Abstract
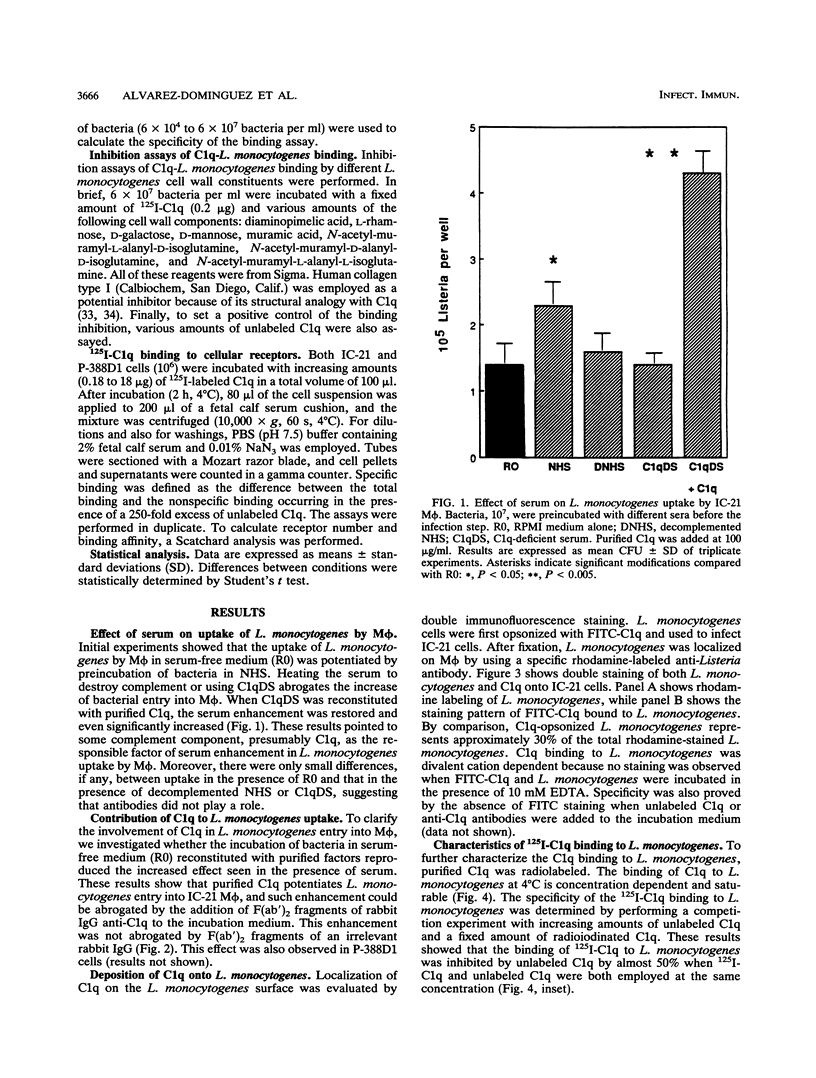
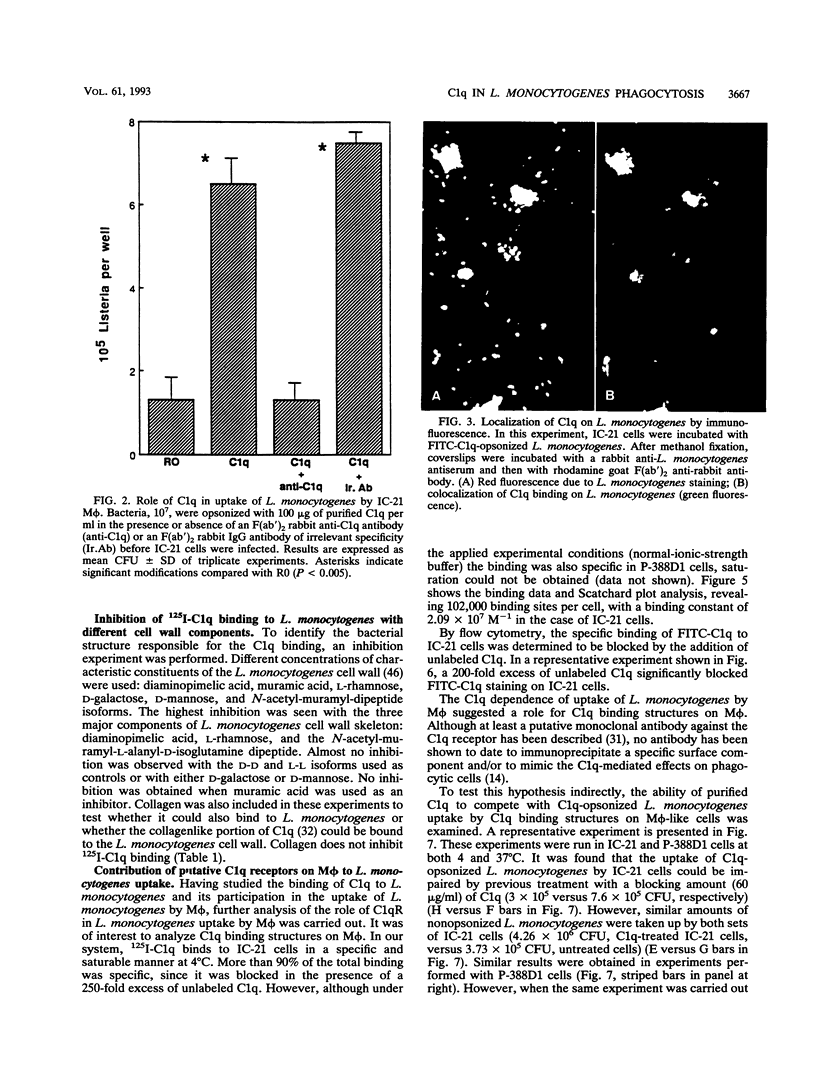
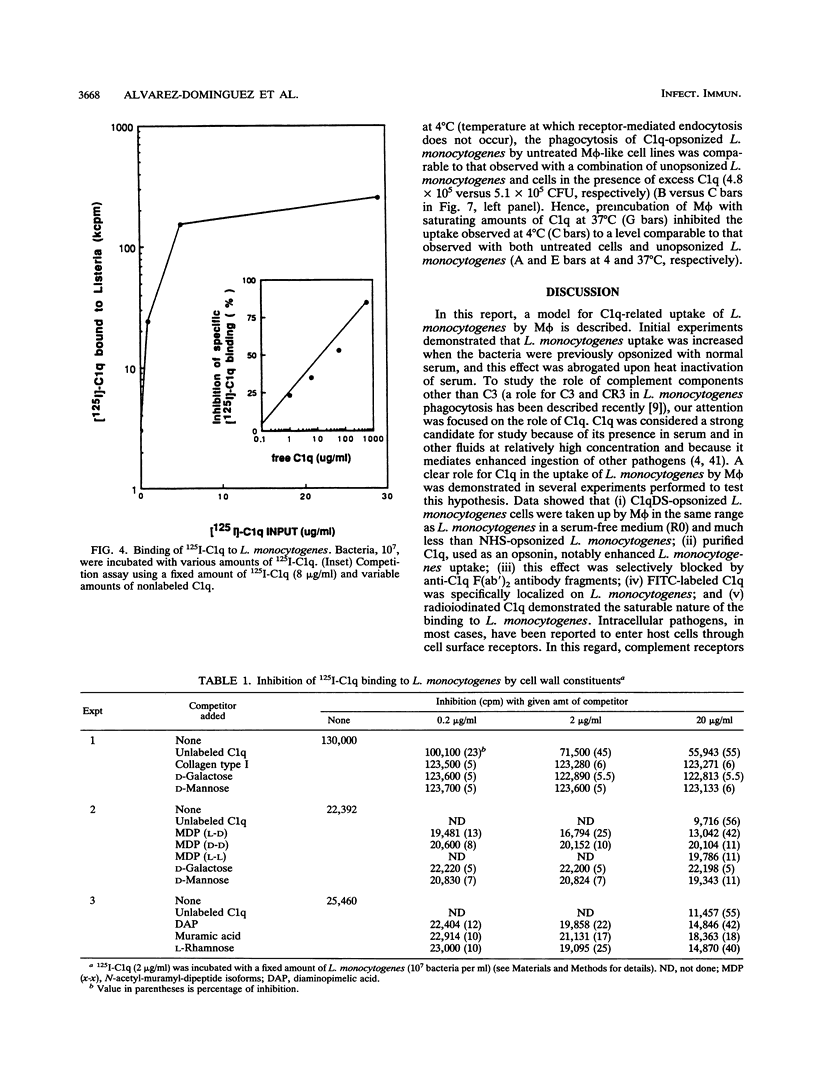
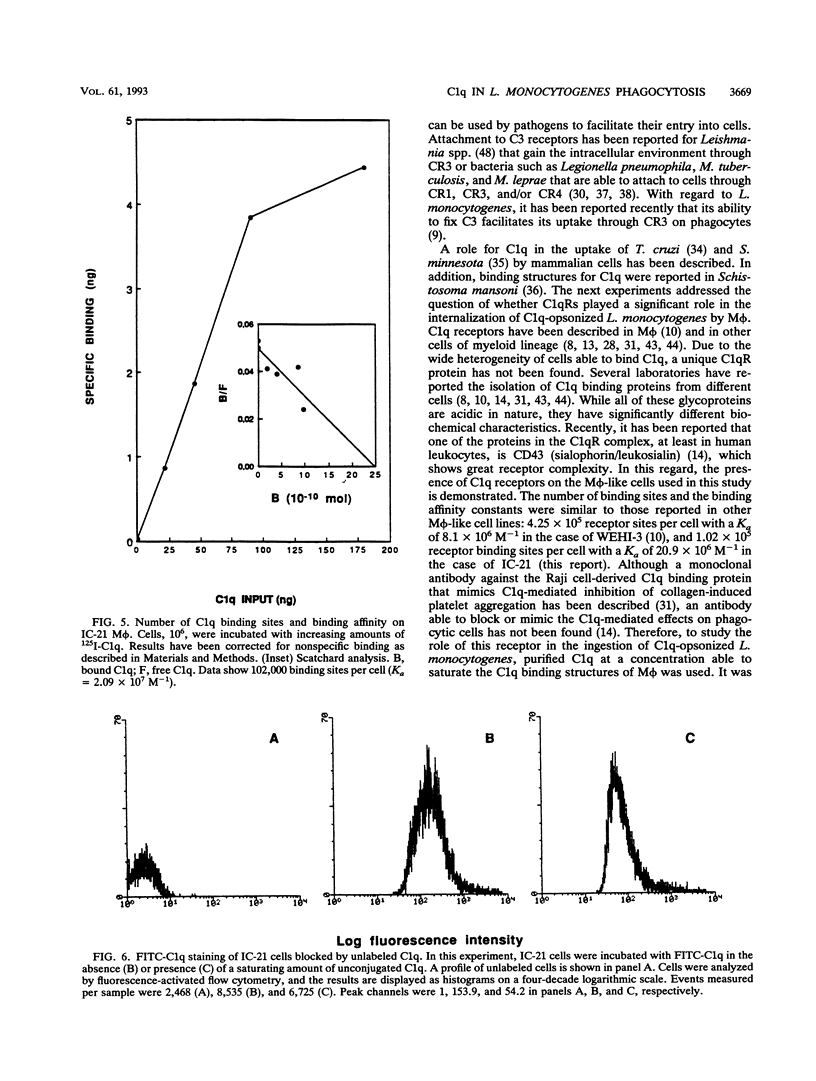
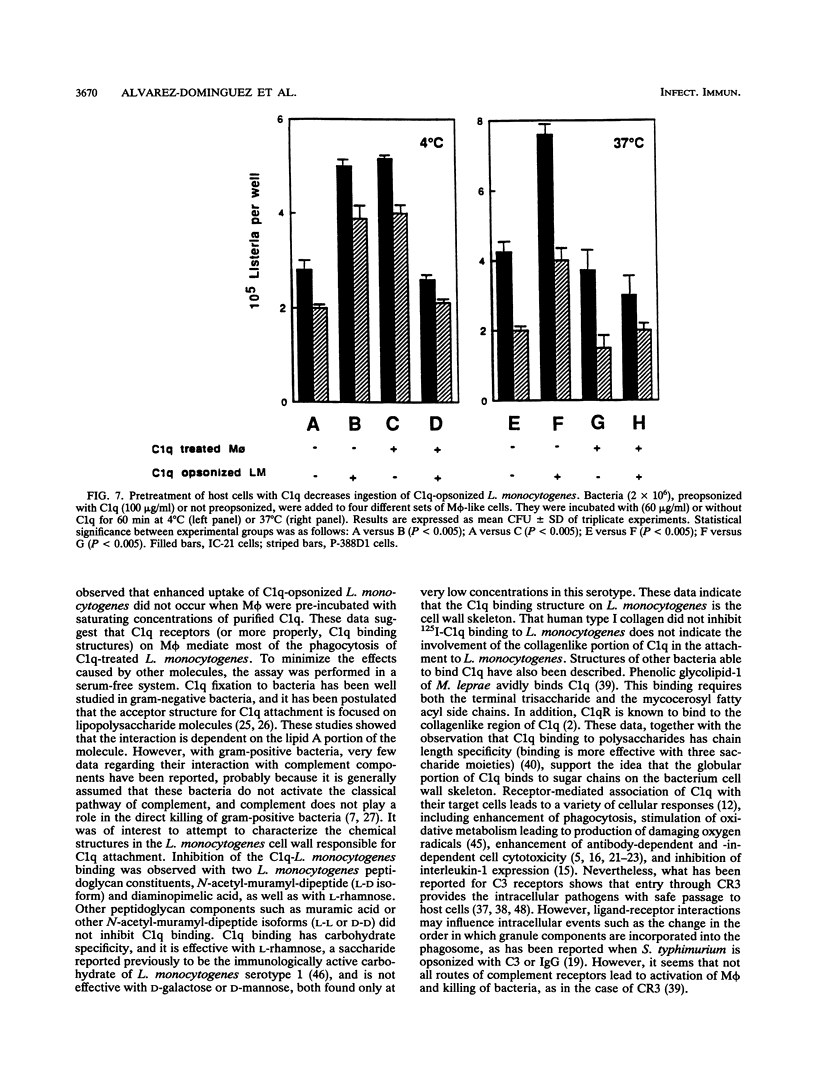
Listeria monocytogenes is a facultative intracellular pathogen of a great variety of cells. Among them, macrophages constitute the major effector cells of listerial immunity during the course of an infection. Although the molecular bases of L. monocytogenes attachment and entry to phagocytes are not completely understood, it has been demonstrated that C3b significantly increases L. monocytogenes uptake by macrophages via complement receptor type 3. The first component of complement, C1q, is present in organic fluids at a relatively high concentration, and C1q receptor sites in macrophages are also abundant. In the present report, results of studies on the role of C1q in the internalization and infectivity of L. monocytogenes by macrophages are presented. L. monocytogenes uptake is enhanced by prior treatment of bacteria with normal sera. Heated serum or C1q-deficient serum abrogates this enhancement. Purified C1q specifically restored uptake. This effect was blocked by the addition of F(ab')2 anti-C1q antibody but not by an irrelevant matched antibody. Direct binding of C1q to L. monocytogenes was specific, saturable, and dose dependent with both fluorescent and radiolabeled C1q. N-Acetyl-D-alanyl-L-isoglutamine, diaminopimelic acid, and L-rhamnose caused a significant dose-dependent inhibition of C1q binding to bacteria, suggesting that these molecules, at least, are involved in the attachment of C1q to L. monocytogenes cell wall. When C1q binding structures on macrophage-like cells were blocked with saturating concentrations of C1q, the uptake of C1q-opsonized bacteria was less than in untreated cells. These experiments demonstrate that, in addition to other reported mechanisms, L. monocytogenes binds C1q, which mediates enhanced uptake by macrophages through C1q binding structures.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvieux J., Reboul A., Bensa J. C., Colomb M. G. Characterization of the C1q receptor on a human macrophage cell line, U937. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 1;218(2):547–555. doi: 10.1042/bj2180547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit Z., Goldman R., Ofek I., Sharon N., Mirelman D. Mannose-binding activity of Escherichia coli: a determinant of attachment and ingestion of the bacteria by macrophages. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):417–424. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.417-424.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R. E. Antibody-independent interactions of fibronectin, C1q, and human neutrophils with Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):456–464. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.456-464.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobak D. A., Gaither T. A., Frank M. M., Tenner A. J. Modulation of FcR function by complement: subcomponent C1q enhances the phagocytosis of IgG-opsonized targets by human monocytes and culture-derived macrophages. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1150–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Wright S. D. Role of the adherence-promoting receptors, CR3, LFA-1, and p150,95, in binding of Histoplasma capsulatum by human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):195–210. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonrod J. D., Rylko-Bauer B. Complement-fixing antibody response in pneumococcal pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):617–623. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.617-623.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drevets D. A., Campbell P. A. Roles of complement and complement receptor type 3 in phagocytosis of Listeria monocytogenes by inflammatory mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2645–2652. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2645-2652.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdei A. C1q receptor on murine cells. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 15;145(6):1754–1760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Frehel C., Gouin E., Cossart P. Entry of L. monocytogenes into cells is mediated by internalin, a repeat protein reminiscent of surface antigens from gram-positive cocci. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1127–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90009-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet B. Functions associated with the C1q receptor. Behring Inst Mitt. 1989 Jul;(84):204–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet B., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Lysis of C1Q-coated chicken erythrocytes by human lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan E. N., Burgess W. H., Robinson S. L., Goodman E. B., McTigue K. J., Tenner A. J. Phagocytic cell molecules that bind the collagen-like region of C1q. Involvement in the C1q-mediated enhancement of phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20345–20355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habicht G. S., Beck G., Ghebrehiwet B. C1q inhibits the expression of B lymphoblastoid cell line interleukin 1 (IL 1). J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2593–2597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada A., Young J., Chmielewski R. A., Greene B. M. C1q enhancement of antibody-dependent granulocyte-mediated killing of nonphagocytosable targets in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):945–949. doi: 10.1172/JCI113702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Leong J. M. Multiple beta 1 chain integrins are receptors for invasin, a protein that promotes bacterial penetration into mammalian cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90099-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Ganz T., Albert J., Rotrosen D. The opsonizing ligand on Salmonella typhimurium influences incorporation of specific, but not azurophil, granule constituents into neutrophil phagosomes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2771–2782. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K., Brown E., Hammer C., Warren K., Frank M. Studies on the mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing. III. C5b-9 deposits stably on rough and type 7 S. pneumoniae without causing bacterial killing. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):845–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Goebel W. Identification of an extracellular protein of Listeria monocytogenes possibly involved in intracellular uptake by mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.55-61.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leu R. W., Kriet D., Zhou A., Herriott M. J., Rummage J. A., Shannon B. J. Reconstitution of murine resident peritoneal macrophages for antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity by homologous serum Clq. Cell Immunol. 1989 Aug;122(1):48–61. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leu R. W., Zhou A. Q., Kennedy M. J., Shannon B. J. Exogenous C1q reconstitutes a secondary deficiency of C5-deficient AKR mouse macrophages for FcR-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1233–1239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leu R. W., Zhou A. Q., Shannon B. J., Herriott M. J. Inhibitors of C1q biosynthesis suppress activation of murine macrophages for both antibody-independent and antibody-dependent tumor cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2281–2286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyva-Cobián F., Moneo I., Mampaso F., Sánchez-Bayle M., Ecija J. L., Bootello A. Familial C1q deficiency associated with renal and cutaneous disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Apr;44(1):173–180. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Bitter-Suermann D., Dierich M. Interaction of the first (C1), the second (C2) and the fourth (C4) component of complement with different preparations of bacterial lipopolysaccharides and with lipid A. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):935–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Brunner H. Complement components (C1, C2, C3, C4) in bronchial secretions after intranasal infection of guinea pigs with Mycoplasma pneumoniae: dissociation of unspecific and specific defense mechanisms. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):583–585. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.583-585.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra R., Thiel S., Reid K. B., Sim R. B. Human leukocyte C1q receptor binds other soluble proteins with collagen domains. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):955–959. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Legionella pneumophila is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1377–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I., Ghebrehiwet B. Platelet C1q receptor interactions with collagen- and C1q-coated surfaces. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2984–2988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B. Amino acid sequence of the N-terminal forty-two amino acid residues of the C chain of subcomponent C1q of the first component of human complement. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 1;161(2):247–251. doi: 10.1042/bj1610247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimoldi M. T., Tenner A. J., Bobak D. A., Joiner K. A. Complement component C1q enhances invasion of human mononuclear phagocytes and fibroblasts by Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1982–1989. doi: 10.1172/JCI114388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Schultz D. R., Goodwin J. D., Vann J. M., Selvaraj M. P., Hart M. A. Role of C1q in phagocytosis of Salmonella minnesota by pulmonary endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1356–1362. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1356-1362.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro F., Ouaissi M. A., Pestel J., Capron A. Interaction between Schistosoma mansoni and the complement system: binding of C1q to schistosomula. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2886–2891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger L. S., Bellinger-Kawahara C. G., Payne N. R., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors and complement component C3. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2771–2780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger L. S., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Mycobacterium leprae by human monocyte-derived macrophages is mediated by complement receptors CR1 (CD35), CR3 (CD11b/CD18), and CR4 (CD11c/CD18) and IFN-gamma activation inhibits complement receptor function and phagocytosis of this bacterium. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1983–1994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger L. S., Horwitz M. A. Phenolic glycolipid-1 of Mycobacterium leprae binds complement component C3 in serum and mediates phagocytosis by human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1031–1038. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz D. R., Arnold P. I. The first component of human complement: on the mechanism of activation by some carbohydrates. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1994–1998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorvillo J. M., Pearlstein E. C1q, a subunit of the first component of complement, enhances binding of plasma fibronectin to bacteria. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):664–669. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.664-669.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P., Gordon S. Expression of a mannosyl-fucosyl receptor for endocytosis on cultured primary macrophages and their hybrids. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):49–56. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J. C1q interactions with cell surface receptors. Behring Inst Mitt. 1989 Jul;(84):220–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Cooper N. R. Analysis of receptor-mediated C1q binding to human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1658–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Cooper N. R. Stimulation of a human polymorphonuclear leukocyte oxidative response by the C1q subunit of the first complement component. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2547–2552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann W. W., Cameron J. A. Immunochemistry of the cell walls of Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.486-493.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicente M. F., Baquero F., Cossart P., Pérez-Díaz J. C. Cloning of two possible haemolysin determinants from Listeria monocytogenes. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 May-Jun;138(3):385–387. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. E., Pearson R. D. Roles of CR3 and mannose receptors in the attachment and ingestion of Leishmania donovani by human mononuclear phagocytes. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):363–369. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.363-369.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



