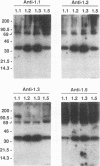
Abstract
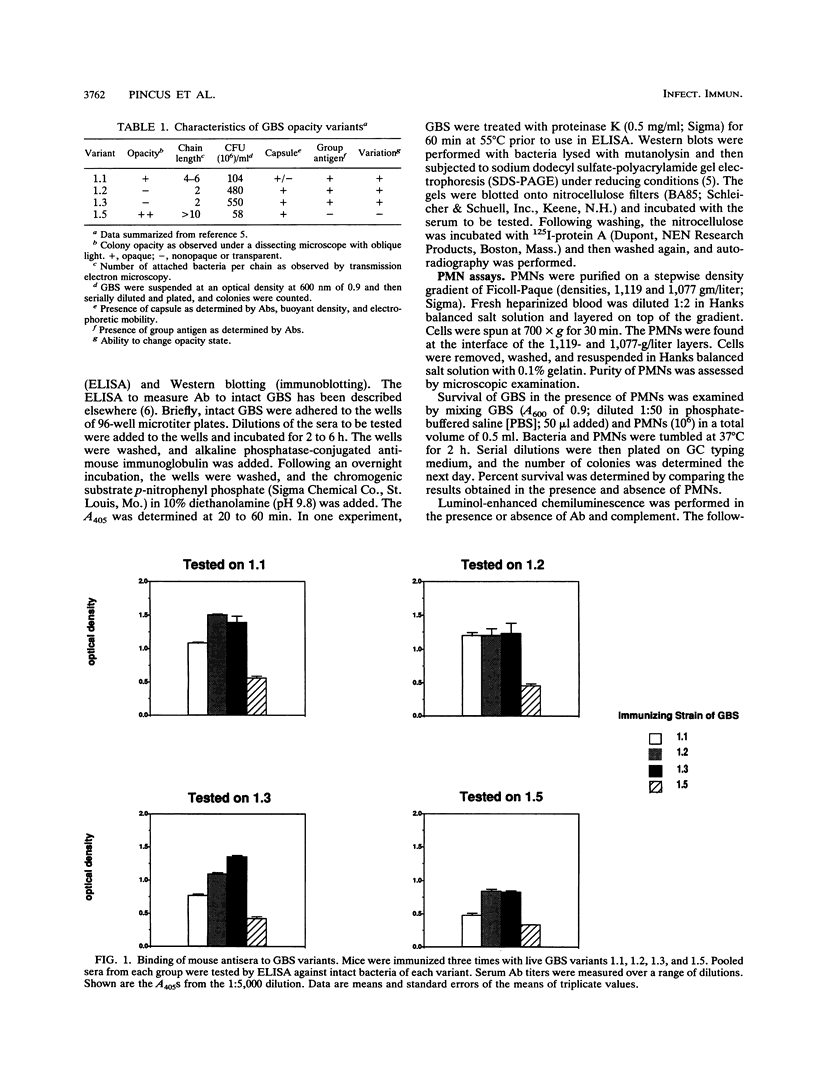
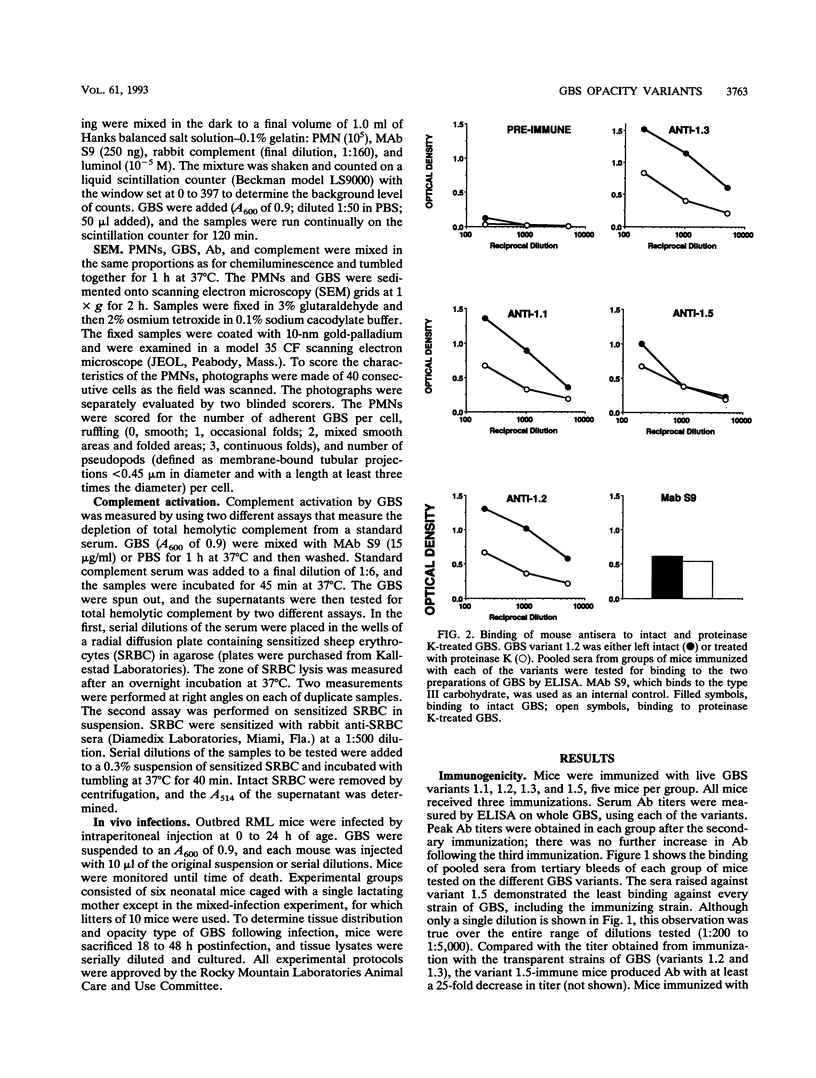
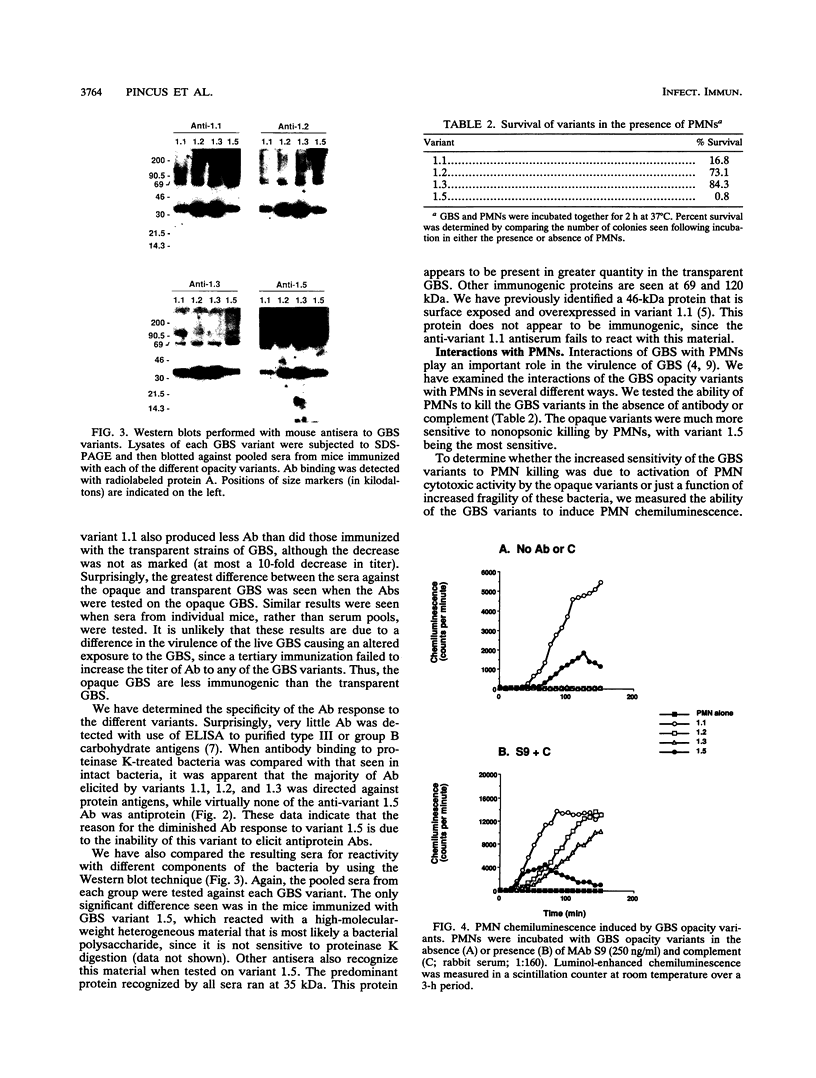
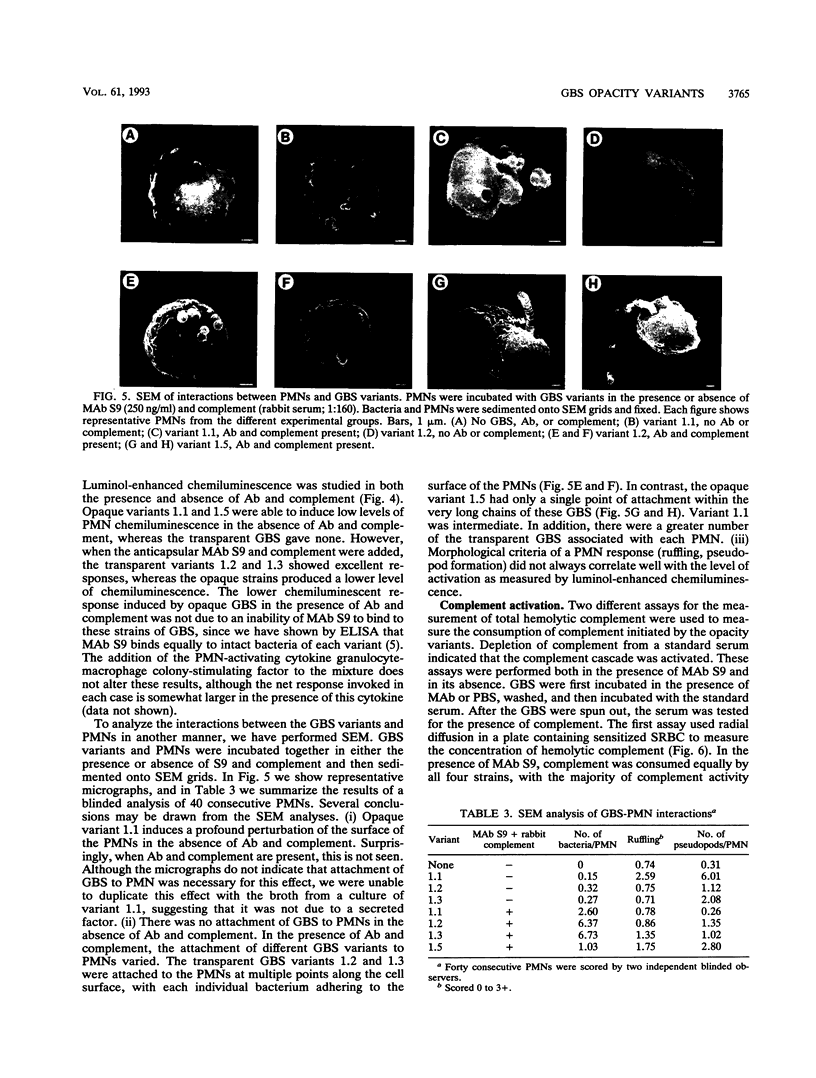
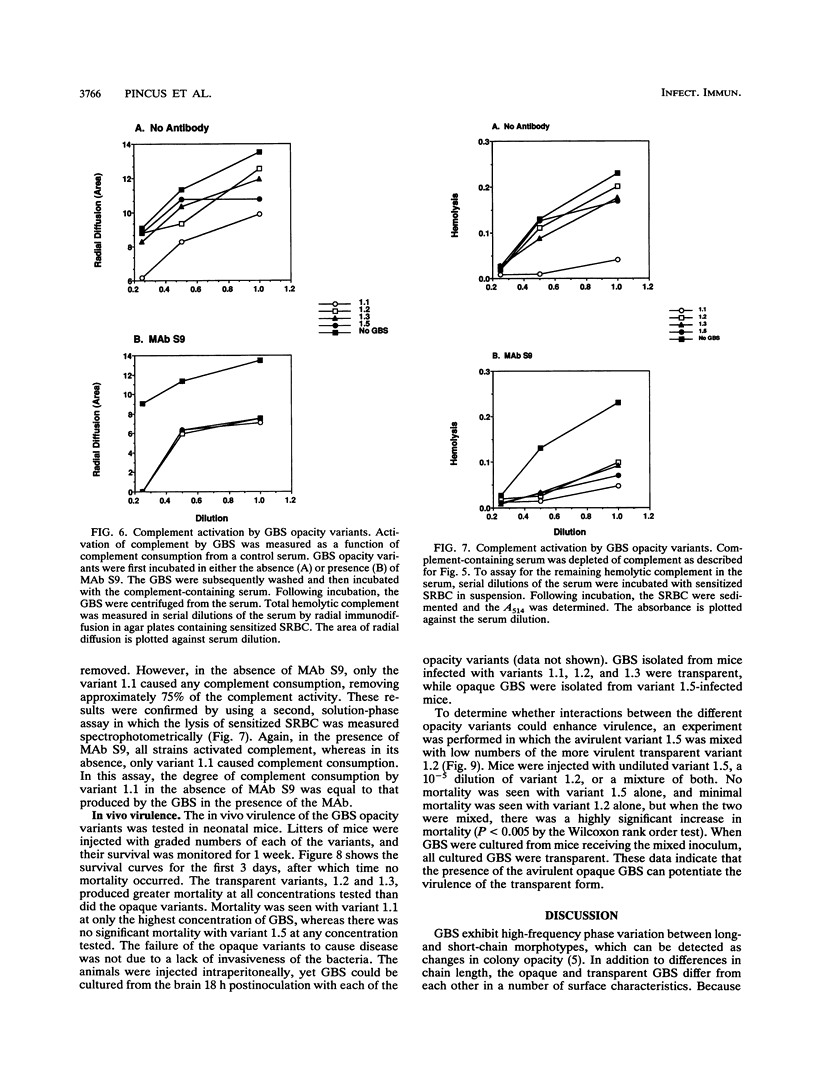
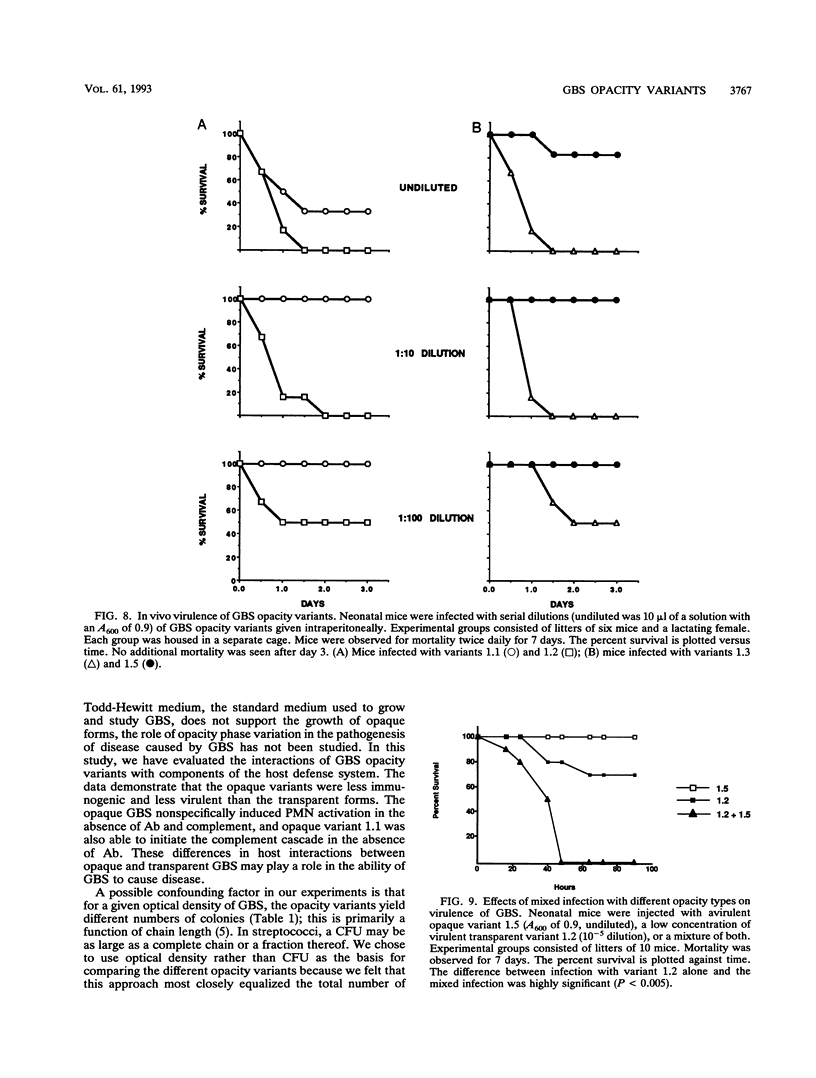
Group B streptococci (GBS) demonstrate high-frequency phase variation of colony opacity. Colony opacity is a function of chain length, with opaque colonies consisting of GBS that form longer chains. Because opaque variants do not grow on standard streptococcal media, the role of opacity variation in GBS infection has not been studied. We have isolated stable variants from type III GBS that are either transparent (variants 1.2 and 1.3) or opaque (variants 1.1 and 1.5). In this study, we evaluated the interactions of these variants with different components of the host immune system both in vitro and in vivo. Opaque GBS were less immunogenic than transparent GBS. Opaque GBS were more susceptible to killing by polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) and could induce a chemiluminescent response of PMNs in the absence of antibody (Ab) or complement. Transparent GBS did not induce neutrophil chemiluminescence in the absence of Ab and complement. However, in the presence of Ab and complement, transparent GBS induced a stronger chemiluminescent response than did opaque GBS. Scanning electron micrographs of PMNs and GBS demonstrated differences in the attachment and engulfment of the different variants by the PMNs as well as different effects of the GBS on the PMNs themselves. Interactions with complement were affected by GBS opacity as well, with opaque variant 1.1 initiating complement activation in the absence of any Ab. The virulence of the GBS opacity variants was studied in vivo by inoculation of graded numbers of GBS into newborn mice. Transparent variants 1.2 and 1.3 were most virulent, with variant 1.1 intermediate and variant 1.5 minimally virulent. However, in mixed infections, variant 1.5 greatly enhanced the virulence of small numbers of transparent GBS. These results indicate that the opacity status of GBS can influence the interaction between the GBS and the host immune system.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. J. Group B streptococcal infection in newborns: prevention at last? N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 26;314(26):1702–1704. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606263142609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. S., Kasper D. L., Jennings H. J., Baker C. J., Nicholson-Weller A. Capsular sialic acid prevents activation of the alternative complement pathway by type III, group B streptococci. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1278–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemming V. G., Hall R. T., Rhodes P. G., Shigeoka A. O., Hill H. R. Assessment of group B streptococcal opsonins in human and rabbit serum by neutrophil chemiluminescence. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1379–1387. doi: 10.1172/JCI108593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Cole R. L., Wessels M. R., Corwin M. D., Kamanga-Sollo E., Hayes S. F., Cieplak W., Jr, Swanson J. Group B streptococcal opacity variants. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3739–3749. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3739-3749.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Shigeoka A. O., Moe A. A., Ewing L. P., Hill H. R. Protective efficacy of IgM monoclonal antibodies in experimental group B streptococcal infection is a function of antibody avidity. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2779–2785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Wessels M. R., Heggen L. M., Kasper D. L. Transposon mutagenesis of type III group B Streptococcus: correlation of capsule expression with virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7208–7212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigeoka A. O., Rote N. S., Santos J. I., Hill H. R. Assessment of the virulence factors of group B streptococci: correlation with sialic acid content. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):857–863. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summary of the workshop on perinatal infections due to group B Streptococcus. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):137–152. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels M. R., Rubens C. E., Benedí V. J., Kasper D. L. Definition of a bacterial virulence factor: sialylation of the group B streptococcal capsule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8983–8987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]