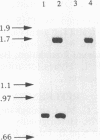
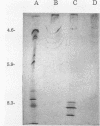
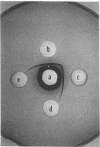
Abstract
Streptococcal proteinase precursor (SPP) is a zymogen secreted by Streptococcus pyogenes that becomes activated to a cysteine proteinase. SPP has been shown to be immunologically identical to streptococcal erythrogenic toxin B (SPE B), and sequence comparison has shown a high degree of homology between the two proteins. In this study, we have constructed a speB mutant strain of S. pyogenes by insertional inactivation. An internal fragment of the cloned speB gene in plasmid pCR1000 was replaced with an erythromycin resistance determinant, and the recombinant plasmid was introduced into strain NZ131 by electrotransformation. Following the selection of erythromycin-resistant clones, Southern hybridization experiments confirmed the presence of the recombinant plasmid containing the erm gene in the chromosome of the resistant strains. Analysis of extracellular proteins produced by the wild-type and speB mutant strains by Ouchterlony immunodiffusion and isoelectric focusing revealed the presence of SPE B in the wild-type strain but not the speB mutant. Additionally, SPP, which has an isoelectric focusing pattern similar to that of SPE B and reacts with SPE B antiserum, was not detected among the extracellular proteins of the speB mutant strain. Proteinase activity as assayed by two different methods was present in the extracellular proteins produced by the wild-type strain, but the speB mutant strain had no extracellular proteinase activity. The mutant strain had a growth rate similar to that of the wild-type strain and produced normal levels of other extracellular products, suggesting that proteinase was not essential for viability as previously suggested. Our data are consistent with the view that a single gene (speB) produces a single protein that has been identified and/or assayed as either SPE B or SPP.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsumian E. L., Cunningham C. M., Schlievert P. M., Watson D. W. Heterogeneity of group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type B. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):512–518. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.512-518.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L., Akesson P., Bohus M., Trojnar J., Abrahamson M., Olafsson I., Grubb A. Bacterial growth blocked by a synthetic peptide based on the structure of a human proteinase inhibitor. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):385–386. doi: 10.1038/337385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borck K., Beggs J. D., Brammar W. J., Hopkins A. S., Murray N. E. The construction in vitro of transducing derivatives of phage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jul 23;146(2):199–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00268089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. T., Niemela S. L., Miller R. H. One-step preparation of competent Escherichia coli: transformation and storage of bacterial cells in the same solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2172–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W., Becker D., Davies J. Plasmid-determined fusidic acid resistance in the Enterobacteriaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jul;83(0):191–196. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füvessy I., Böszörményi J., Veress A. The effect of the physico-chemical parameters of Streptococcus pyogenes cultures on the formation of O-streptolysin. II. The role of reducing agents in the formation of O-streptolysin. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1967;24(4):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach D., Knöll H., Köhler W., Ozegowski J. H., Hríbalova V. Isolation and characterization of erythrogenic toxins. V. Communication: identity of erythrogenic toxin type B and streptococcal proteinase precursor. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Sep;255(2-3):221–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser A. R., Schlievert P. M. Nucleotide sequence of the streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type B gene and relationship between the toxin and the streptococcal proteinase precursor. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4536–4542. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4536-4542.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes W. L., Ferretti J. J., Gilmore M. S., Segarra R. A. PCR amplification of streptococcal DNA using crude cell lysates. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Jul 1;73(1-2):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90597-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortt A. A., Liu T. Y. On the mechanism of action of streptococcal proteinase. I. Active-site titration. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 16;12(2):320–327. doi: 10.1021/bi00726a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU T. Y., ELLIOTT S. D. ACTIVATION OF STREPTOCOCCAL PROTEINASE AND ITS ZYMOGEN BY BACTERIAL CELL WALLS. Nature. 1965 Apr 3;206:33–34. doi: 10.1038/206033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. II. Prog Allergy. 1962;6:30–154. doi: 10.1159/000313795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Chopin A. Construction of a vector plasmid family and its use for molecular cloning in Streptococcus lactis. Biochimie. 1988 Apr;70(4):559–566. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Ferretti J. J. Electrotransformation of Streptococcus pyogenes with plasmid and linear DNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Aug 1;66(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai J. Y., Kortt A. A., Liu T. Y., Elliott S. D. Primary structure of streptococcal proteinase. III. Isolation of cyanogen bromide peptides: complete covalent structure of the polypeptide chain. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1955–1959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. E., Ferretti J. J. Frequency of the erythrogenic toxin B and C genes (speB and speC) among clinical isolates of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):211–215. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.211-215.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. E., Ferretti J. J. Molecular epidemiologic analysis of the type A streptococcal exotoxin (erythrogenic toxin) gene (speA) in clinical Streptococcus pyogenes strains. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3715–3719. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3715-3719.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]