Abstract
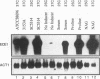
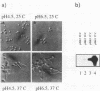
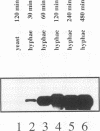
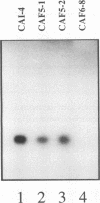
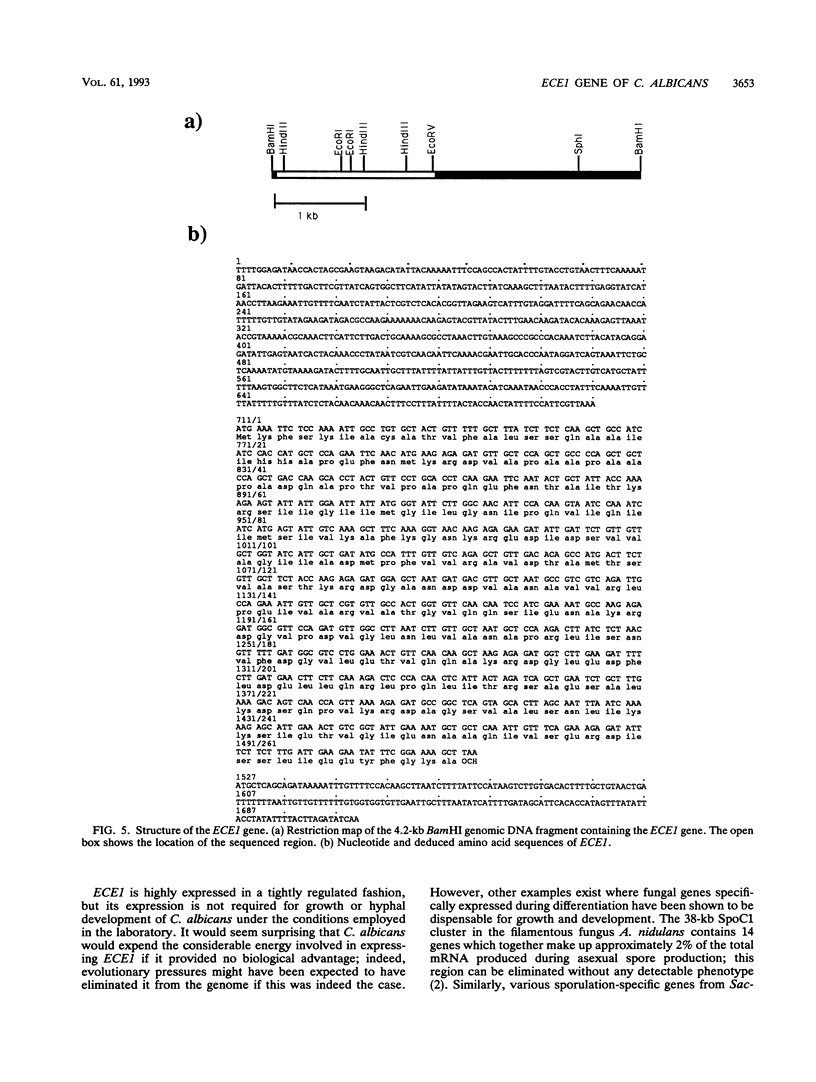
The gene ECE1 (extent of cell elongation 1) was isolated by differential hybridization screening of a Candida albicans cDNA library by using probes derived from populations of yeast cells or hyphae. Expression of this gene was not detected when C. albicans grew as a budding yeast cell but was observed within 30 min after cells had been induced to form hyphae. In all strains tested, regardless of the induction signal, ECE1 expression correlated with the extent of cell elongation. The genomic version of ECE1 was cloned and sequenced. The deduced 271-amino-acid polypeptide consisted of eight tandem repeats of a degenerate 34-amino-acid sequence which contained no discernible homology with other known sequences. An ECE1 null mutant displayed no morphological alterations, which demonstrated that ECE1 is not essential for cell elongation or hypha formation despite the strict morphological association of its expression.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahrens J. C., Daneo-Moore L., Buckley H. R. Differential protein synthesis in Candida albicans during blastospore formation at 24.5 degrees C and during germ tube formation at 37 degrees C. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Apr;129(4):1133–1139. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-4-1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aramayo R., Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. A large cluster of highly expressed genes is dispensable for growth and development in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):65–71. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin V., Yanofsky C. Isolation and characterization of genes differentially expressed during conidiation of Neurospora crassa. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):849–855. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E., Beatty W. L. Caveats in the investigation of form-specific molecules of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):378–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.378-383.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. A., Chaffin W. L. Differential expression of cytoplasmic proteins during yeast bud and germ tube formation in Candida albicans. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Jun;27(6):580–585. doi: 10.1139/m81-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buell G. N., Wickens M. P., Payvar F., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of full length cDNAs from four partially purified oviduct mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2471–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon R. D. Isolation of a mycelial mutant of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Aug;132(8):2405–2407. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-8-2405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova M., Gil M. L., Cardeñoso L., Martinez J. P., Sentandreu R. Identification of wall-specific antigens synthesized during germ tube formation by Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):262–271. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.262-271.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaffin W. L., Skudlarek J., Morrow K. J. Variable expression of a surface determinant during proliferation of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):302–309. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.302-309.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung K. J., Hill W. B. Studies on the pink, adenine-deficient strains of Candida albicans. I. Cultural and morphological characteristics. Sabouraudia. 1970 May;8(1):48–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowa N., Howard D. H. Proline uptake in Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):391–397. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney R., Langtimm C. J., Soll D. R. The programs of protein synthesis accompanying the establishment of alternative phenotypes in Candida albicans. Mycopathologia. 1985 Jul;91(1):3–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00437280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber A. T., Segall J. The SPS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a major sporulation-specific mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4478–4485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil C., Pomés R., Nombela C. Isolation and characterization of Candida albicans morphological mutants derepressed for the formation of filamentous hypha-type structures. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2384–2391. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2384-2391.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M., Yanagida M. The TPR snap helix: a novel protein repeat motif from mitosis to transcription. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 May;16(5):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90070-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlin-Ninfa E., Kaback D. B. Isolation and functional analysis of sporulation-induced transcribed sequences from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2185–2197. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynne D. I., Miller B. L., Miller K. Y., Timberlake W. E. Structure and regulated expression of the SpoC1 gene cluster from Aspergillus nidulans. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):91–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90432-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard M. J., Markie D., Poulter R. T. Isolation and morphological characterization of a mycelial mutant of Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):61–65. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.61-65.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R., Miller S. M., Kurtz M. B., Kirsch D. R. Directed mutagenesis in Candida albicans: one-step gene disruption to isolate ura3 mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):199–208. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura L. H., Pearsall N. N. Relationship between germination of Candida albicans and increased adherence to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):464–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.464-468.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz M. B., Cortelyou M. W., Kirsch D. R. Integrative transformation of Candida albicans, using a cloned Candida ADE2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):142–149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Gallwitz D. Evidence for an intron-contained sequence required for the splicing of yeast RNA polymerase II transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. L., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. An amino acid liquid synthetic medium for the development of mycelial and yeast forms of Candida Albicans. Sabouraudia. 1975 Jul;13(2):148–153. doi: 10.1080/00362177585190271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson-Davies L. A., Odds F. C. A morphology index for characterization of cell shape in Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Nov;135(11):3143–3152. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-11-3143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olaiya A. F., Sogin S. J. Ploidy determination of Canadida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1043–1049. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1043-1049.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival-Smith A., Segall J. Characterization and mutational analysis of a cluster of three genes expressed preferentially during sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2443–2451. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petko L., Lindquist S. Hsp26 is not required for growth at high temperatures, nor for thermotolerance, spore development, or germination. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90563-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponton J., Jones J. M. Identification of two germ-tube-specific cell wall antigens of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):864–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.864-868.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D., Tronchin G., Lefebvre B., Husson M. O. Antigenic variability between Candida albicans blastospores isolated from healthy subjects and patients with Candida infection. Sabouraudia. 1982 Sep;20(3):173–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhyner T. A., Biguet N. F., Berrard S., Borbély A. A., Mallet J. An efficient approach for the selective isolation of specific transcripts from complex brain mRNA populations. J Neurosci Res. 1986;16(1):167–181. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490160116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Stevens D. A. A Candida albicans dispersed, repeated gene family and its epidemiologic applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1452–1456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd M. G., Sullivan P. A. The production and growth characteristics of yeast and mycelial forms of Candida albicans in continuous culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Apr;93(2):361–370. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-2-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd M. G., Yin C. Y., Ram S. P., Sullivan P. A. Germ tube induction in Candida albicans. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Jan;26(1):21–26. doi: 10.1139/m80-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P. M., Tam M. R., Nichols E. J., Kenny G. E. Antigenic differences in the surface mannoproteins of Candida albicans as revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):601–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.601-606.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syverson R. E., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. Cytoplasmic antigens unique to the mycelial or yeast phase of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1184–1188. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1184-1188.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E. Developmental gene regulation in Aspergillus nidulans. Dev Biol. 1980 Aug;78(2):497–510. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90349-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan W. L., Partridge R. M., Magee P. T. Heterozygosity and segregation in Candida albicans. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(1):107–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00267358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]