Abstract
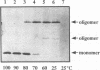
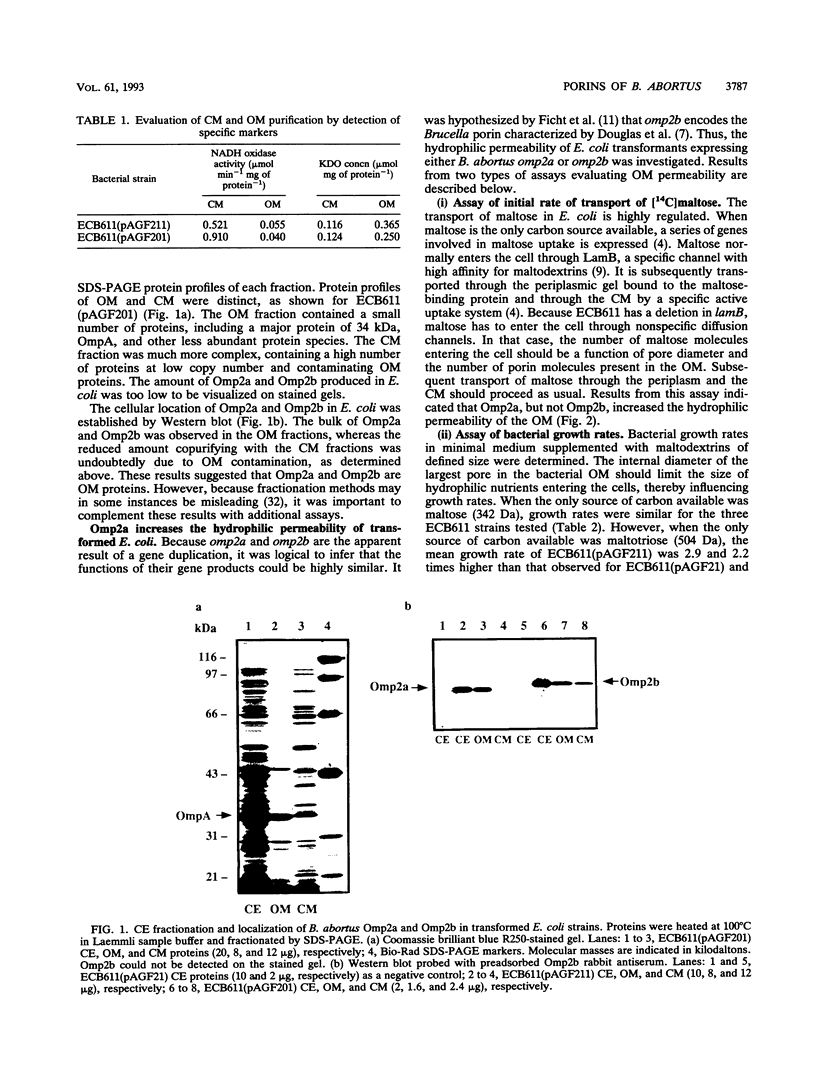
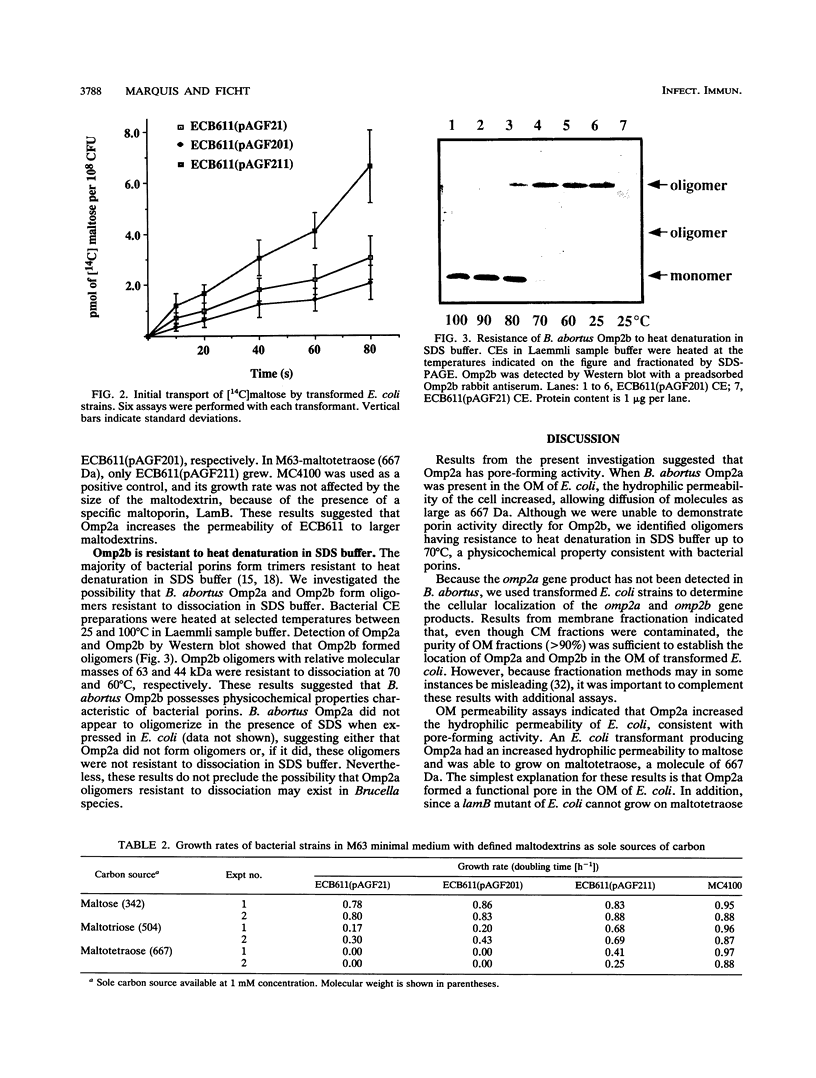
In Brucella abortus, a gene encoding a major cell envelope protein, omp2, is duplicated within a short segment of the large chromosomal DNA. Although both genes contain open reading frames, encoding proteins of high identity, expression from only one, omp2b, has been detected in laboratory-grown B. abortus. In the present study, we wished to determine whether omp2b encodes the previously studied Brucella porin and to characterize the omp2a gene product. Experiments were performed with Escherichia coli transformants expressing either omp2a or omp2b. Our results indicated that both gene products localized to the outer membrane of E. coli. Initial rates of transport of [14C]maltose and growth rates in the presence of maltodextrins of defined size indicated an increased hydrophilic permeability of transformants expressing omp2a. These cells were also shown to grow on maltotetraose, a molecule with a molecular mass of 667 Da. Activity consistent with the formation of pores could not be demonstrated in transformants expressing omp2b. However, Omp2b formed oligomers resistant to heat denaturation up to 70 degrees C in sodium dodecyl sulfate buffer, a property characteristic of bacterial porins. Overall, these results suggest that the omp2a gene product has pore-forming activity and that the omp2b gene encodes the previously characterized Brucella porin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alphen W. V., Lugtenberg B. Influence of osmolarity of the growth medium on the outer membrane protein pattern of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):623–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.623-630.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson S. A., Decloux A. Isolation and characterization of outer membrane permeability mutants in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):361–367. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.361-367.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R. Structure and function of porins from gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:359–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass J. M., Boos W., Hengge R. Reconstitution of maltose transport in malB mutants of Escherichia coli through calcium-induced disruptions of the outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):10–17. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.10-17.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass J. M. The cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria: new aspects of its function in transport and chemotaxis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;129:1–92. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71399-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan S. W., Schirmer T., Rummel G., Steiert M., Ghosh R., Pauptit R. A., Jansonius J. N., Rosenbusch J. P. Crystal structures explain functional properties of two E. coli porins. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):727–733. doi: 10.1038/358727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. T., Rosenberg E. Y., Nikaido H., Verstreate D. R., Winter A. J. Porins of Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.16-21.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Charriaut C. Evidence of three major polypeptide species and two major polysaccharide species in the Brucella outer membrane. Ann Rech Vet. 1983;14(3):311–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ficht T. A., Bearden S. W., Sowa B. A., Adams L. G. A 36-kilodalton Brucella abortus cell envelope protein is encoded by repeated sequences closely linked in the genomic DNA. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2036–2046. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2036-2046.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ficht T. A., Bearden S. W., Sowa B. A., Adams L. G. DNA sequence and expression of the 36-kilodalton outer membrane protein gene of Brucella abortus. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3281–3291. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3281-3291.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ficht T. A., Bearden S. W., Sowa B. A., Marquis H. Genetic variation at the omp2 porin locus of the brucellae: species-specific markers. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1135–1142. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00688.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-del Portillo F., Foster J. W., Maguire M. E., Finlay B. B. Characterization of the micro-environment of Salmonella typhimurium-containing vacuoles within MDCK epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(22):3289–3297. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Egli C., Benz R., Siehnel R. J. Overexpression in Escherichia coli and functional analysis of a novel PPi-selective porin, oprO, from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):471–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.471-476.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Siehnel R., Martin N. Outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1069–1075. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundrigan M. D., Earhart C. F. Gene envY of Escherichia coli K-12 affects thermoregulation of major porin expression. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):262–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.262-268.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutkenhaus J. F., Moore B. A., Masters M., Donachie W. D. Individual proteins are synthesized continuously throughout the Escherichia coli cell cycle. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.352-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier C., Bremer E., Schmid A., Benz R. Pore-forming activity of the Tsx protein from the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Demonstration of a nucleoside-specific binding site. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2493–2499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra R., Benson S. A. Isolation and characterization of OmpC porin mutants with altered pore properties. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):528–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.528-533.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Mizushima S. Signal transduction and gene regulation through the phosphorylation of two regulatory components: the molecular basis for the osmotic regulation of the porin genes. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1077–1082. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Porins and specific channels of bacterial outer membranes. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):435–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Reid J. Biogenesis of prokaryotic pores. Experientia. 1990 Feb 15;46(2):174–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J., Fung H., Gehring K., Klebba P. E., Nikaido H. Targeting of porin to the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Rate of trimer assembly and identification of a dimer intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7753–7759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowa B. A., Kelly K. A., Ficht T. A., Frey M., Adams L. G. SDS-soluble and peptidoglycan-bound proteins in the outer membrane-peptidoglycan complex of Brucella abortus. Vet Microbiol. 1991 May;27(3-4):351–369. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90160-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara E., Nikaido H. Pore-forming activity of OmpA protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2507–2511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J. Fallacies of E. coli cell fractionations and consequences thereof for protein export models. Microb Pathog. 1986 Jun;1(3):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstreate D. R., Creasy M. T., Caveney N. T., Baldwin C. L., Blab M. W., Winter A. J. Outer membrane proteins of Brucella abortus: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):979–989. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.979-989.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]