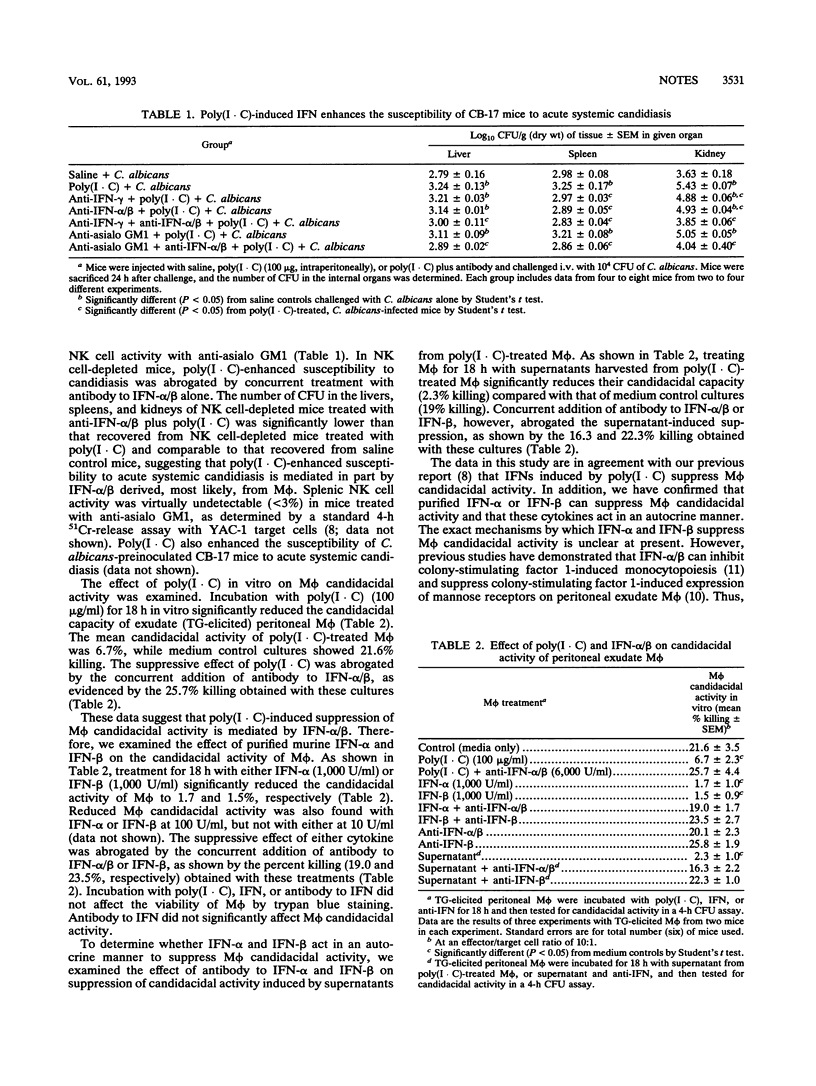
Abstract
Poly(I . C) enhanced the susceptibility of CB-17 (BALB/c) mice to acute systemic candidiasis. Poly(I . C), supernatants from poly(I . C)-treated macrophages, or alpha and beta interferons suppressed macrophage candidacidal activity in vitro. Thus, poly(I . C)-induced interferons may enhance the susceptibility of CB-17 mice to candidiasis by suppressing macrophage candidacidal activity in an autocrine fashion.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blasi E., Farinelli S., Varesio L., Bistoni F. Augmentation of GG2EE macrophage cell line-mediated anti-Candida activity by gamma interferon, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin-1. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1073–1077. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1073-1077.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer E., Stevens D. A. Candidacidal mechanisms of peritoneal macrophages activated with lymphokines or gamma-interferon. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Mar;28(3):173–181. doi: 10.1099/00222615-28-3-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Haudenschild C. C. Monocyte-mediated serum-independent damage to hyphal and pseudohyphal forms of Candida albicans in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):173–182. doi: 10.1172/JCI110010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Heinbaugh J. A., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Augmentation of mouse natural killer cell activity by interferon and interferon inducers. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):175–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleit H. B., Rabinovitch M. Production of interferon by in vitro derived bone marrow macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jan 15;57(2):495–504. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner R. E., Kuruganti U., Czarniecki C. W., Chiu H. H., Domer J. E. In vivo immune responses to Candida albicans modified by treatment with recombinant murine gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1800–1808. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1800-1808.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi T., Ozaki M., Onodera T., Ami Y., Yamamoto H. Macrophage function in the acute phase of lactic dehydrogenase virus-infection of mice: suppression of superoxide anion production in normal mouse peritoneal macrophages by interferon-alpha in vitro. J Comp Pathol. 1992 Feb;106(2):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(92)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J., Vazquez-Torres A., Balish E. Poly(I.C)-induced interferons enhance susceptibility of SCID mice to systemic candidiasis. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4549–4557. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4549-4557.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jullien P., De Maeyer-Guignard J., De Maeyer E. Interferon synthesis in x-irradiated animals v. Origin of mouse serum interferon induced by polyinosinic-polycytidylic Acid and encephalomyocarditis virus. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1023–1028. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1023-1028.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karbassi A., Becker J. M., Foster J. S., Moore R. N. Enhanced killing of Candida albicans by murine macrophages treated with macrophage colony-stimulating factor: evidence for augmented expression of mannose receptors. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):417–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. N., Pitruzzello F. J., Larsen H. S., Rouse B. T. Feedback regulation of colony-stimulating factor (CSF-1)-induced macrophage proliferation by endogenous E prostaglandins and interferon-alpha/beta. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):541–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck R. Gamma interferon induces monocyte killing of Listeria monocytogenes by an oxygen-dependent pathway; alpha- or beta-interferons by oxygen-independent pathways. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Nov;46(5):434–440. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.5.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Lamerson C. L., Banks S. M., Saini S. S., Wahl L. M., Calderone R. A., Wahl S. M. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor augments human monocyte fungicidal activity for Candida albicans. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecchiarelli A., Todisco T., Puliti M., Dottorini M., Bistoni F. Modulation of anti-Candida activity of human alveolar macrophages by interferon-gamma or interleukin-1-alpha. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1989 Jul;1(1):49–55. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/1.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


