Abstract
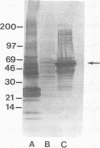
A clone expressing a 58-kDa protein reactive with human convalescent-phase serum was isolated from a recombinant library of Ehrlichia chaffeensis, the etiologic agent of human ehrlichiosis. Sequencing identified two open reading frames, one encoding a 10.3-kDa polypeptide consisting of 94 amino acids and another encoding a 58-kDa polypeptide consisting of 550 amino acids. The sequences of the 10.3- and 58-kDa polypeptides were homologous to those of the Escherichia coli GroES and GroEL heat shock proteins, respectively.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. E., Dawson J. E., Jones D. C., Wilson K. H. Ehrlichia chaffeensis, a new species associated with human ehrlichiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2838–2842. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2838-2842.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. E., Sumner J. W., Dawson J. E., Tzianabos T., Greene C. R., Olson J. G., Fishbein D. B., Olsen-Rasmussen M., Holloway B. P., George E. H. Detection of the etiologic agent of human ehrlichiosis by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):775–780. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.775-780.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch G. A., Ching W. M., Kim P. Y., Pham H., Stover C. K., Oaks E. V., Dobson M. E., Weiss E. A structural and immunological comparison of rickettsial HSP60 antigens with those of other species. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:352–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. E., Anderson B. E., Fishbein D. B., Sanchez J. L., Goldsmith C. S., Wilson K. H., Duntley C. W. Isolation and characterization of an Ehrlichia sp. from a patient diagnosed with human ehrlichiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2741–2745. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2741-2745.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein D. B., Sawyer L. A., Holland C. J., Hayes E. B., Okoroanyanwu W., Williams D., Sikes K., Ristic M., McDade J. E. Unexplained febrile illnesses after exposure to ticks. Infection with an Ehrlichia? JAMA. 1987 Jun 12;257(22):3100–3104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindersson P., Petersen C. S., Pedersen N. S., Høiby N., Axelsen N. H. Immunological cross-reaction between antigen Tp-4 of Treponema pallidum and an antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1984 Aug;92(4):183–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb02818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Heat shock proteins and the immune response. Immunol Today. 1990 Apr;11(4):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90050-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda K., Markowitz N., Hawley R. C., Ristic M., Cox D., McDade J. E. Human infection with Ehrlichia canis, a leukocytic rickettsia. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 2;316(14):853–856. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704023161406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. Ocular hypersensitivity elicited by a genus-specific 57-kD protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):663–675. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Su H., Lyng K., Yuan Y. The Chlamydia trachomatis hyp operon is homologous to the groE stress response operon of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2701–2705. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2701-2705.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Polypeptide chain binding proteins: catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis 65-kilodalton antigen is a heat shock protein which corresponds to common antigen and to the Escherichia coli GroEL protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):446–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.446-451.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. P., Betz T. G., Fishbein D. B., Roberts M. A., Dawson J., Ristic M. Serological evidence of possible human infection with Ehrlichia in Texas. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):217–220. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzianabos T., Anderson B. E., McDade J. E. Detection of Rickettsia rickettsii DNA in clinical specimens by using polymerase chain reaction technology. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2866–2868. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2866-2868.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]