Abstract
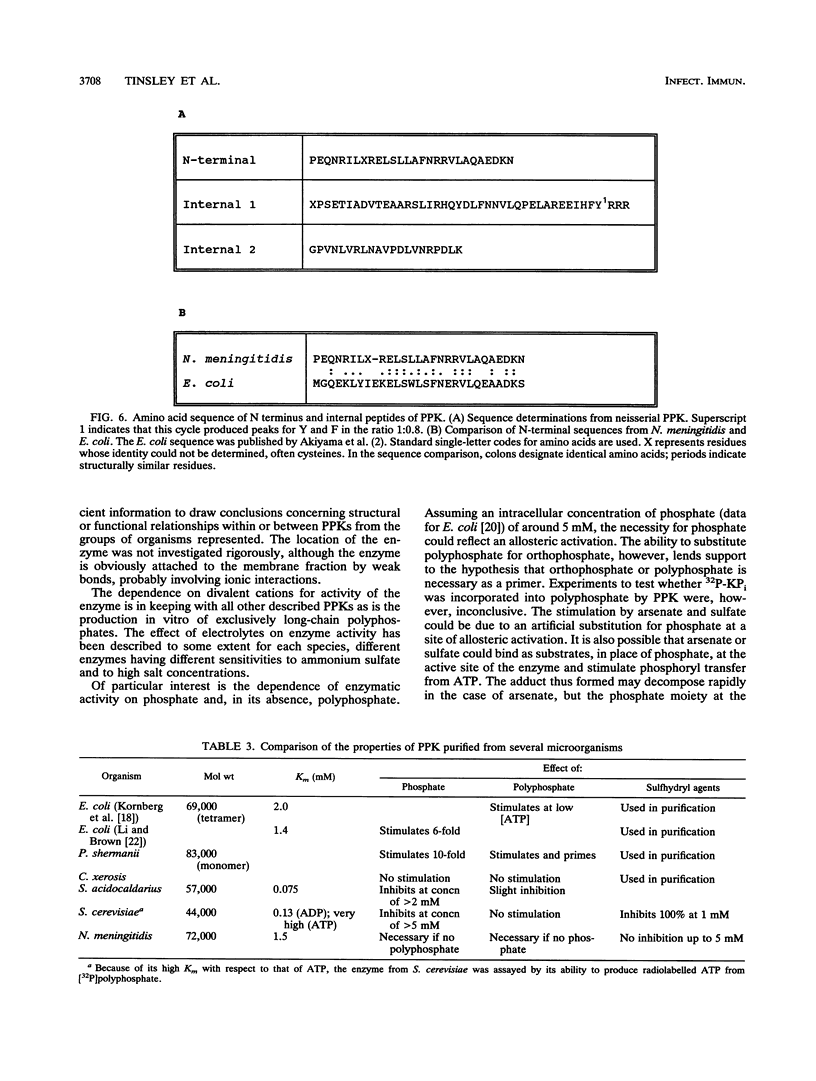
The important human pathogens Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae accumulate phosphate in the form of polyphosphate (A. Noegel and E. C. Gotschlich, J. Exp. Med. 157:2049-2060, 1983), and the localization of more than half of this long-chain polymer on the exterior of the cells suggests a function as a protective, capsule-like coating. To enable further genetic investigation of the role of polyphosphate in Neisseria spp., the enzyme polyphosphate kinase (PPK), which catalyzes the synthesis of polyphosphate from ATP, was purified from N. meningitidis BNCV. The activity is dependent on Mg2+ and phosphate or polyphosphate and is inhibited by ADP. The Km for ATP is 1.5 mM, and the turnover number is 47 phosphate residues per polypeptide per s. Analysis of PPK labelled with [gamma-32P]ATP indicates that the enzyme is phosphorylated during the reaction, probably at an arginine residue. N-terminal and two internal amino acid sequences were derived from the purified protein and will allow the design of synthetic oligonucleotides for cloning and genetic manipulation of the ppk gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn K., Kornberg A. Polyphosphate kinase from Escherichia coli. Purification and demonstration of a phosphoenzyme intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11734–11739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama M., Crooke E., Kornberg A. The polyphosphate kinase gene of Escherichia coli. Isolation and sequence of the ppk gene and membrane location of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22556–22561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton F. E., Ryan A., Diena B., Jennings H. J. A new serogroup (L) of Neisseria meningitidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):722–727. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.722-727.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee A. K., Jennings H. J., Kenny C. P. Structural elucidation of the 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid containing meningococcal 29-e capsular polysaccharide antigen using carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):645–651. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. E., Wood H. G. Preparation of standards and determination of sizes of long-chain polyphosphates by gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1987 Mar;161(2):280–290. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90452-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duclos B., Marcandier S., Cozzone A. J. Chemical properties and separation of phosphoamino acids by thin-layer chromatography and/or electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:10–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01004-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felter S., Stahl A. J. Enzymes du métabolisme des polyphosphates dans la levure. 3. Purification et propriétés de la polyphosphate-ADP-phosphotransferase. Biochimie. 1973;55(3):245–251. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J., DeMott M., Atherton D., Mische S. M. Internal protein sequence analysis: enzymatic digestion for less than 10 micrograms of protein bound to polyvinylidene difluoride or nitrocellulose membranes. Anal Biochem. 1992 Mar;201(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90336-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Chapman S. S. Classification of Neisseria meningitidis group B into distinct serotypes. I. Serological typing by a microbactericidal method. Infect Immun. 1972 Jan;5(1):98–102. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.1.98-102.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Inorganic polyphosphates in biology: structure, metabolism, and function. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Dec;30(4):772–794. doi: 10.1128/br.30.4.772-794.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendley J. W., Powell K. R., Rodewald R., Holzgrefe H. H., Lyles R. Demonstration of a capsule on Neisseria gonorrhoeae. N Engl J Med. 1977 Mar 17;296(11):608–611. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197703172961105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. F., Swanson J. The capsule of the gonococcus. J Exp Med. 1977 Apr 1;145(4):1082–1086. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.4.1082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Bhattacharjee A. K., Bundle D. R., Kenny C. P., Martin A., Smith I. C. Strucutres of the capsular polysaccharides of Neisseria meningitidis as determined by 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S78–S83. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALTWASSER H. [The role of polyphosphate in phosphorus metabolism of an oxyhydrogen gas bacterium (Hydrogenomonas strain 20)]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;41:282–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG A., KORNBERG S. R., SIMMS E. S. Metaphosphate synthesis by an enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Apr;20(1):215–227. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90280-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulaev I. S., Vagabov V. M. Polyphosphate metabolism in micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol. 1983;24:83–171. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. C., Brown G. G. Orthophosphate and histone dependent polyphosphate kinase from E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):875–881. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUHAMMED A. Studies on biosynthesis of polymetaphosphate by an enzyme from Corynebacterium xerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Nov 25;54:121–132. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90945-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlradt P. F. Synthesis of high molecular weight polyphosphate with a partially purified enzyme from Salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Sep;68(1):115–122. doi: 10.1099/00221287-68-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A., Gotschlich E. C. Isolation of a high molecular weight polyphosphate from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):2049–2060. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.2049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pas H. H., Robillard G. T. S-phosphocysteine and phosphohistidine are intermediates in the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent mannitol transport catalyzed by Escherichia coli EIIMtl. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):5835–5839. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepin C. A., Wood H. G. Polyphosphate glucokinase from Propionibacterium shermanii. Kinetics and demonstration that the mechanism involves both processive and nonprocessive type reactions. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4476–4480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reusch R. N., Sadoff H. L. Putative structure and functions of a poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate/calcium polyphosphate channel in bacterial plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4176–4180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson N. A., Clark J. E., Wood H. G. Polyphosphate kinase from Propionibacterium shermanii. Demonstration that polyphosphates are primers and determination of the size of the synthesized polyphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5216–5222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson N. A., Goss N. H., Wood H. G. Polyphosphate kinase from Propionibacterium shermanii: formation of an enzymatically active insoluble complex with basic proteins and characterization of synthesized polyphosphate. Biochem Int. 1984 Jun;8(6):757–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZYMONA M., OSTROWSKI W. INORGANIC POLYPHOSPHATE GLUCOKINASE OF MYCOBACTERIUM PHLEI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 4;85:283–295. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90249-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skórko R., Osipiuk J., Stetter K. O. Glycogen-bound polyphosphate kinase from the archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5162–5164. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5162-5164.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Halpern R. M., Bruegger B. B., Dunlap A. K., Fricke O. Chromosomal protein phosphorylation on basic amino acids. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;19:153–159. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]