Abstract
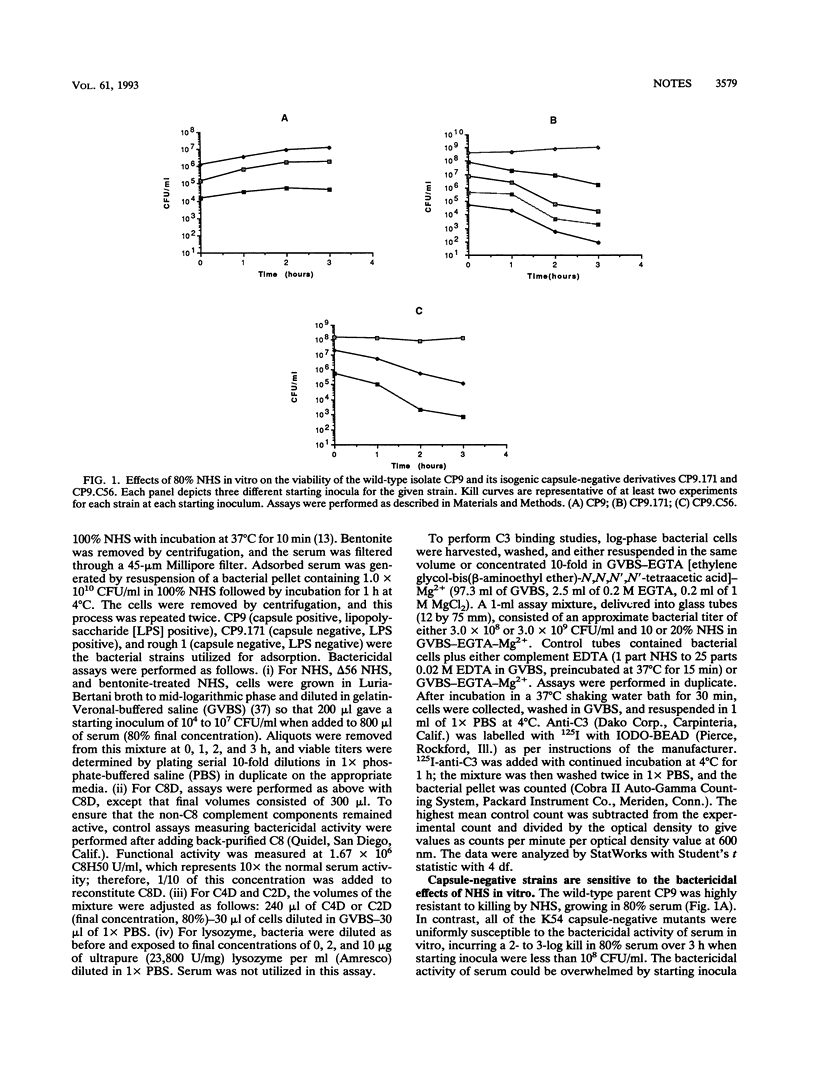
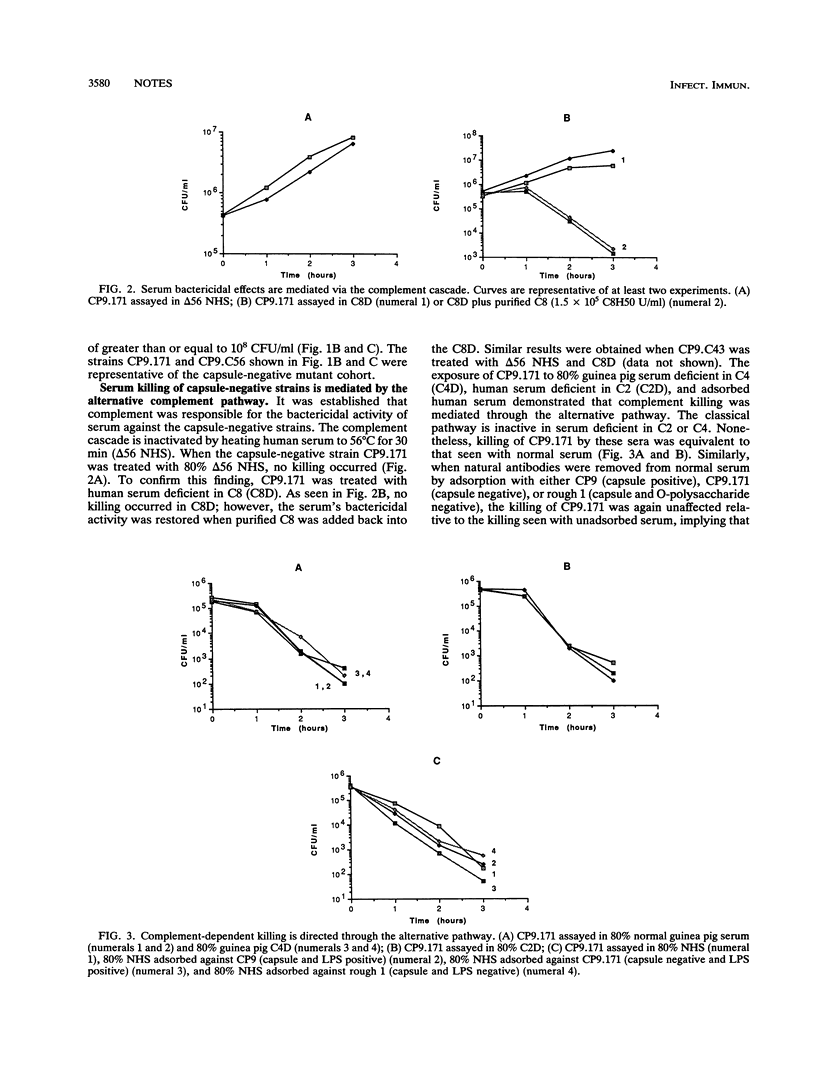
To assess whether non-K1, group 2 capsular serotypes are important in conferring serum resistance to extraintestinal isolates of Escherichia coli, a K54 blood isolate (CP9) was evaluated as a model pathogen. Transposon mutagenesis (TnphoA) was used to generate isogenic capsule-negative mutants. CP9 was resistant to the bactericidal effects of serum, growing in 80% serum. In contrast, all of the capsule-negative mutants had an increased sensitivity to 80% normal human serum, undergoing a 2- to 3-log kill over 3 h when starting inocula of 10(4) to 10(7) CFU/ml were used. The killing of the capsule-negative strains was mediated through the alternative complement pathway and not by lysozyme or beta-lysins. The protective effect of the K54 capsule against the bactericidal activity of serum was not through inhibition of the complement cascade, nor did it appear to be through a difference in the binding of C3.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agüero M. E., Cabello F. C. Relative contribution of ColV plasmid and K1 antigen to the pathogenicity of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):359–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.359-368.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen P. M., Roberts I., Boulnois G. J., Saunders J. R., Hart C. A. Contribution of capsular polysaccharide and surface properties to virulence of Escherichia coli K1. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2662–2668. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2662-2668.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks H. J., O'Grady F., McSherry M. A., Cattell W. R. Uropathogenic properties of Escherichia coli in recurrent urinary-tract infection. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):57–68. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Gemski P., Sadoff J. C., Orskov F., Orskov I. The importance of the K1 capsule in invasive infections caused by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):184–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson D. M., Roberts R. R., Larsen H. S., Tew J. G. Interrelationship between serum beta-lysin, lysozyme, and the antibody-complement system in killing Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):657–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.657-666.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I., Jones G. W. The spectrum of infections and pathogenic mechanisms of Escherichia coli. Adv Intern Med. 1988;33:231–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Regulation by membrane sialic acid of beta1H-dependent decay-dissociation of amplification C3 convertase of the alternative complement pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1971–1975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Mclean R. H., Michael A. F., Quie P. G. Studies of the alternate pathway in chelated serum. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Jun;85(6):904–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Howard C. J. The sensitivity to complement of strains of Escherichia coli related to their K antigens. Immunology. 1970 Mar;18(3):331–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Milne C. M. A kinetic study of the bacteriolytic and bactericidal action of human serum. Immunology. 1967 Jun;12(6):639–653. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Joiner K., Leive L. Serum-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli O111 contain increased lipopolysaccharide, lack an O antigen-containing capsule, and cover more of their lipid A core with O antigen. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):877–882. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.877-882.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gransden W. R., Eykyn S. J., Phillips I., Rowe B. Bacteremia due to Escherichia coli: a study of 861 episodes. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Nov-Dec;12(6):1008–1018. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.6.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann P., Jann B., Jann K. Structure of the amino acid-containing capsular polysaccharide (K54 antigen) from Escherichia coli O6:K54:H10. Carbohydr Res. 1985 Jun 15;139:261–271. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(85)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Glynn A. A. The virulence for mice of strains of Escherichia coli related to the effects of K antigens on their resistance to phagocytosis and killing by complement. Immunology. 1971 May;20(5):767–777. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann K., Jann B. Polysaccharide antigens of Escherichia coli. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9 (Suppl 5):S517–S526. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_5.s517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. R. Virulence factors in Escherichia coli urinary tract infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):80–128. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.1.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A. Studies on the mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing and on the mechanism of action of bactericidal antibody. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;121:99–133. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-45604-6_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leying H., Suerbaum S., Kroll H. P., Stahl D., Opferkuch W. The capsular polysaccharide is a major determinant of serum resistance in K-1-positive blood culture isolates of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):222–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.222-227.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H. Bactericidal activity of normal serum against bacterial cultures. II. Activity against Eschericha coli strains. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Mar;103:632–636. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R., Kaijser B., Olling S., Uwaydah M., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli in bacteremia: K and O antigens and serum sensitivity of strains from adults and neonates. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):33–41. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngeleka M., Harel J., Jacques M., Fairbrother J. M. Characterization of a polysaccharide capsular antigen of septicemic Escherichia coli O115:K "V165" :F165 and evaluation of its role in pathogenicity. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5048–5056. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5048-5056.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Yasuda T., Okada H. Restriction of alternative complement pathway activation by sialosylglycolipids. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):261–263. doi: 10.1038/299261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement C3 convertase: cell surface restriction of beta1H control and generation of restriction on neuraminidase-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2416–2420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke G., Mayden J., Achtman M., Levine R. P. Role of the capsule and the O antigen in resistance of O18:K1 Escherichia coli to complement-mediated killing. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):907–913. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.907-913.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porat R., Johns M. A., McCabe W. R. Selective pressures and lipopolysaccharide subunits as determinants of resistance of clinical isolates of gram-negative bacilli to human serum. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):320–328. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.320-328.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J., Rantz L. A. A STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP OF THE NORMAL BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY OF HUMAN SERUM TO BACTERIAL INFECTION. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39(1):72–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI104029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. P., Aaronson W., Vann W. F. The K1 capsular polysaccharide of Escherichia coli. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S282–S286. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm W. E., Hooton T. M., Johnson J. R., Johnson C., Stapleton A., Roberts P. L., Moseley S. L., Fihn S. D. Urinary tract infections: from pathogenesis to treatment. J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):400–406. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanborg-Edén C., Hagberg L., Hull R., Hull S., Magnusson K. E., Ohman L. Bacterial virulence versus host resistance in the urinary tracts of mice. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1224–1232. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1224-1232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W. Bactericidal and bacteriolytic activity of serum against gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):46–83. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.46-83.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W. Genetical studies of serum resistance in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jul;89(1):57–66. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen C., Cross A., Byrne W. R., Zollinger W. Quantitative relationship between capsular content and killing of K1-encapsulated Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2723–2730. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2723-2730.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verweij-van Vught A. M., van den Bosch J. F., Namavar F., Sparrius M., MacLaren D. M. K antigens of Escherichia coli and virulence in urinary-tract infection: studies in a mouse model. J Med Microbiol. 1983 May;16(2):147–155. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-2-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosti K. L., Randall E. Sensitivity of serologically classified strains of escherichia coli of human origin to the serum bactericidal system. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Feb;259(2):114–119. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197002000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Levine R. P. How complement kills E. coli. I. Location of the lethal lesion. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1146–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



