337-343.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Linehan L., Wadsworth E., Sandberg A. L. Identification of C3d receptors on Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):252–258. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.252-258.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassone A., Torosantucci A., Boccanera M., Pellegrini G., Palma C., Malavasi F. Production and characterisation of a monoclonal antibody to a cell-surface, glucomannoprotein constituent of Candida albicans and other pathogenic Candida species. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Dec;27(4):233–238. doi: 10.1099/00222615-27-4-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaffin W. L., Morrow K. J., Jr Two screening methods show different antigen recognition patterns for four monoclonal antibodies to Candida albicans cell surface. Immunol Lett. 1989 Jul;22(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(89)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaffin W. L., Ringler L., Larsen H. S. Interactions of monospecific antisera with cell surface determinants of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3294–3296. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3294-3296.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaffin W. L., Skudlarek J., Morrow K. J. Variable expression of a surface determinant during proliferation of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):302–309. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.302-309.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaffin W. L., Sogin S. J. Germ tube formation from zonal rotor fractions of Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):771–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.771-776.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardès T., Piechaczyk M., Cavaillès V., Salhi S. L., Pau B., Bastide J. M. Production and partial characterization of anti-Candida monoclonal antibodies. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1986 Mar-Apr;137C(2):117–125. doi: 10.1016/s0771-050x(86)80019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. E., Ballou C. E. Linkage and sequence analysis of mannose-rich glycoprotein core oligosaccharides by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 2;19(18):4345–4358. doi: 10.1021/bi00559a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Lynn K. T., Seshan K. R., Pope L. M. Gastrointestinal and systemic candidosis in immunocompromised mice. J Med Vet Mycol. 1989;27(6):363–380. doi: 10.1080/02681218980000491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E., Brawner D. L., Hazen K. C., Jutila M. A. Characteristics of Candida albicans adherence to mouse tissues. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1902–1908. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1902-1908.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faille C., Wieruszeski J. M., Lepage G., Michalski J. C., Poulain D., Strecker G. 1H-NMR spectroscopy of manno-oligosaccharides of the beta-1,2-linked series released from the phosphopeptidomannan of Candida albicans VW-32 (serotype A). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):1251–1258. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92073-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASENCLEVER H. F., MITCHELL W. O. Antigenic studies of Candida. I. Observation of two antigenic groups in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:570–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.570-573.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood V., Poulain D., Fortier B., Evans G., Vernes A. A monoclonal antibody to a cell wall component of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):222–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.222-227.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagaya K., Miyakawa Y., Fujihara H., Suzuki M., Soe G., Fukazawa Y. Immunologic significance of diverse specificity of monoclonal antibodies against mannans of Candida albicans. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3353–3358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Giummelly P., Takahashi S., Ishida M., Sato J., Takaku M., Nishidate Y., Shibata N., Okawa Y., Suzuki S. Candida albicans serotype A strains grow in yeast extract-added Sabouraud liquid medium at pH 2.0, elaborating mannans without beta-1,2 linkage and phosphate group. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 29;175(3):1003–1009. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91664-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Shibata N., Mitobe H., Ohkubo Y., Suzuki S. Structural study of phosphomannan of yeast-form cells of Candida albicans J-1012 strain with special reference to application of mild acetolysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Aug 1;272(2):364–375. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Shibata N., Nakada M., Chaki S., Mizugami K., Ohkubo Y., Suzuki S. Structural study of cell wall phosphomannan of Candida albicans NIH B-792 (serotype B) strain, with special reference to 1H and 13C NMR analyses of acid-labile oligomannosyl residues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Apr;278(1):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90248-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Shibata N., Osaka T., Miyagawa Y., Ohkubo Y., Suzuki S. Structural study of cell wall mannan of a Candida albicans (serotype A) strain. Phytochemistry. 1992 Apr;31(4):1147–1153. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(92)80250-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Shibata N., Suzuki S. Evidence for oligomannosyl residues containing both beta-1,2 and alpha-1,2 linkages as a serotype A-specific epitope(s) in mannans of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):2106–2109. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.2106-2109.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Shibata N., Yonezu T., Suzuki S. Structural study of phosphomannan-protein complex of Citeromyces matritensis containing beta-1,2 linkage. Application of partial acid degradation and acetolysis techniques under mild conditions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Jul;256(1):381–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90459-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocourek J., Ballou C. E. Method for fingerprinting yeast cell wall mannans. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1175–1181. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1175-1181.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogan G., Pavliak V., Masler L. Structural studies of mannans from the cell walls of the pathogenic yeasts Candida albicans serotypes A and B and Candida parapsilosis. Carbohydr Res. 1988 Feb 1;172(2):243–253. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90858-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. L., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. An amino acid liquid synthetic medium for the development of mycelial and yeast forms of Candida Albicans. Sabouraudia. 1975 Jul;13(2):148–153. doi: 10.1080/00362177585190271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons S., Nelson N. An immunological method for detecting gene expression in yeast colonies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7426–7430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa Y., Kagaya K., Fukazawa Y., Soe G. Production and characterization of agglutinating monoclonal antibodies against predominant antigenic factors for Candida albicans. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):881–886. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.881-886.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa Y., Kuribayashi T., Kagaya K., Suzuki M., Nakase T., Fukazawa Y. Role of specific determinants in mannan of Candida albicans serotype A in adherence to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2493–2499. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2493-2499.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss E., de Repentigny L., Kuykendall R. J., Carter A. W., Galindo R., Auger P., Bragg S. L., Kaufman L. Monoclonal antibodies against Candida tropicalis mannan: antigen detection by enzyme immunoassay and immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):796–802. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.796-802.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena A., Hammer C. F., Cihlar R. L. Analysis of mannans of two relatively avirulent mutant strains of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):413–419. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.413-419.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena A., McElhaney-Feser G. E., Cihlar R. L. Mannan composition of the hyphal form of two relatively avirulent mutants of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2061–2066. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2061-2066.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata N., Fukasawa S., Kobayashi H., Tojo M., Yonezu T., Ambo A., Ohkubo Y., Suzuki S. Structural analysis of phospho-D-mannan-protein complexes isolated from yeast and mold form cells of Candida albicans NIH A-207 serotype A strain. Carbohydr Res. 1989 Apr 15;187(2):239–253. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(89)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata N., Kobayashi H., Takahashi S., Okawa Y., Hisamichi K., Suzuki S., Suzuki S. Structural study on a phosphorylated mannotetraose obtained from the phosphomannan of Candida albicans NIH B-792 strain by acetolysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Nov 1;290(2):535–542. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90578-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata N., Kobayashi H., Tojo M., Suzuki S. Characterization of phosphomannan-protein complexes isolated from viable cells of yeast and mycelial forms of Candida albicans NIH B-792 strain by the action of Zymolyase-100T. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Dec;251(2):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90379-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa O., Nakayama H. Isolation of a Candida albicans mutant with reduced content of cell wall mannan and deficient mannan phosphorylation. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(4):315–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P. M., Tam M. R., Nichols E. J., Kenny G. E. Antigenic differences in the surface mannoproteins of Candida albicans as revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):601–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.601-606.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Fukazawa Y. Immunochemical characterization of Candida albicans cell wall antigens: specific determinant of Candida albicans serotype A mannan. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(5):387–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo M., Shibata N., Kobayashi M., Mikami T., Suzuki M., Suzuki S. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies reactive with beta-1,2-linked oligomannosyl residues in the phosphomannan-protein complex of Candida albicans NIH B-792 strain. Clin Chem. 1988 Mar;34(3):539–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinel P. A., Faille C., Jacquinot P. M., Cailliez J. C., Poulain D. Mapping of Candida albicans oligomannosidic epitopes by using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3845–3851. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3845-3851.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan W. L., Delga J. M., Wadsworth E., Walsh T. J., Kwon-Chung K. J., Calderone R., Lipke P. N. Isolation and characterization of cell surface mutants of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1552–1557. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1552-1557.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



