Abstract
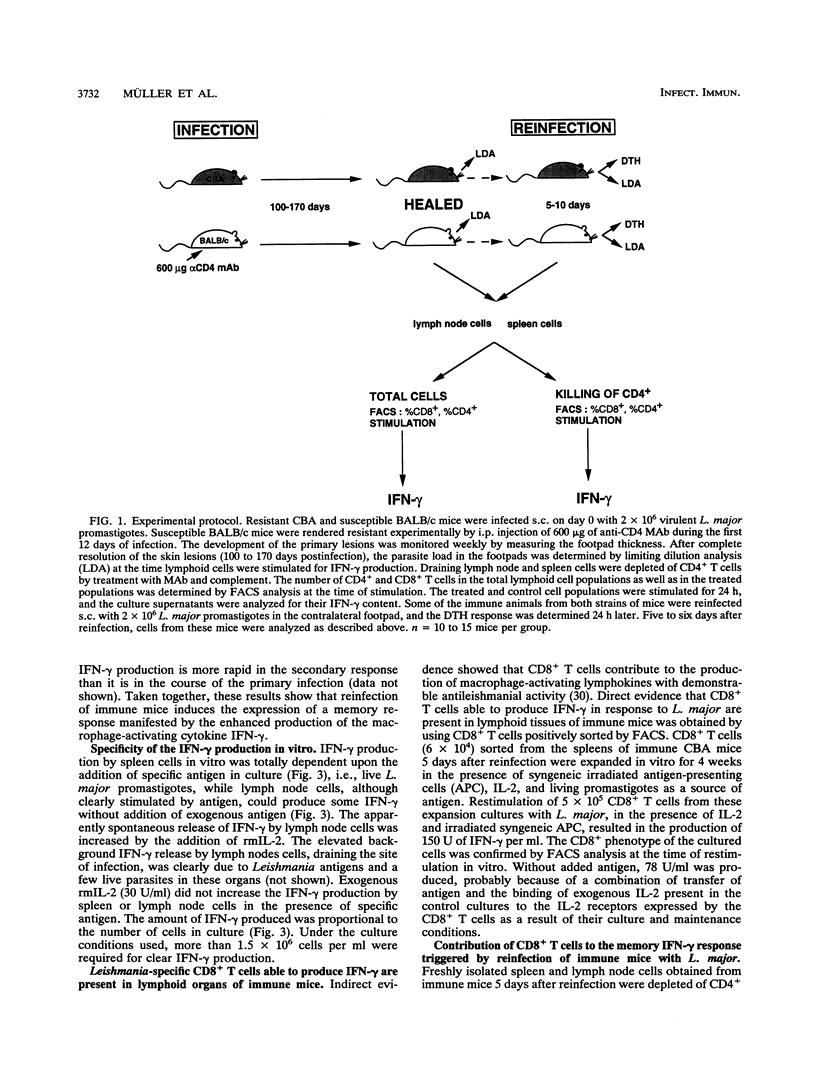
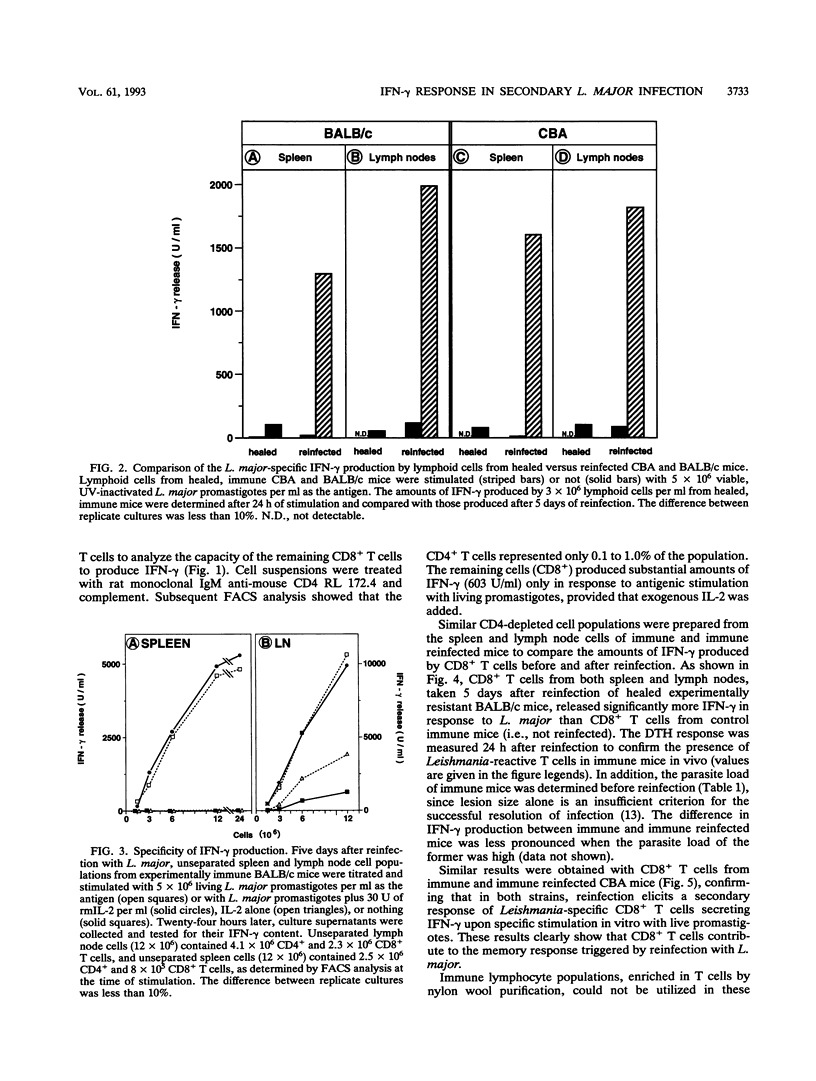
CD8+ T cells have been shown to contribute to the rapid resolution of secondary lesions developing in immune mice challenged with Leishmania major. In the present study, we assessed directly the participation of specific CD8+ T cells in the memory response induced in immune mice by reinfection. Lymphocyte populations from reinfected immune mice exhibit marked secondary gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) responses. The participation of IFN-gamma-producing CD8+ T cells in the memory response elicited by secondary infectious challenge was demonstrated in both genetically resistant immune CBA mice and genetically susceptible immune BALB/c mice that were rendered resistant by administration of anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody in the early phase of the primary infection. The protective function of CD8+ T cells in experimental murine cutaneous leishmaniasis might thus be explained in part by their ability to secrete IFN-gamma. In this context, the neutralization of IFN-gamma at the time of reinfection reduced the Leishmania-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity response, showing that this cytokine is involved in the recall of immunological memory to L. major in vivo.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behin R., Mauel J., Sordat B. Leishmania tropica: pathogenicity and in vitro macrophage function in strains of inbred mice. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Aug;48(1):81–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan C., Moll H., Solbach W., Röllinghoff M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha in combination with interferon-gamma, but not with interleukin 4 activates murine macrophages for elimination of Leishmania major amastigotes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):1131–1135. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceredig R., Lowenthal J. W., Nabholz M., MacDonald H. R. Expression of interleukin-2 receptors as a differentiation marker on intrathymic stem cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):98–100. doi: 10.1038/314098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherwinski H. M., Schumacher J. H., Brown K. D., Mosmann T. R. Two types of mouse helper T cell clone. III. Further differences in lymphokine synthesis between Th1 and Th2 clones revealed by RNA hybridization, functionally monospecific bioassays, and monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1229–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Quan Z. S., Wall K. A., Pierres A., Quintáns J., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Fitch F. W. Characterization of the murine T cell surface molecule, designated L3T4, identified by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: similarity of L3T4 to the human Leu-3/T4 molecule. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2445–2451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell J. P., Muller I., Louis J. A. A role for Lyt-2+ T cells in resistance to cutaneous leishmaniasis in immunized mice. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):2052–2056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzinelli R. T., Hakim F. T., Hieny S., Shearer G. M., Sher A. Synergistic role of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes in IFN-gamma production and protective immunity induced by an attenuated Toxoplasma gondii vaccine. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):286–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzinelli R., Xu Y., Hieny S., Cheever A., Sher A. Simultaneous depletion of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes is required to reactivate chronic infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. J., Nacy C. A., Meltzer M. S. Cytokine-induced synthesis of nitrogen oxides in macrophages: a protective host response to Leishmania and other intracellular pathogens. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Jul;50(1):93–103. doi: 10.1002/jlb.50.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Ceredig R., Mitchell G. F. Murine cutaneous leishmaniasis: disease patterns in intact and nude mice of various genotypes and examination of some differences between normal and infected macrophages. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1979 Feb;57(1):9–29. doi: 10.1038/icb.1979.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. O., Awwad M., North R. J. Elimination of CD4+ suppressor T cells from susceptible BALB/c mice releases CD8+ T lymphocytes to mediate protective immunity against Leishmania. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1819–1827. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. O., North R. J., Collins F. M. Advantages of measuring changes in the number of viable parasites in murine models of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1087–1094. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1087-1094.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. O. Reduced numbers of CD4+ suppressor cells with subsequent expansion of CD8+ protective T cells as an explanation for the paradoxical state of enhanced resistance to Leishmania in T-cell deficient BALB/c mice. Immunology. 1991 Feb;72(2):282–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Immunological regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. IV. Prophylactic effect of sublethal irradiation as a result of abrogation of suppressor T cell generation in mice genetically susceptible to Leishmania tropica. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):557–568. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. L. The effector function of nitrogen oxides in host defense against parasites. Exp Parasitol. 1991 Aug;73(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(91)90025-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Melchers F. Establishment of mouse cell lines which constitutively secrete large quantities of interleukin 2, 3, 4 or 5, using modified cDNA expression vectors. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):97–104. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Hug E., De Libero G. Listeria monocytogenes-reactive T lymphocyte clones with cytolytic activity against infected target cells. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):363–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye P. M., Cooke A., Lund T., Wattie M., Blackwell J. M. Altered course of visceral leishmaniasis in mice expressing transgenic I-E molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Feb;22(2):357–364. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelso A., MacDonald H. R., Smith K. A., Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Interleukin 2 enhancement of lymphokine secretion by T lymphocytes: analysis of established clones and primary limiting dilution microcultures. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2932–2938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y. Functional heterogeneity of CD4+ T cells in leishmaniasis. Immunol Today. 1989 Feb;10(2):40–45. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90302-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Millott S., Lelchuk R., Cobbold S., Waldmann H. Effect of CD4 monoclonal antibody in vivo on lesion development, delayed-type hypersensitivity and interleukin 3 production in experimental murine cutaneous leishmaniasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Mar;75(3):438–443. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Lees R. K., Sordat B., Zaech P., Maryanski J. L., Bron C. Age-associated increase in expression of the T cell surface markers Thy-1, Lyt-1, and Lyt-2 in congenitally athymic (nu/nu) mice: analysis by flow microfluorometry. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):865–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElrath M. J., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. The dynamics of granuloma formation in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1927–1937. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milon G., Titus R. G., Cerottini J. C., Marchal G., Louis J. A. Higher frequency of Leishmania major-specific L3T4+ T cells in susceptible BALB/c as compared with resistant CBA mice. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1467–1471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Spitalny G. L., Nathan C. F. Activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro and in vivo by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1619–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Squires K. E., Miralles C. D., Stoeckle M. Y., Granger A. M., Granelli-Piperno A., Bogdan C. Acquired resistance and granuloma formation in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Differential T cell and lymphokine roles in initial versus established immunity. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1858–1863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller I., Garcia-Sanz J. A., Titus R., Behin R., Louis J. Analysis of the cellular parameters of the immune responses contributing to resistance and susceptibility of mice to infection with the intracellular parasite, Leishmania major. Immunol Rev. 1989 Dec;112:95–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller I., Pedrazzini T., Kropf P., Louis J., Milon G. Establishment of resistance to Leishmania major infection in susceptible BALB/c mice requires parasite-specific CD8+ T cells. Int Immunol. 1991 Jun;3(6):587–597. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.6.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller I., Pedrazzini T., Louis J. A. Experimentally induced cutaneous leishmaniasis: are L3T4+ T cells that promote parasite growth distinct from those mediating resistance? Immunol Lett. 1988 Nov;19(3):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(88)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller I. Role of T cell subsets during the recall of immunologic memory to Leishmania major. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Dec;22(12):3063–3069. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Nelson B. J., Meltzer M. S., Green S. J. Cytokines that regulate macrophage production of nitrogen oxides and expression of antileishmanial activities. Res Immunol. 1991 Sep;142(7):573–576. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(91)90105-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres M., Goridis C., Golstein P. Inhibition of murine T cell-mediated cytolysis and T cell proliferation by a rat monoclonal antibody immunoprecipitating two lymphoid cell surface polypeptides of 94 000 and 180 000 molecular weight. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jan;12(1):60–69. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat M., Gribaudo G., Comoglio P. M., Cavallo G., Landolfo S. Monoclonal antibodies against murine gamma interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4515–4519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadick M. D., Heinzel F. P., Holaday B. J., Pu R. T., Dawkins R. S., Locksley R. M. Cure of murine leishmaniasis with anti-interleukin 4 monoclonal antibody. Evidence for a T cell-dependent, interferon gamma-independent mechanism. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):115–127. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadick M. D., Heinzel F. P., Shigekane V. M., Fisher W. L., Locksley R. M. Cellular and humoral immunity to Leishmania major in genetically susceptible mice after in vivo depletion of L3T4+ T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1303–1309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. IgG or IgM monoclonal antibodies reactive with different determinants on the molecular complex bearing Lyt 2 antigen block T cell-mediated cytolysis in the absence of complement. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2665–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P., Pearce E., Cheever A. W., Coffman R. L., Sher A. Role of cytokines and CD4+ T-cell subsets in the regulation of parasite immunity and disease. Immunol Rev. 1989 Dec;112:161–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00557.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slade S. J., Langhorne J. Production of interferon-gamma during infection of mice with Plasmodium chabaudi chabaudi. Immunobiology. 1989 Oct;179(4-5):353–365. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(89)80041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. E., Rodrigues M., Russell D. G. The interaction between CD8+ cytotoxic T cells and Leishmania-infected macrophages. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):499–505. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitalny G. L., Havell E. A. Monoclonal antibody to murine gamma interferon inhibits lymphokine-induced antiviral and macrophage tumoricidal activities. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1560–1565. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. J., Oca M. J., Rubin B. Y., Anderson S. L., Murray H. W. Role of L3T4+ and LyT-2+ cells in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3971–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Ceredig R., Cerottini J. C., Louis J. A. Therapeutic effect of anti-L3T4 monoclonal antibody GK1.5 on cutaneous leishmaniasis in genetically-susceptible BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2108–2114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Kelso A., Louis J. A. Intracellular destruction of Leishmania tropica by macrophages activated with macrophage activating factor/interferon. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jan;55(1):157–165. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Marchand M., Boon T., Louis J. A. A limiting dilution assay for quantifying Leishmania major in tissues of infected mice. Parasite Immunol. 1985 Sep;7(5):545–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1985.tb00098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Sakata T. Highly efficient action of autocrine mouse interferon-gamma expressed via a retroviral vector. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1627–1630. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



